Intro
Discover 5 cures amoxicillin fixes for common infections, including respiratory, skin, and urinary tract issues, with this antibiotic medication, also treating bacterial infections, ear infections, and pneumonia, with amoxicillin uses.
Amoxicillin is a widely used antibiotic that belongs to the penicillin class of drugs. It is effective against a broad range of bacterial infections, including those affecting the respiratory tract, skin, and urinary tract. Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, ultimately leading to their death. This mechanism of action makes it a valuable treatment option for various infections. The importance of understanding the cures that amoxicillin fixes lies in its ability to combat bacterial infections effectively, thereby improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
The rise of antibiotic resistance has made it crucial to use antibiotics like amoxicillin judiciously. Overuse or misuse of antibiotics can contribute to the development of resistant bacteria, making infections harder to treat. Therefore, it is essential to use amoxicillin and other antibiotics only when prescribed by a healthcare professional and to follow the prescribed dosage and treatment duration. By doing so, we can ensure that these valuable medications remain effective against bacterial infections.
Bacterial infections can range from mild to severe and can affect various parts of the body. Understanding the types of infections that amoxicillin can treat is vital for its appropriate use. Amoxicillin is commonly prescribed for infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, urinary tract infections, and skin infections. Its effectiveness against these conditions makes it a frequently prescribed antibiotic. However, it is crucial to remember that amoxicillin is not effective against viral infections, such as the common cold or flu, and its use in such cases can contribute to antibiotic resistance.
Introduction to Amoxicillin

Benefits of Amoxicillin

Common Uses of Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin is commonly used to treat various bacterial infections, including: - Respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis - Urinary tract infections - Skin and soft tissue infections - Dental infections Its efficacy in treating these conditions has made it a staple in the treatment of bacterial infections.Working Mechanism of Amoxicillin
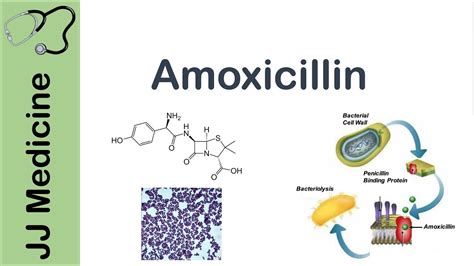
Resistance to Amoxicillin
The overuse and misuse of amoxicillin and other antibiotics have contributed to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Resistance to amoxicillin can occur through several mechanisms, including the production of beta-lactamase enzymes that degrade the antibiotic, alterations in PBPs that reduce the binding of amoxicillin, and changes in the bacterial cell membrane that prevent the entry of the antibiotic. The development of resistance highlights the need for responsible use of antibiotics and the development of new antimicrobial agents.Steps to Take Amoxicillin

Precautions and Side Effects
While amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects, including: - Gastrointestinal upset (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) - Allergic reactions (rash, itching, swelling) - Yeast infections - Interactions with other medications It is essential to discuss any concerns or potential interactions with a healthcare professional before starting treatment with amoxicillin.Examples of Amoxicillin Use

Statistical Data on Amoxicillin Use
According to statistical data, amoxicillin is one of the most commonly prescribed antibiotics worldwide. Its effectiveness and safety profile make it a preferred choice for treating various bacterial infections. However, the rise of antibiotic resistance has led to a decrease in its use in some regions, highlighting the need for responsible antibiotic use and the development of new antimicrobial agents.Conclusion and Future Directions
As we look to the future, it is essential to remember that the effective use of amoxicillin and other antibiotics requires a comprehensive approach, including responsible prescribing practices, patient education, and ongoing research into new antimicrobial agents. By working together, we can ensure that these valuable medications remain effective against bacterial infections, improving patient outcomes and reducing the risk of complications.
What is amoxicillin used for?
+Amoxicillin is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and dental infections.
How does amoxicillin work?
+Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, which is essential for the survival of bacteria. This leads to the weakening and eventual death of the bacterial cell.
What are the common side effects of amoxicillin?
+Common side effects of amoxicillin include gastrointestinal upset, allergic reactions, yeast infections, and interactions with other medications.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with amoxicillin in the comments below. Your input can help others understand the benefits and potential drawbacks of this medication. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can promote responsible antibiotic use and ensure the continued effectiveness of these valuable medications.
