Intro
Discover how Amoxicillin treats bacterial infections, including pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and skin infections, with its antibiotic properties, dosage, and side effects, for effective infection control and prevention.
The discovery of antibiotics has been one of the most significant advancements in the field of medicine, saving countless lives and improving the quality of life for millions of people around the world. Among these antibiotics, amoxicillin is one of the most commonly prescribed medications for treating bacterial infections. Its effectiveness, safety, and affordability have made it a staple in the treatment of various bacterial infections, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding how amoxicillin works, its benefits, and its potential side effects is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike.
Bacterial infections can affect any part of the body and can range from mild, self-limiting conditions to severe, life-threatening diseases. The key to managing these infections lies in identifying the causative bacteria and selecting the most appropriate antibiotic. Amoxicillin, a broad-spectrum penicillin antibiotic, is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, making it a versatile option for treating various infections. Its mechanism of action involves inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to the death of the bacteria.
The importance of amoxicillin in modern medicine cannot be overstated. It is used to treat a variety of infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and urinary tract infections, among others. The drug's efficacy, combined with its relatively low cost and safety profile, has made it a preferred choice for many healthcare providers. Furthermore, amoxicillin is available in various formulations, including capsules, tablets, and suspensions, which can be tailored to the patient's needs and age, enhancing its accessibility and compliance.
How Amoxicillin Works

Amoxicillin belongs to the class of beta-lactam antibiotics, which work by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall. This process is crucial for the survival of bacteria, as the cell wall provides structural support and maintains the internal environment of the cell. By interfering with cell wall synthesis, amoxicillin effectively kills the bacteria, thereby treating the infection. The drug's spectrum of activity includes many common pathogens, making it a valuable tool in the treatment of bacterial infections.
Benefits of Amoxicillin
The benefits of amoxicillin are numerous, contributing to its widespread use in clinical practice. Some of the key advantages include: - Broad-spectrum activity: Amoxicillin is effective against a wide range of bacteria, making it suitable for treating various infections. - Oral administration: The drug can be taken orally, which enhances patient compliance, especially in outpatient settings. - Safety profile: Amoxicillin has a relatively safe profile, with common side effects being mild and transient. - Cost-effectiveness: Compared to newer antibiotics, amoxicillin is generally less expensive, making it more accessible to a broader population.Common Uses of Amoxicillin

Amoxicillin is prescribed for a variety of bacterial infections, including:
- Respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis.
- Skin and soft tissue infections like cellulitis and abscesses.
- Urinary tract infections, including cystitis and pyelonephritis.
- Dental infections, where amoxicillin may be used as an adjunct to dental procedures.
Side Effects and Precautions
While amoxicillin is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects include: - Gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. - Allergic reactions, which can range from mild rashes to severe anaphylaxis. - Superinfections, where the use of amoxicillin can lead to the overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms.Resistance to Amoxicillin
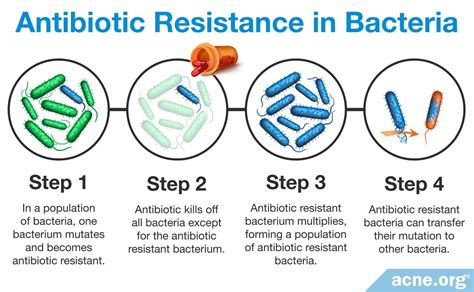
The increasing resistance to antibiotics, including amoxicillin, is a significant public health concern. Bacteria can develop resistance through various mechanisms, such as the production of beta-lactamase enzymes that degrade the antibiotic, alterations in the target site of the antibiotic, and changes in the permeability of the bacterial cell membrane. The misuse and overuse of antibiotics have accelerated the development of resistance, highlighting the need for responsible prescribing practices and the development of new antimicrobial agents.
Prevention of Resistance
Preventing the development of antibiotic resistance requires a multifaceted approach: - Responsible prescribing: Ensuring that antibiotics are prescribed only when necessary and in appropriate doses and durations. - Public awareness: Educating patients about the proper use of antibiotics and the risks associated with their misuse. - Infection control practices: Implementing strict infection control measures in healthcare settings to prevent the spread of resistant organisms.Dosage and Administration
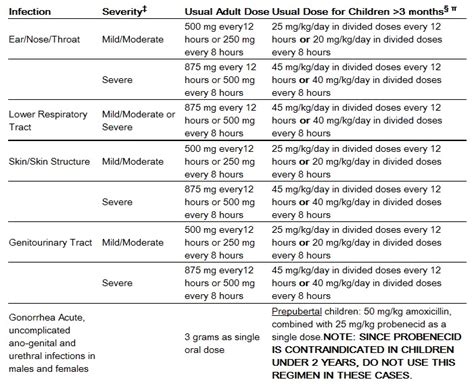
The dosage of amoxicillin varies depending on the infection being treated, the age and weight of the patient, and the severity of the infection. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage regimen to ensure effective treatment and minimize the risk of side effects. The drug can be taken with or without food, but it is recommended to take it at the start of a meal to reduce gastrointestinal side effects.
Special Considerations
Certain patient populations require special consideration when prescribing amoxicillin: - Pediatric patients: The dosage of amoxicillin in children is based on their weight, and the drug is often administered in a suspension form for younger children. - Geriatric patients: Older adults may have impaired renal function, which can affect the clearance of amoxicillin. Dosage adjustments may be necessary in these patients. - Pregnant and breastfeeding women: Amoxicillin is generally considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but it should only be used when clearly needed and under medical supervision.Interactions with Other Medications
Amoxicillin can interact with other medications, which may affect its efficacy or increase the risk of side effects. Some notable interactions include:
- Anticoagulants: Amoxicillin can increase the effects of anticoagulants, such as warfarin, by enhancing their anticoagulant activity.
- Methotrexate: The concurrent use of amoxicillin and methotrexate can increase the levels of methotrexate, potentially leading to toxicity.
- Probenecid: This drug can decrease the renal excretion of amoxicillin, leading to increased amoxicillin levels.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients taking amoxicillin should be monitored for signs of infection resolution, as well as potential side effects. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to: - Assess the effectiveness of the treatment. - Identify any adverse reactions early. - Adjust the treatment plan as necessary.Conclusion and Future Perspectives

In conclusion, amoxicillin remains a vital component in the treatment of bacterial infections, offering a broad spectrum of activity, ease of administration, and a favorable safety profile. However, the rising concern of antibiotic resistance underscores the need for prudent use of these medications, along with ongoing research into new antimicrobial agents and strategies to combat resistance. As we move forward, it is essential to adopt a holistic approach to infection management, incorporating not only antibiotic therapy but also preventive measures, diagnostic advancements, and innovative treatments to ensure the continued effectiveness of antibiotics like amoxicillin.
What is amoxicillin used for?
+Amoxicillin is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and urinary tract infections.
How does amoxicillin work?
+Amoxicillin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to the death of the bacteria.
What are the common side effects of amoxicillin?
+Common side effects of amoxicillin include gastrointestinal disturbances, allergic reactions, and superinfections.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with amoxicillin, as well as any questions they may have regarding its use. Your input is valuable in creating a comprehensive understanding of this important antibiotic and its role in managing bacterial infections. Please feel free to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards responsible antibiotic use and the development of new strategies to combat bacterial infections.
