Intro
Discover the 5 common ways gum disease starts, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, and genetics, and learn how to prevent periodontal disease and promote healthy gums through regular dental care and treatment.
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a bacterial infection that causes inflammation and damage to the gums and bone surrounding the teeth, leading to a range of problems from mild discomfort to tooth loss. Despite its prevalence, many people are unaware of the ways in which gum disease can start, and therefore, may not take the necessary steps to prevent it. Understanding the causes of gum disease is crucial for maintaining good oral health and preventing its onset.
Gum disease can have serious consequences if left untreated, including tooth loss, bad breath, and even links to systemic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. Moreover, gum disease can be a sign of other underlying health issues, making it essential to address the problem as soon as possible. Fortunately, gum disease is preventable, and with the right knowledge and practices, individuals can reduce their risk of developing this condition. By recognizing the early signs and understanding how gum disease starts, people can take proactive steps towards maintaining healthy gums and teeth.
Preventing gum disease requires a combination of good oral hygiene practices, a healthy diet, and regular dental check-ups. While many people are aware of the importance of brushing and flossing, few understand the specific mechanisms by which gum disease develops. Gum disease often begins with the accumulation of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, on the teeth. If plaque is not removed regularly, it can lead to the formation of tartar, which can cause inflammation and infection of the gums. However, there are several other factors that can contribute to the onset of gum disease, and being aware of these can help individuals take a more comprehensive approach to prevention.
Introduction to Gum Disease
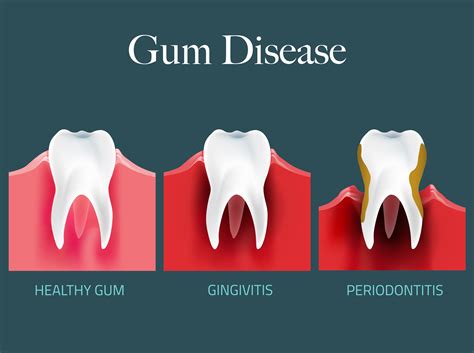
Gum disease is a complex condition that involves the interplay of multiple factors, including bacterial infection, immune response, and environmental influences. At its core, gum disease is caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth, which leads to inflammation and infection of the gums. However, other factors such as smoking, diabetes, and poor oral hygiene can increase an individual's risk of developing gum disease. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of gum disease is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Causes of Gum Disease
Gum disease is primarily caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth, and if not removed regularly, can lead to the formation of tartar. Tartar is a hard, yellowish deposit that can cause inflammation and infection of the gums. Other factors that can contribute to the onset of gum disease include: * Poor oral hygiene * Smoking * Diabetes * Genetic predisposition * Hormonal changes * Certain medicationsHow Gum Disease Progresses
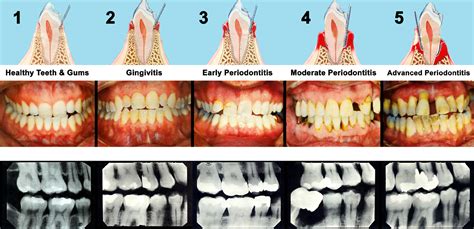
Gum disease progresses through several stages, each with distinct symptoms and consequences. The early stage of gum disease is known as gingivitis, which is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more advanced stage of gum disease that involves the destruction of the bone and tissue surrounding the teeth. Periodontitis can lead to the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums, which can trap bacteria and food particles, further exacerbating the condition.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
The symptoms of gum disease can vary depending on the stage and severity of the condition. Common symptoms of gum disease include: * Red, swollen, and bleeding gums * Bad breath * Receding gums * Loose teeth * Painful chewing * Sensitive teethPrevention of Gum Disease

Preventing gum disease requires a combination of good oral hygiene practices, a healthy diet, and regular dental check-ups. Some of the ways to prevent gum disease include:
- Brushing teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste
- Flossing once a day to remove plaque and food particles
- Using an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce bacteria
- Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Avoiding sugary and acidic foods and drinks
- Quitting smoking and avoiding tobacco products
Benefits of Preventing Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease has numerous benefits, including: * Maintaining healthy gums and teeth * Preventing tooth loss and bad breath * Reducing the risk of systemic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease * Boosting confidence and self-esteem * Saving money on dental treatments and proceduresTreatment of Gum Disease
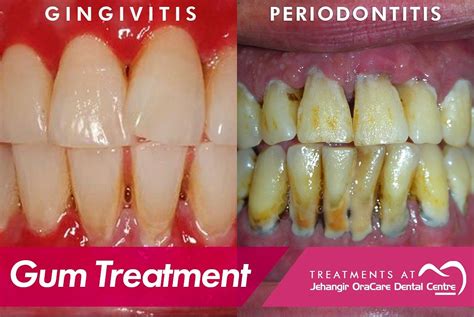
Treating gum disease depends on the stage and severity of the condition. Mild cases of gum disease can be treated with professional cleaning and good oral hygiene practices. More advanced cases may require surgical procedures such as pocket reduction surgery or bone grafting. In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
Types of Gum Disease Treatment
Some of the common types of gum disease treatment include: * Professional cleaning * Scaling and root planing * Pocket reduction surgery * Bone grafting * Antibiotics * Laser therapyConclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, gum disease is a common and preventable condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. By understanding the causes and symptoms of gum disease, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining healthy gums and teeth. Preventing gum disease requires a combination of good oral hygiene practices, a healthy diet, and regular dental check-ups. If you suspect that you may have gum disease, it is essential to consult with a dentist or periodontist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with gum disease in the comments below. If you found this article helpful, please share it with your friends and family to help spread awareness about the importance of oral health. By working together, we can promote healthy gums and teeth and reduce the risk of gum disease.
What are the early signs of gum disease?
+The early signs of gum disease include red, swollen, and bleeding gums, bad breath, and receding gums.
How can I prevent gum disease?
+You can prevent gum disease by brushing your teeth at least twice a day, flossing once a day, using an antibacterial mouthwash, and eating a healthy diet.
What are the consequences of untreated gum disease?
+Untreated gum disease can lead to tooth loss, bad breath, and an increased risk of systemic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease.
Can gum disease be treated?
+Yes, gum disease can be treated with professional cleaning, scaling and root planing, pocket reduction surgery, bone grafting, antibiotics, and laser therapy.
How often should I visit my dentist for check-ups?
+You should visit your dentist for check-ups at least twice a year to maintain good oral health and prevent gum disease.
