Intro
Discover the meaning of swollen glands, including causes, symptoms, and treatments for glandular swelling, lymph node enlargement, and neck swelling, to understand underlying health issues.
The human body is a complex system, comprising various organs and systems that work in harmony to maintain overall health and well-being. One of the essential components of the immune system is the lymphatic system, which includes lymph nodes, also known as swollen glands. These small, bean-shaped structures play a vital role in protecting the body against infections and diseases. When swollen glands are present, it can be a sign of an underlying health issue that requires attention. In this article, we will delve into the world of swollen glands, exploring their meaning, causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels, organs, and tissues responsible for defending the body against infections and diseases. Lymph nodes, or swollen glands, are an integral part of this system, filtering lymph fluid and trapping pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances. When the body detects an infection or disease, the lymph nodes become swollen as they work to fight off the invader. This swelling can occur in various parts of the body, including the neck, armpits, groin, and abdomen.
Swollen glands can be a cause for concern, as they often indicate an underlying health issue. The swelling can be painful and tender to the touch, making everyday activities uncomfortable. In some cases, swollen glands can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as a bacterial or viral infection, autoimmune disorder, or even cancer. It is essential to seek medical attention if the swelling persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, or weight loss.
Understanding Swollen Glands
To comprehend the meaning of swollen glands, it is crucial to understand the different types of lymph nodes and their functions. There are over 600 lymph nodes in the human body, each playing a unique role in the immune system. The most common areas where swollen glands occur include the neck, armpits, and groin. The swelling can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. In some cases, swollen glands can be a sign of a more serious condition, such as lymphoma or leukemia.
Types of Swollen Glands
Swollen glands can be classified into different types, depending on their location and cause. The most common types of swollen glands include:- Cervical lymphadenopathy: Swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck
- Axillary lymphadenopathy: Swelling of the lymph nodes in the armpits
- Inguinal lymphadenopathy: Swelling of the lymph nodes in the groin
- Abdominal lymphadenopathy: Swelling of the lymph nodes in the abdomen
Each type of swollen gland has its unique set of causes and symptoms. For instance, cervical lymphadenopathy can be caused by a throat infection, while axillary lymphadenopathy can be caused by a breast infection.
Causes of Swollen Glands
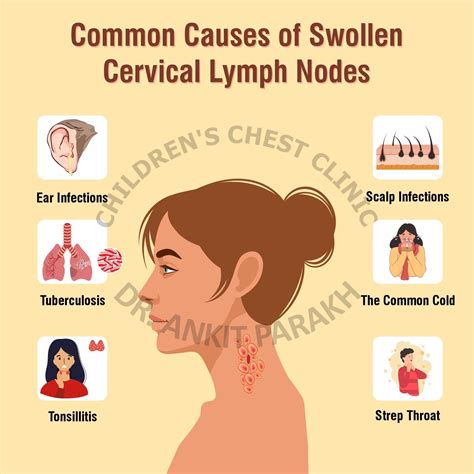
The causes of swollen glands can be diverse, ranging from infections to autoimmune disorders. Some of the most common causes of swollen glands include:
- Viral infections, such as mononucleosis or influenza
- Bacterial infections, such as strep throat or tuberculosis
- Fungal infections, such as histoplasmosis or coccidioidomycosis
- Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Cancer, such as lymphoma or leukemia
In some cases, swollen glands can be caused by other factors, such as allergies, injuries, or certain medications. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of the swelling.
Symptoms of Swollen Glands
The symptoms of swollen glands can vary depending on the location and cause of the swelling. Some common symptoms include:- Pain or tenderness in the affected area
- Swelling or enlargement of the lymph nodes
- Redness or inflammation of the skin
- Fever or chills
- Fatigue or weakness
- Weight loss or loss of appetite
In some cases, swollen glands can be accompanied by other symptoms, such as a sore throat, cough, or difficulty breathing. It is crucial to seek medical attention if the symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Treatment Options for Swollen Glands
The treatment options for swollen glands depend on the underlying cause of the swelling. Some common treatment options include:
- Antibiotics or antiviral medications to treat infections
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling and pain
- Immunotherapy to treat autoimmune disorders
- Surgery or radiation therapy to treat cancer
- Rest and hydration to help the body recover from illness or infection
In some cases, swollen glands may require no treatment at all, as they can resolve on their own. However, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment.
Home Remedies for Swollen Glands
There are several home remedies that can help alleviate the symptoms of swollen glands. Some of these remedies include:- Applying a warm compress to the affected area to reduce pain and swelling
- Drinking plenty of fluids to stay hydrated and help the body recover
- Getting plenty of rest to help the body fight off infection
- Practicing good hygiene to prevent the spread of infection
- Avoiding tight clothing or jewelry that can irritate the affected area
It is essential to note that home remedies should not replace medical treatment. If the symptoms persist or worsen, it is crucial to seek medical attention.
Prevention of Swollen Glands

Preventing swollen glands requires a combination of good hygiene, a healthy lifestyle, and regular medical check-ups. Some ways to prevent swollen glands include:
- Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands regularly and avoiding close contact with people who are sick
- Getting vaccinated against certain diseases, such as flu or HPV
- Eating a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Exercising regularly to boost the immune system
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
By following these tips, individuals can reduce their risk of developing swollen glands and maintain overall health and well-being.
Risk Factors for Swollen Glands
There are several risk factors that can increase the likelihood of developing swollen glands. Some of these risk factors include:- Age: Older adults are more likely to develop swollen glands due to a weakened immune system
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to swollen glands
- Certain medical conditions: Individuals with conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or lupus are more likely to develop swollen glands
- Family history: Individuals with a family history of autoimmune disorders or cancer may be more likely to develop swollen glands
It is essential to be aware of these risk factors and take steps to reduce the risk of developing swollen glands.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, swollen glands can be a sign of an underlying health issue that requires attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to prevent and manage swollen glands. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional if the symptoms persist or worsen over time. By working together, individuals can maintain overall health and well-being.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with swollen glands in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with your friends and family on social media.
What are swollen glands?
+Swollen glands, also known as lymph nodes, are small, bean-shaped structures that play a vital role in protecting the body against infections and diseases.
What causes swollen glands?
+Swollen glands can be caused by a variety of factors, including infections, autoimmune disorders, and cancer.
How are swollen glands treated?
+The treatment options for swollen glands depend on the underlying cause of the swelling and may include antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, immunotherapy, or surgery.
