Intro
Discover 7 ways to treat gastritis, alleviating stomach inflammation and symptoms. Learn natural remedies, dietary changes, and lifestyle modifications to manage gastric pain, acid reflux, and digestive issues, promoting gut health and relief from gastritis symptoms.
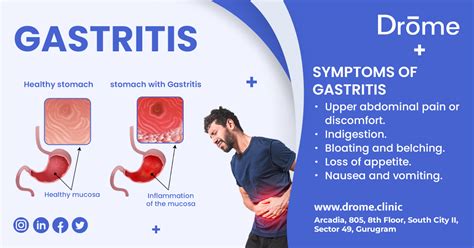
Gastritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing inflammation and irritation in the stomach lining. This condition can lead to various symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and bloating. If left untreated, gastritis can lead to more severe complications, such as stomach ulcers and increased risk of stomach cancer. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gastritis to manage the condition effectively.
The importance of treating gastritis cannot be overstated. Gastritis can significantly impact a person's quality of life, making it challenging to perform daily activities and enjoy favorite foods. Moreover, if left untreated, gastritis can lead to more severe health complications, making it crucial to seek medical attention if symptoms persist. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available for gastritis, ranging from lifestyle changes to medical interventions. By understanding the different treatment options, individuals can take control of their condition and manage their symptoms effectively.
Gastritis is often caused by a combination of factors, including a poor diet, stress, and bacterial infections. The most common cause of gastritis is a bacterial infection, specifically Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori). This bacterium can infect the stomach lining, leading to inflammation and irritation. Other causes of gastritis include long-term use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), excessive alcohol consumption, and stress. Understanding the underlying causes of gastritis is crucial in developing an effective treatment plan.
Understanding Gastritis

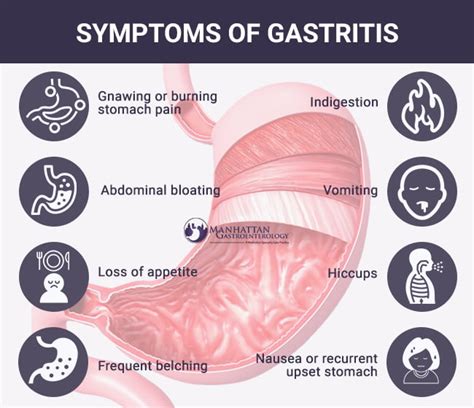
Causes and Symptoms of Gastritis
Treatment Options for Gastritis

Lifestyle Changes for Gastritis
Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in managing gastritis. Dietary modifications, such as avoiding spicy and fatty foods, can help reduce symptoms. Stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga, can also help reduce stress and promote healing. Additionally, quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can help prevent complications and promote overall health.Medical Interventions for Gastritis

Alternative Therapies for Gastritis
Alternative therapies, such as probiotics and herbal remedies, can also help manage symptoms and promote healing. Probiotics can help restore the balance of gut bacteria, while herbal remedies, such as ginger and turmeric, can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.7 Ways to Treat Gastritis

Preventing Gastritis
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with gastritis in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may be struggling with gastritis.
What are the common causes of gastritis?
+Gastritis is often caused by a combination of factors, including a poor diet, stress, and bacterial infections, specifically Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori).
What are the symptoms of gastritis?
+The symptoms of gastritis can vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual, but common symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, bloating, and loss of appetite.
How can gastritis be treated?
+Gastritis can be treated with lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and alternative therapies, such as dietary modifications, stress management, antibiotics, acid-reducing medications, probiotics, and herbal remedies.
Can gastritis be prevented?
+Yes, gastritis can be prevented by practicing good hygiene, avoiding spicy and fatty foods, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption.
What are the complications of gastritis?
+If left untreated, gastritis can lead to more severe complications, such as stomach ulcers, perforation, and increased risk of stomach cancer.
