Intro
Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatment of Slap Tear Injury, a common shoulder condition affecting labrum, rotator cuff, and joint stability, often caused by sports trauma or falls, requiring physical therapy and sometimes surgery for full recovery.
The human body is a complex and fascinating machine, with numerous components working together in harmony to enable us to move, function, and live our daily lives. However, when one of these components is damaged or injured, it can have a significant impact on our overall well-being and quality of life. One such injury that can have a profound effect on our daily activities and overall health is a slap tear injury. A slap tear, also known as a superior labrum anterior-posterior lesion, is a specific type of injury that occurs in the shoulder joint. In this article, we will delve into the world of slap tear injuries, exploring what they are, how they occur, and what treatment options are available.
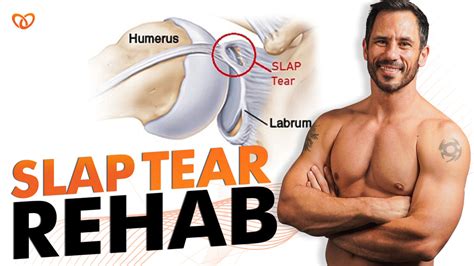
The shoulder joint is a complex and dynamic structure that consists of multiple components, including bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. The labrum, a ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint, plays a crucial role in maintaining the stability and integrity of the joint. A slap tear injury occurs when the labrum is torn, typically in the superior (upper) region, and can be caused by a variety of factors, including sports injuries, falls, or repetitive strain. The symptoms of a slap tear injury can vary depending on the severity of the tear, but common complaints include pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the affected shoulder.
Understanding the causes and symptoms of slap tear injuries is essential for developing effective treatment plans and preventing further complications. In the following sections, we will explore the anatomy of the shoulder joint, the different types of slap tears, and the various treatment options available. Whether you are an athlete, a healthcare professional, or simply someone interested in learning more about this complex injury, this article aims to provide a comprehensive and informative guide to slap tear injuries.
What is a Slap Tear Injury?

Anatomy of the Shoulder Joint
The shoulder joint, also known as the glenohumeral joint, is a complex and dynamic structure that consists of multiple components, including bones, ligaments, tendons, and cartilage. The joint is formed by the humerus (upper arm bone) and the scapula (shoulder blade), and is surrounded by a ring of cartilage called the labrum. The labrum helps to deepen the socket of the joint, increasing the stability and integrity of the joint. The shoulder joint is also surrounded by a group of muscles and tendons called the rotator cuff, which helps to stabilize and move the joint.Causes of Slap Tear Injuries

Symptoms of Slap Tear Injuries
The symptoms of a slap tear injury can vary depending on the severity of the tear, but common complaints include pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the affected shoulder. Patients may also experience a sensation of instability or looseness in the joint, and may hear a clicking or snapping sound when moving the arm. In some cases, patients may experience numbness or tingling in the arm or hand, particularly if the tear is large enough to compress nearby nerves.Treatment Options for Slap Tear Injuries

Surgical Repair of Slap Tear Injuries
Surgical repair of slap tear injuries typically involves arthroscopic surgery, which allows the surgeon to visualize the joint and repair the tear through tiny incisions. The surgeon will typically use sutures or anchors to reattach the torn labrum to the surrounding bone. In some cases, the surgeon may also need to repair or reconstruct nearby tissues, such as the rotator cuff or ligaments. Post-operative rehabilitation is an essential part of the recovery process, and may involve physical therapy and pain management to help the patient regain strength and mobility in the affected shoulder.Recovery and Rehabilitation after Slap Tear Injury
Prevention of Slap Tear Injuries
Prevention of slap tear injuries is essential, particularly for athletes and individuals who participate in activities that involve throwing or repetitive strain. Proper warm-up and stretching exercises can help to reduce the risk of injury, as can strengthening the muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder joint. Athletes should also avoid overtraining and take regular breaks to rest and recover. Additionally, using proper technique and form when participating in sports or activities can help to reduce the risk of injury.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
Slap tear injuries are a significant concern for athletes and individuals who participate in activities that involve throwing or repetitive strain. By taking the time to understand the causes and symptoms of slap tear injuries, patients can take the first step towards recovery and rehabilitation. Whether you are an athlete, a healthcare professional, or simply someone interested in learning more about this complex injury, we hope that this article has provided a comprehensive and informative guide to slap tear injuries.What is a slap tear injury?
+A slap tear injury is a specific type of injury that occurs in the shoulder joint, where the labrum, a ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the joint, is torn.
What are the symptoms of a slap tear injury?
+The symptoms of a slap tear injury can vary depending on the severity of the tear, but common complaints include pain, stiffness, and limited mobility in the affected shoulder.
How are slap tear injuries treated?
+Treatment options for slap tear injuries depend on the severity of the tear and the patient's overall health and lifestyle, and may include conservative treatment options, such as physical therapy and pain management, or surgical intervention to repair or reconstruct the labrum.
We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive and informative guide to slap tear injuries. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Remember to take care of your shoulders and joints, and to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms or pain. By working together, we can promote health, wellness, and injury prevention for all.
