Intro
Discover 5 key facts about Z Pack, including its uses, dosage, and potential side effects, to understand this antibiotic treatment for bacterial infections, respiratory issues, and sinusitis, and learn how it works.
The Z Pack, also known as azithromycin, is a widely prescribed antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections. Its popularity stems from its effectiveness, ease of use, and relatively mild side effects. However, like any medication, it's crucial to understand its benefits and potential drawbacks. Let's delve into the world of the Z Pack and explore five key facts about this commonly used antibiotic.
The Z Pack has been a staple in the medical community for decades, prescribed for infections ranging from pneumonia and bronchitis to sinusitis and skin infections. Its broad-spectrum activity means it can target a wide range of bacteria, making it a versatile tool in the fight against bacterial infections. Despite its widespread use, many people are not fully aware of how the Z Pack works, its potential side effects, or the importance of using it responsibly to prevent antibiotic resistance.
One of the reasons the Z Pack is so popular among both doctors and patients is its convenience. The standard regimen typically consists of a single dose on the first day, followed by a series of doses over the next four days, making it easy to adhere to the treatment plan. This simplicity, combined with its effectiveness, has made the Z Pack a go-to choice for many common bacterial infections. However, it's essential to follow the prescribed dosage and complete the full course of treatment to ensure the infection is fully cleared and to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Introduction to the Z Pack
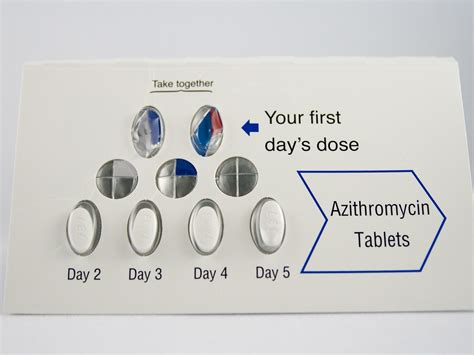
The Z Pack, or azithromycin, is a type of macrolide antibiotic that works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, ultimately leading to the death of the bacterial cells. This mechanism of action is crucial for understanding how the Z Pack can effectively treat bacterial infections without significantly affecting the host's cells. Its ability to accumulate within cells also allows it to target intracellular pathogens, making it particularly useful against certain types of infections.
How the Z Pack Works
The Z Pack's effectiveness is attributed to its ability to bind to the bacterial ribosome, which is responsible for protein synthesis. By doing so, it prevents the bacteria from producing essential proteins needed for growth and replication, leading to the bacteria's demise. This targeted approach helps minimize the impact on the body's natural flora, reducing the risk of side effects compared to broader-spectrum antibiotics.Benefits of the Z Pack
The benefits of the Z Pack are numerous. It offers a convenient once-daily dosing regimen for most infections, improving patient compliance. Its broad-spectrum activity means it can be used against a variety of bacterial infections, and its relatively mild side effect profile makes it suitable for a wide range of patients. Additionally, the Z Pack has been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial in certain types of infections.
Some of the key benefits include:
- Convenience: The Z Pack is typically prescribed in a 5-day course, with some infections requiring only a single dose.
- Broad-spectrum activity: It is effective against a wide range of Gram-positive and some Gram-negative bacteria.
- Mild side effects: Compared to other antibiotics, the Z Pack tends to have fewer side effects, making it a preferred choice for many patients.
- Anti-inflammatory properties: Beyond its antibacterial effects, the Z Pack may help reduce inflammation in certain conditions.
Potential Side Effects and Interactions
While the Z Pack is generally well-tolerated, like any medication, it can cause side effects. Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, as well as headache and dizziness. More severe but rare side effects can include allergic reactions, liver damage, and cardiac arrhythmias. It's also important to note that the Z Pack can interact with other medications, including blood thinners, diabetes medications, and certain antidepressants, which can lead to increased risk of side effects.Uses of the Z Pack
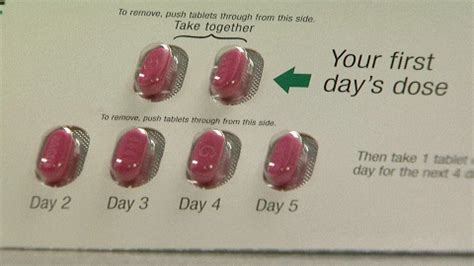
The Z Pack is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including:
- Respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis.
- Skin and soft tissue infections.
- Genital infections such as chlamydia.
- Certain types of eye infections.
Its effectiveness against these conditions makes it a valuable asset in the treatment of bacterial infections. However, it's crucial to use the Z Pack responsibly and only when prescribed by a healthcare provider to prevent misuse and the development of antibiotic resistance.
Importance of Responsible Use
The rise of antibiotic resistance is a global health concern, and the irresponsible use of antibiotics like the Z Pack contributes to this issue. It's essential to use antibiotics only when necessary and to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed. This not only ensures the infection is fully treated but also helps prevent the development of resistant bacterial strains.Antibiotic Resistance and the Z Pack
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria develop mechanisms to evade the effects of antibiotics, making infections harder to treat. The overuse and misuse of antibiotics, including the Z Pack, accelerate this process. It's vital for healthcare providers to prescribe antibiotics judiciously and for patients to use them as directed to slow the development of resistance.
Strategies to combat antibiotic resistance include:
- Improving antibiotic prescribing practices to ensure they are used only when necessary.
- Developing new antibiotics to replace those that are no longer effective.
- Enhancing infection control practices to prevent the spread of infections.
Future Perspectives on the Z Pack
As the medical community continues to face the challenge of antibiotic resistance, the role of the Z Pack and other antibiotics will evolve. Research into new antibiotics and alternative treatments is ongoing, aiming to provide healthcare providers with more tools to combat bacterial infections effectively. Additionally, efforts to improve prescribing practices and patient education on the responsible use of antibiotics will be crucial in extending the usefulness of the Z Pack and similar medications.Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, the Z Pack is a valuable antibiotic that offers a convenient and effective treatment option for various bacterial infections. However, its use must be balanced with the need to prevent antibiotic resistance. By understanding how the Z Pack works, its benefits, potential side effects, and the importance of responsible use, patients and healthcare providers can work together to ensure this medication remains a useful tool in the fight against bacterial infections.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the Z Pack and antibiotic resistance. Have you or a loved one used the Z Pack? What are your concerns about antibiotic resistance? Share your experiences and questions in the comments below, and let's continue the conversation on this critical health topic.
What is the Z Pack used for?
+The Z Pack, or azithromycin, is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, and genital infections.
How does the Z Pack work?
+The Z Pack works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria, which leads to the death of the bacterial cells. It binds to the bacterial ribosome, preventing the production of essential proteins.
What are the potential side effects of the Z Pack?
+Common side effects of the Z Pack include gastrointestinal upset, headache, and dizziness. Rare but more severe side effects can include allergic reactions, liver damage, and cardiac arrhythmias.
