Intro
Discover what Albuterol is used for, its benefits, and side effects. Learn about this bronchodilators role in asthma, COPD, and respiratory issues, and how it works as a reliever medication for wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
Albuterol is a medication that has been widely used for decades to treat various respiratory conditions. It is a bronchodilator, which means it helps to open up the airways in the lungs, making it easier to breathe. The importance of albuterol lies in its ability to provide quick relief from symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath. This makes it an essential medication for people suffering from respiratory diseases, and its proper use can significantly improve the quality of life for these individuals.
The need for effective respiratory medications like albuterol has become increasingly important due to the rising prevalence of respiratory diseases worldwide. Conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) affect millions of people globally, causing significant morbidity and mortality. The economic burden of these diseases is also substantial, highlighting the need for cost-effective treatments that can manage symptoms effectively. Albuterol, with its proven track record and relatively low cost, has become a cornerstone in the management of these conditions.
As research into respiratory diseases continues to advance, the role of albuterol in treatment protocols is being continually reassessed. Newer medications and therapies are being developed, but albuterol remains a first-line treatment for many respiratory conditions due to its efficacy, safety profile, and cost-effectiveness. Understanding how albuterol works, its benefits, and its potential side effects is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. This knowledge enables the optimization of treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive the most appropriate care for their specific condition.
What is Albuterol?

Albuterol, also known as salbutamol, is a short-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist (SABA). It works by stimulating the β2 receptors in the lungs, which causes the bronchial tubes to relax and dilate. This action improves airflow to the lungs, making it easier to breathe. Albuterol is commonly used to treat bronchospasm associated with conditions like asthma, COPD, and other respiratory diseases. It is available in various forms, including inhalers, nebulizer solutions, and tablets, though inhalation routes are the most common due to their rapid onset of action.
How Does Albuterol Work?
The mechanism of action of albuterol involves the activation of β2 adrenergic receptors on the surface of smooth muscle cells in the airways. This activation triggers a signaling cascade that leads to the relaxation of these muscles, resulting in the dilation of the airways. The dilation of the airways reduces airway resistance, increases airflow, and makes breathing easier. This effect is rapid, typically starting within 5 minutes of administration and lasting for about 4 to 6 hours, depending on the individual and the specific formulation used.Benefits of Albuterol
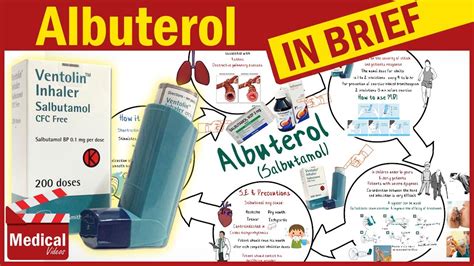
The benefits of albuterol are numerous and well-documented. It provides quick relief from acute bronchospasm, making it an essential rescue medication for asthma attacks and COPD exacerbations. Albuterol can also be used preventatively before exposure to known triggers of bronchospasm, such as exercise or allergens. Its effectiveness in improving lung function and symptoms has been demonstrated in numerous clinical trials, and it is generally well-tolerated, with most side effects being mild and transient.
Common Uses of Albuterol
Albuterol is used for a variety of respiratory conditions, including: - Asthma: To relieve bronchospasm and prevent exercise-induced asthma. - COPD: To improve breathing and reduce symptoms of bronchospasm. - Chronic bronchitis and emphysema: As part of the treatment plan to manage symptoms. - Acute bronchospasm: As a rescue medication to provide quick relief.Side Effects of Albuterol

While albuterol is generally safe, it can cause side effects, especially at higher doses. Common side effects include:
- Tremors
- Nervousness
- Headache
- Tachycardia (rapid heart rate)
- Palpitations
- Muscle cramps
These side effects are usually mild and temporary, resolving on their own once the medication is stopped or the dose is adjusted. However, in some cases, more serious side effects can occur, such as allergic reactions, arrhythmias, or severe hypokalemia (low potassium levels). It is essential for patients to report any side effects to their healthcare provider to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Precautions and Interactions
Albuterol can interact with other medications, and certain precautions need to be taken. For example, it should be used with caution in patients with heart disease, high blood pressure, or diabetes. Albuterol can also interact with beta-blockers, diuretics, and certain antidepressants, among other medications. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications they are taking before starting albuterol.Administration and Dosage
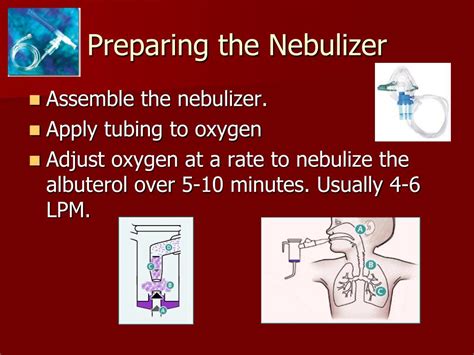
The dosage and administration of albuterol depend on the patient's condition, age, and the specific formulation being used. For inhalers, the typical dose for adults and children over 4 years old is 2 puffs every 4 to 6 hours as needed. For nebulizer solutions, the dose is usually 2.5 to 5 mg administered every 4 to 6 hours as needed. It is crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and to use the medication only as directed by a healthcare provider.
Storage and Disposal
Albuterol inhalers and solutions should be stored at room temperature, away from heat and moisture. The inhaler should be cleaned regularly, and the canister should be replaced when empty. Unused or expired medications should be disposed of properly, following local guidelines for medication disposal.Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, albuterol is a vital medication in the management of respiratory diseases, offering quick relief from bronchospasm and improving the quality of life for millions of people worldwide. As research continues to uncover the complexities of respiratory diseases, the role of albuterol and other bronchodilators will likely evolve. Future directions may include the development of new formulations with longer durations of action, combination therapies that target multiple pathways in respiratory disease, and personalized treatment approaches based on genetic and environmental factors.
Final Thoughts
The importance of understanding albuterol and its role in respiratory health cannot be overstated. By educating patients and healthcare providers about the benefits, risks, and proper use of albuterol, we can optimize treatment outcomes and improve patient care. As we look to the future, it is clear that albuterol will remain a cornerstone in the treatment of respiratory diseases, and its continued use will depend on our ability to balance its benefits with its potential risks and to adapt to the evolving landscape of respiratory medicine.What is the most common use of albuterol?
+Albuterol is most commonly used to treat bronchospasm associated with asthma and COPD, providing quick relief from symptoms such as wheezing, coughing, and shortness of breath.
How long does albuterol take to work?
+Albuterol typically starts working within 5 minutes of administration and its effects can last for about 4 to 6 hours, depending on the individual and the specific formulation used.
Can albuterol be used by anyone?
+No, albuterol should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider. It is not suitable for everyone, especially those with certain heart conditions, high blood pressure, or diabetes, and it can interact with other medications.
How should albuterol be stored?
+Albuterol inhalers and solutions should be stored at room temperature, away from heat and moisture. The inhaler should be cleaned regularly, and the canister should be replaced when empty.
What are the common side effects of albuterol?
+Common side effects of albuterol include tremors, nervousness, headache, tachycardia, palpitations, and muscle cramps. These side effects are usually mild and temporary but can be more serious in some cases.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with albuterol in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us create content that addresses the needs and concerns of our readers.
