Intro
Learn about Ectopic Pregnancy Definition, causes, symptoms, and treatment. Understand abnormal implantation, tubal pregnancy, and related complications like miscarriage and infertility, to grasp this life-threatening condition.
An ectopic pregnancy is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tube. This can happen when the fertilized egg has difficulty passing through the fallopian tube and into the uterus, or when the fallopian tube is damaged or blocked. As a result, the embryo begins to grow in the wrong location, leading to a range of complications. It is essential to understand the risks and symptoms associated with ectopic pregnancy to ensure prompt medical attention and prevent severe consequences.
The importance of recognizing ectopic pregnancy cannot be overstated, as it is a leading cause of maternal mortality and morbidity worldwide. According to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), ectopic pregnancy accounts for approximately 1-2% of all pregnancies, resulting in around 3-4% of all pregnancy-related deaths. The condition can affect any woman, regardless of age or reproductive history, although certain risk factors may increase the likelihood of an ectopic pregnancy. By understanding the definition, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ectopic pregnancy, individuals can better navigate this complex and potentially life-threatening condition.
Ectopic pregnancy is often referred to as a "tubal pregnancy" due to the fallopian tube being the most common site of implantation. However, it is crucial to note that the term "ectopic" encompasses a broader range of implantation sites, including the ovary, cervix, and abdominal cavity. Each of these locations presents unique challenges and complications, emphasizing the need for prompt diagnosis and treatment. As medical technology and research continue to advance, our understanding of ectopic pregnancy and its management is evolving, offering new hope for individuals affected by this condition.
Ectopic Pregnancy Causes and Risk Factors

Ectopic pregnancy is often the result of a combination of factors, including anatomical abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, and environmental influences. Some of the most significant risk factors for ectopic pregnancy include:
- Previous ectopic pregnancy or history of ectopic pregnancy in the family
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or other infections that cause scarring in the fallopian tubes
- Endometriosis or other conditions that affect the reproductive organs
- Use of assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF)
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- History of abdominal or pelvic surgery
- Use of an intrauterine device (IUD) for contraception Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive steps to reduce their likelihood of developing an ectopic pregnancy.
Understanding the Role of the Fallopian Tube
The fallopian tube plays a critical role in the development of an ectopic pregnancy. When the fertilized egg travels through the fallopian tube, it is normally propelled into the uterus by the tube's muscular contractions and cilia. However, if the fallopian tube is damaged or blocked, the egg may become trapped, leading to implantation in the wrong location. Factors such as scarring, inflammation, or congenital abnormalities can affect the fallopian tube's function, increasing the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.Ectopic Pregnancy Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of ectopic pregnancy can vary widely, making diagnosis challenging. Some common signs and symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain or tenderness, often on one side
- Vaginal bleeding or spotting
- Shoulder pain or discomfort
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Abnormal vaginal discharge It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if any of these symptoms occur, as prompt diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes.
Diagnostic Techniques
Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. These may include: * Pelvic exam to check for tenderness or abnormalities * Ultrasound to visualize the reproductive organs and detect any abnormalities * Blood tests to measure human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) levels and detect any signs of pregnancy * Laparoscopy to visually examine the fallopian tubes and surrounding tissues By using these diagnostic techniques, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose ectopic pregnancy and develop an effective treatment plan.Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
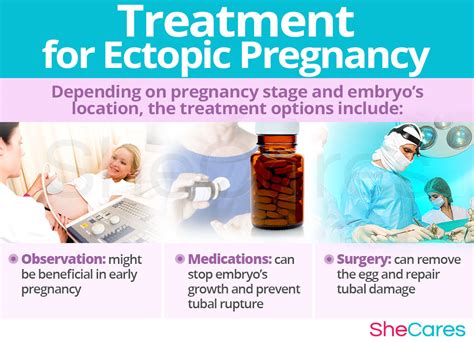
Treatment for ectopic pregnancy depends on the severity of the condition, the location of the embryo, and the individual's overall health. Some common treatment options include:
- Expectant management, where the individual is closely monitored for signs of complications
- Medical management, using medications such as methotrexate to stop the growth of the embryo
- Surgical management, such as laparoscopic surgery to remove the embryo and repair any damage to the fallopian tube
- Hysterectomy, in severe cases where the embryo has implanted in the uterus
Medical Management
Medical management is often the preferred treatment option for ectopic pregnancy, as it can help preserve the fallopian tube and reduce the risk of complications. Methotrexate, a chemotherapy medication, is commonly used to stop the growth of the embryo. This treatment is typically effective in around 90% of cases, although it may require multiple doses and close monitoring.Preventing Ectopic Pregnancy

While it is not always possible to prevent ectopic pregnancy, there are steps that individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Practicing safe sex to reduce the risk of PID and other infections
- Avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke
- Maintaining a healthy weight and diet
- Managing any underlying medical conditions, such as endometriosis or diabetes
- Seeking regular prenatal care during pregnancy
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of ectopic pregnancy. This includes: * Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains * Engaging in regular exercise, such as walking or swimming * Getting enough sleep and managing stress * Avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption By incorporating these lifestyle changes into daily routine, individuals can reduce their risk of ectopic pregnancy and promote overall reproductive health.Conclusion and Next Steps

Ectopic pregnancy is a complex and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt medical attention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk and ensure the best possible outcomes. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately. We encourage you to share this article with others, and to comment below with any questions or concerns.
What is the most common cause of ectopic pregnancy?
+The most common cause of ectopic pregnancy is a combination of factors, including anatomical abnormalities, hormonal imbalances, and environmental influences. Previous ectopic pregnancy or history of ectopic pregnancy in the family, pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), and endometriosis are also significant risk factors.
What are the symptoms of ectopic pregnancy?
+The symptoms of ectopic pregnancy can vary widely, but common signs include abdominal pain or tenderness, vaginal bleeding or spotting, shoulder pain or discomfort, nausea and vomiting, dizziness or lightheadedness, and abnormal vaginal discharge.
How is ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
+Diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, including pelvic exam, ultrasound, blood tests, and laparoscopy.
What are the treatment options for ectopic pregnancy?
+Treatment options for ectopic pregnancy depend on the severity of the condition and may include expectant management, medical management using medications such as methotrexate, surgical management, or hysterectomy in severe cases.
Can ectopic pregnancy be prevented?
+While it is not always possible to prevent ectopic pregnancy, individuals can reduce their risk by practicing safe sex, avoiding smoking and secondhand smoke, maintaining a healthy weight and diet, managing underlying medical conditions, and seeking regular prenatal care during pregnancy.
