Intro
Discover key facts about Clindamycin, a broad-spectrum antibiotic, including its uses, side effects, and interactions, to understand its role in treating bacterial infections and skin conditions effectively.
Clindamycin is an antibiotic that has been widely used to treat various bacterial infections. Its effectiveness and broad spectrum of activity have made it a staple in the treatment of infections caused by anaerobic bacteria, as well as certain types of aerobic bacteria. Understanding the properties, uses, and potential side effects of clindamycin is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients. Here, we delve into five key facts about clindamycin, exploring its mechanism of action, indications, side effects, and more.
Clindamycin belongs to the class of antibiotics known as lincosamides, which work by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. This action prevents the bacteria from producing essential proteins, leading to the death of the bacterial cells. The drug is particularly effective against Gram-positive cocci, including Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae, as well as anaerobic bacteria such as Bacteroides fragilis. Its broad spectrum of activity makes it a valuable option for treating a range of infections, from skin and soft tissue infections to more severe conditions like pneumonia and septicemia.
The versatility of clindamycin is also reflected in its various formulations, including oral capsules, topical gels and creams, and injectable solutions. This range of formulations allows healthcare providers to tailor the treatment to the specific needs of the patient, depending on the type and severity of the infection. For example, oral clindamycin may be prescribed for mild to moderate skin infections, while injectable clindamycin may be used in hospital settings for more severe infections. Topical formulations are useful for treating acne and other skin conditions where the infection is localized.
Introduction to Clindamycin
Benefits of Clindamycin

Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Clindamycin's anti-inflammatory properties are an added advantage in the treatment of certain conditions. In the case of acne, for example, clindamycin not only reduces the population of Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a bacterium that plays a significant role in the development of acne, but it also decreases the inflammation associated with acne lesions. This dual action can lead to faster and more effective clearance of acne, improving the patient's quality of life. Similarly, in the treatment of other inflammatory skin conditions, the anti-inflammatory effects of clindamycin can contribute to a more favorable outcome.Side Effects of Clindamycin

Minimizing Side Effects
To minimize the risk of side effects, it is crucial to use clindamycin only as directed by a healthcare provider. Patients should complete the full course of treatment, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure that the infection is fully cleared. Additionally, maintaining good hydration and taking probiotics may help mitigate gastrointestinal side effects. In cases where side effects do occur, patients should consult their healthcare provider, who can provide guidance on managing these effects or adjusting the treatment plan as necessary.Clindamycin Resistance
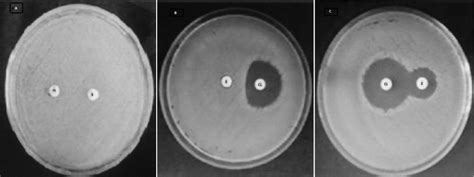
Stewardship Programs
Antibiotic stewardship programs play a critical role in promoting the appropriate use of antibiotics, including clindamycin. These programs aim to improve patient outcomes, reduce antibiotic resistance, and decrease the spread of infections. Through education, guidelines, and monitoring, healthcare facilities can ensure that antibiotics are used effectively and safely. This approach not only helps in preserving the efficacy of existing antibiotics but also in extending their lifespan, thereby ensuring that effective treatments remain available for future generations.Clindamycin in Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Precautions and Warnings
Precautions and warnings associated with clindamycin use are essential for minimizing risks. Patients with a history of gastrointestinal disease, particularly colitis, should use clindamycin with caution. Similarly, patients with allergies to lincosamides or any component of the formulation should avoid clindamycin. Monitoring for signs of hypersensitivity reactions, such as rash, itching, or difficulty breathing, is crucial, and patients should seek immediate medical attention if they experience any of these symptoms.Conclusion and Future Directions
As we move forward, it is essential to adopt a responsible and sustainable approach to antibiotic use, emphasizing antibiotic stewardship, research into new antimicrobial agents, and public awareness campaigns to combat misuse. By working together, healthcare professionals, researchers, and the public can help preserve the efficacy of antibiotics like clindamycin, ensuring that these lifesaving medications continue to be effective against bacterial infections.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with clindamycin, as well as any questions they may have about its use or the broader topic of antibiotic treatment. Your input can help foster a more informed discussion about the responsible use of antibiotics and the importance of developing new treatments for bacterial infections.
What is clindamycin used for?
+Clindamycin is used to treat various bacterial infections, including skin and soft tissue infections, respiratory tract infections, and infections of the bones and joints.
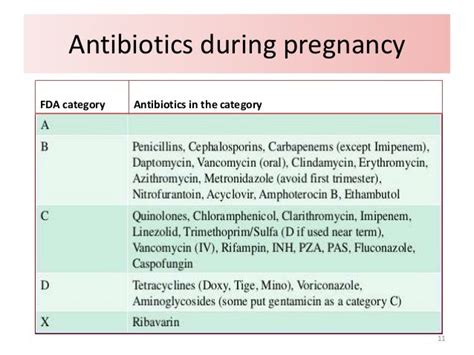
Can clindamycin be used during pregnancy?
+Clindamycin can be used during pregnancy, but its use should be reserved for cases where the benefits outweigh the risks. Pregnant women should only use clindamycin under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
What are the common side effects of clindamycin?
+Common side effects of clindamycin include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. More severe side effects can include pseudomembranous colitis and hypersensitivity reactions.
