Intro
Discover how Diltiazem works through its calcium channel blocking effects, managing hypertension, angina, and arrhythmias, while also exploring its role in coronary artery spasms and cardiac conditions.
The importance of understanding how certain medications work cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to managing chronic conditions. One such medication is Diltiazem, a calcium channel blocker used primarily to treat high blood pressure and control angina. Its mechanism of action is complex and multifaceted, impacting various bodily systems to achieve its therapeutic effects. For individuals prescribed Diltiazem, grasping its working mechanisms can provide insight into its benefits and potential side effects, fostering a more informed approach to health management.
Diltiazem's role in cardiovascular health is particularly noteworthy. By influencing the heart's rhythm and the blood vessels' diameter, it can significantly reduce the strain on the heart, thereby lowering blood pressure and alleviating symptoms of angina. This dual effect not only improves the quality of life for those with heart conditions but also plays a critical role in preventing more severe cardiovascular events. As research continues to uncover the nuances of Diltiazem's action, its application in clinical settings has become more refined, offering tailored treatment plans for patients.
The therapeutic applications of Diltiazem extend beyond its primary uses, highlighting the drug's versatility and potential for addressing a range of cardiovascular issues. Its ability to modulate calcium ion influx into cardiac and vascular smooth muscles underlies its efficacy in treating conditions characterized by abnormal heart rhythms and vascular spasms. Furthermore, the drug's pharmacokinetic profile, including its metabolism and excretion, influences its dosing regimen and interaction with other medications, making a comprehensive understanding of its mechanisms crucial for safe and effective use.
Introduction to Diltiazem

Pharmacological Effects
The pharmacological profile of Diltiazem is characterized by its selective inhibition of L-type calcium channels, which are predominantly found in cardiac and smooth muscle cells. This selectivity underlies its therapeutic benefits, including: - Reduced myocardial contractility, which decreases the heart's oxygen demand. - Dilatation of peripheral arteries, leading to decreased vascular resistance and lowered blood pressure. - Increased coronary blood flow, which can help alleviate ischemic symptoms.Mechanism of Action
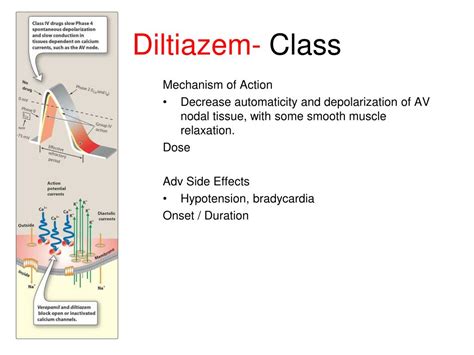
Clinical Applications
The clinical applications of Diltiazem are diverse, reflecting its efficacy in managing various cardiovascular conditions: - **Hypertension**: Diltiazem is used as a monotherapy or in combination with other antihypertensive agents to manage high blood pressure. - **Angina Pectoris**: By reducing myocardial oxygen demand and increasing coronary blood flow, Diltiazem helps in controlling symptoms of angina. - **Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter**: The drug's ability to slow the ventricular rate in cases of atrial fibrillation or flutter makes it useful in the management of these arrhythmias.Benefits and Side Effects

It's essential for patients to discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare provider to ensure that Diltiazem is the right choice for their specific condition.
Practical Considerations
When initiating Diltiazem therapy, several practical considerations must be taken into account: - **Dosing**: The dosage of Diltiazem should be individualized based on the patient's response and tolerance. - **Drug Interactions**: Patients should be aware of potential drug interactions, especially with other cardiovascular agents, to minimize the risk of adverse effects. - **Monitoring**: Regular monitoring of blood pressure, heart rate, and electrolyte levels can help in adjusting the treatment plan as needed.Conclusion and Future Directions
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, Diltiazem is a valuable medication in the management of cardiovascular diseases, offering a unique mechanism of action that underlies its therapeutic effects. By grasping the complexities of its working mechanisms, individuals can better navigate their treatment plans and make informed decisions about their health.We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with Diltiazem, as well as any questions they may have regarding its use and effects. Your engagement can help foster a community of support and knowledge, ultimately contributing to better health outcomes for those affected by cardiovascular conditions.
What is Diltiazem used for?
+Diltiazem is primarily used to treat high blood pressure and control angina. It can also be used to manage certain types of arrhythmias.
How does Diltiazem work?
+Diltiazem works by blocking calcium channels in the heart and blood vessels, which leads to a reduction in blood pressure and a decrease in the heart's workload.
What are the common side effects of Diltiazem?
+Common side effects of Diltiazem include edema, dizziness, headache, nausea, and fatigue. It's essential to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
