Intro
Learn about Flu Influenza, its symptoms, causes, and treatments. Understand the differences between seasonal, avian, and swine flu, and discover preventive measures to avoid influenza virus outbreaks and complications.
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the influenza virus. It affects millions of people worldwide every year, causing significant morbidity and mortality. The flu is a major public health concern, particularly among vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and people with underlying medical conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of influenza, exploring its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
The flu is a complex and multifaceted disease, with various strains and subtypes circulating globally. The most common types of influenza viruses are influenza A and influenza B, which are further divided into subtypes based on their surface proteins. The flu virus is highly mutable, meaning it can change rapidly, which makes it challenging to develop effective vaccines and treatments. Despite these challenges, researchers and healthcare professionals continue to work tirelessly to improve our understanding of the flu and develop innovative solutions to combat it.
The symptoms of the flu can range from mild to severe and may include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, muscle or body aches, headaches, fatigue, and vomiting or diarrhea. In some cases, the flu can lead to serious complications, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, or sinus and ear infections. People with underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, or chronic lung disease, are at increased risk of developing these complications. It is essential to seek medical attention if you or a loved one is experiencing severe flu symptoms or if you are at high risk of developing complications.
Understanding Influenza

Understanding influenza is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. The flu virus is spread through respiratory droplets, contact with contaminated surfaces, and close contact with infected individuals. The virus can survive on surfaces for up to 48 hours, making it essential to practice good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and disinfecting high-touch areas. Additionally, getting vaccinated against the flu is one of the most effective ways to prevent infection and reduce the risk of complications.
How the Flu Spreads
The flu virus can spread through various routes, including: * Respiratory droplets: When an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes, they release respiratory droplets that can contain the flu virus. * Contact with contaminated surfaces: The flu virus can survive on surfaces for up to 48 hours, making it essential to practice good hygiene. * Close contact with infected individuals: People who are in close contact with someone who has the flu are at increased risk of infection.Types of Influenza
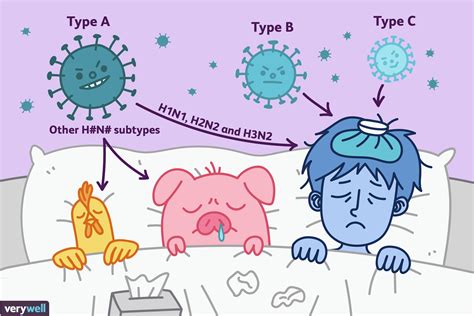
There are several types of influenza, including:
- Influenza A: This type of flu is further divided into subtypes based on their surface proteins, such as H1N1 and H3N2.
- Influenza B: This type of flu is also divided into subtypes, such as B/Yamagata and B/Victoria.
- Influenza C: This type of flu is generally mild and does not cause significant illness.
Influenza A Subtypes
Influenza A subtypes are further divided into: * H1N1: This subtype is also known as swine flu and was responsible for the 2009 pandemic. * H3N2: This subtype is a common cause of seasonal flu and can lead to severe illness, particularly among older adults.Treatment and Prevention

Treatment and prevention of the flu are crucial for reducing the risk of complications and transmission. Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the duration of illness. Additionally, getting vaccinated against the flu is one of the most effective ways to prevent infection and reduce the risk of complications. The flu vaccine is updated annually to protect against the most common strains circulating during the flu season.
Flu Vaccine
The flu vaccine is: * Updated annually to protect against the most common strains circulating during the flu season. * Available in various forms, including injections, nasal sprays, and egg-free options. * Recommended for everyone 6 months and older, particularly those at high risk of developing complications.Complications of Influenza
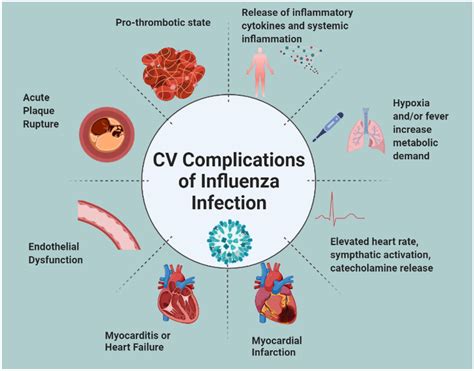
Complications of influenza can be severe and even life-threatening. People with underlying medical conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, or chronic lung disease, are at increased risk of developing complications. Additionally, older adults, young children, and pregnant women are also at high risk. Common complications of the flu include:
- Pneumonia: A bacterial infection that can cause severe illness and even death.
- Bronchitis: An inflammation of the bronchial tubes that can lead to chronic cough and shortness of breath.
- Sinus and ear infections: Bacterial infections that can cause severe pain and discomfort.
High-Risk Groups
High-risk groups for developing complications from the flu include: * Older adults: People 65 years and older are at increased risk of developing complications. * Young children: Children under the age of 5 are at increased risk of developing complications. * Pregnant women: Pregnant women are at increased risk of developing complications, particularly during the second and third trimesters.Diagnosis and Testing

Diagnosis and testing for the flu are essential for confirming the presence of the virus and guiding treatment. Healthcare professionals use various tests, including:
- Rapid influenza diagnostic tests (RIDTs): These tests can provide quick results but may not be as accurate as other tests.
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests: These tests are highly sensitive and can detect the flu virus in respiratory specimens.
- Viral culture: This test involves growing the virus in a laboratory and can provide definitive results.
Interpreting Test Results
Interpreting test results is crucial for guiding treatment and prevention. A positive test result indicates the presence of the flu virus, while a negative result may indicate that the symptoms are caused by another illness. However, it is essential to note that false-negative results can occur, particularly if the test is performed too early in the course of illness.Management and Treatment

Management and treatment of the flu are crucial for reducing the risk of complications and transmission. Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the duration of illness. Additionally, rest, hydration, and over-the-counter medications can help manage symptoms and support recovery.
Antiviral Medications
Antiviral medications are: * Oseltamivir (Tamiflu): This medication can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the duration of illness. * Zanamivir (Relenza): This medication can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the duration of illness. * Peramivir (Rapivab): This medication can help alleviate symptoms and reduce the duration of illness.Prevention Strategies
Prevention strategies are essential for reducing the risk of transmission and infection. Getting vaccinated against the flu is one of the most effective ways to prevent infection and reduce the risk of complications. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing and disinfecting high-touch areas, can help reduce the risk of transmission.
Good Hygiene Practices
Good hygiene practices include: * Frequent handwashing with soap and water. * Disinfecting high-touch areas, such as doorknobs and light switches. * Avoiding close contact with people who are sick. * Staying home from work or school if you are sick.What is the best way to prevent the flu?
+Getting vaccinated against the flu is one of the most effective ways to prevent infection and reduce the risk of complications.
How long does the flu last?
+The flu can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the severity of the illness and the individual's overall health.
Can I get the flu from the vaccine?
+No, you cannot get the flu from the vaccine. The flu vaccine is made from inactivated or weakened viruses, which cannot cause the flu.
In conclusion, the flu is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to prevention and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and transmission of the flu, we can develop effective strategies to reduce the risk of infection and complications. Getting vaccinated against the flu, practicing good hygiene, and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist are essential for managing and treating the flu. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the flu in the comments section below and to explore our website for more information on this topic.
