Intro
Discover what Furosemide is, a loop diuretic medication, and learn about its uses, side effects, and interactions, including edema treatment and fluid retention management, in this informative guide.
Furosemide, also known as Lasix, is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs called loop diuretics. It is primarily used to treat fluid build-up (edema) and swelling that is caused by various medical conditions, such as congestive heart failure, liver disease, and kidney disease. Furosemide works by increasing the amount of urine produced by the kidneys, which helps to remove excess fluid from the body.
The importance of furosemide lies in its ability to provide relief from symptoms associated with fluid retention, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and ankles. By promoting the excretion of excess fluid, furosemide helps to reduce the workload on the heart and improve overall cardiovascular function. This medication is often prescribed by doctors to patients who are experiencing edema, high blood pressure, or other conditions that require the removal of excess fluid from the body.
Furosemide has been widely used for decades to treat a range of medical conditions, and its effectiveness has been well-documented in numerous clinical studies. The medication is available in various forms, including oral tablets, injections, and intravenous solutions, making it a versatile treatment option for patients with different needs and preferences. With its proven track record of safety and efficacy, furosemide remains a popular choice among healthcare professionals for the management of fluid-related disorders.
How Furosemide Works
Furosemide works by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions in the kidneys, which leads to an increase in the amount of urine produced. This process occurs in the loop of Henle, a critical region of the kidney responsible for regulating electrolyte balance and fluid levels. By blocking the reabsorption of sodium and chloride, furosemide promotes the excretion of excess fluid, thereby reducing swelling and alleviating symptoms associated with edema.
The mechanism of action of furosemide involves the binding of the medication to a specific receptor in the kidney, called the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter. This receptor plays a crucial role in regulating the balance of electrolytes and fluid in the body. When furosemide binds to this receptor, it prevents the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions, leading to an increase in the amount of urine produced. The resulting diuretic effect helps to remove excess fluid from the body, providing relief from symptoms associated with fluid retention.
Benefits of Furosemide
The benefits of furosemide are numerous and well-documented. Some of the most significant advantages of this medication include: * Rapid relief from symptoms associated with fluid retention * Improved cardiovascular function and reduced workload on the heart * Effective treatment of edema, high blood pressure, and other fluid-related disorders * Availability in various forms, including oral tablets, injections, and intravenous solutions * Proven safety and efficacy in numerous clinical studiesUses of Furosemide

Furosemide is used to treat a range of medical conditions, including:
- Congestive heart failure: Furosemide helps to reduce the workload on the heart and improve overall cardiovascular function.
- Edema: Furosemide is effective in treating swelling caused by fluid retention, particularly in the legs and ankles.
- High blood pressure: Furosemide can help to lower blood pressure by reducing the amount of fluid in the body.
- Liver disease: Furosemide is used to treat fluid build-up associated with liver disease, such as cirrhosis.
- Kidney disease: Furosemide helps to remove excess fluid from the body, which can help to alleviate symptoms associated with kidney disease.
Side Effects of Furosemide
While furosemide is generally well-tolerated, it can cause some side effects, including: * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Headache and fatigue * Nausea and vomiting * Diarrhea and stomach cramps * Increased urination and dehydrationIt is essential to note that furosemide can also cause more severe side effects, such as:
- Allergic reactions
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Kidney damage
- Hearing loss
Interactions with Other Medications
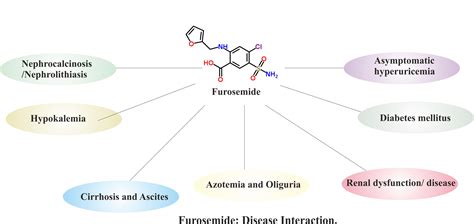
Furosemide can interact with other medications, including:
- Diuretics: Furosemide can increase the risk of dehydration and electrolyte imbalance when used with other diuretics.
- Blood thinners: Furosemide can increase the risk of bleeding when used with blood thinners, such as warfarin.
- Lithium: Furosemide can increase the risk of lithium toxicity when used with this medication.
- Corticosteroids: Furosemide can increase the risk of electrolyte imbalance when used with corticosteroids.
It is crucial to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications, to minimize the risk of interactions.
Dosage and Administration
The dosage and administration of furosemide vary depending on the medical condition being treated and the individual patient's needs. Typical dosages range from 20 to 80 mg per day, taken orally or intravenously. It is essential to follow the dosage instructions provided by your doctor and to attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor your condition and adjust the dosage as needed.Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, furosemide is a highly effective medication for the treatment of fluid-related disorders, including edema, high blood pressure, and congestive heart failure. Its mechanism of action, benefits, and uses make it a popular choice among healthcare professionals. However, it is essential to be aware of the potential side effects and interactions with other medications to minimize the risk of adverse reactions.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with furosemide in the comments section below. If you have any questions or concerns about this medication, please do not hesitate to ask. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information.
What is the primary use of furosemide?
+Furosemide is primarily used to treat fluid build-up (edema) and swelling caused by various medical conditions, such as congestive heart failure, liver disease, and kidney disease.
How does furosemide work?
+Furosemide works by inhibiting the reabsorption of sodium and chloride ions in the kidneys, leading to an increase in the amount of urine produced and helping to remove excess fluid from the body.
What are the potential side effects of furosemide?
+Furosemide can cause side effects such as dizziness, headache, nausea, and increased urination. More severe side effects can include allergic reactions, electrolyte imbalance, kidney damage, and hearing loss.
