Intro
Discover Glimepiride uses and benefits for diabetes management, including blood sugar control, insulin regulation, and weight management, to improve overall health and reduce disease risks.
Glimepiride is a medication that has been widely used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. It belongs to the class of sulfonylureas, which work by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, thereby helping to lower blood sugar levels. The importance of managing diabetes cannot be overstated, as uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to a range of serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. In this article, we will delve into the uses and benefits of glimepiride, as well as its mechanism of action, potential side effects, and practical considerations for its use.
The management of type 2 diabetes is a complex process that involves lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, as well as pharmacological interventions. Glimepiride is one such intervention that has been shown to be effective in lowering blood sugar levels and improving glycemic control. By stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, glimepiride helps to increase the uptake of glucose by cells, thereby reducing blood sugar levels. This can help to alleviate symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, fatigue, and blurred vision, which are commonly associated with high blood sugar levels.
The benefits of glimepiride extend beyond its ability to lower blood sugar levels. By improving glycemic control, glimepiride can also help to reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. Additionally, glimepiride has been shown to have a positive effect on lipid profiles, which can help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Overall, the use of glimepiride can be an important part of a comprehensive treatment plan for type 2 diabetes, and its benefits can be significant for individuals who are able to achieve good glycemic control.
How Glimepiride Works
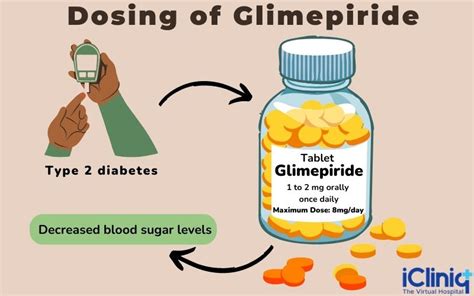
Key Mechanisms of Action
The key mechanisms of action of glimepiride include: * Stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas * Increasing the sensitivity of cells to insulin * Reducing the production of glucose in the liver * Increasing the release of insulin from the pancreas in response to meals These mechanisms of action help to lower blood sugar levels and improve glycemic control, which can help to reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes.Benefits of Glimepiride

Practical Considerations
While glimepiride can be an effective treatment for type 2 diabetes, there are a number of practical considerations that should be taken into account. These include: * Dosage: The dosage of glimepiride will depend on the individual's response to the medication and their overall health status. * Side effects: Glimepiride can cause a number of side effects, including hypoglycemia, weight gain, and gastrointestinal disturbances. * Interactions: Glimepiride can interact with a number of other medications, including beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and warfarin. * Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is necessary to assess the effectiveness of glimepiride and to make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.Side Effects of Glimepiride

Managing Side Effects
While side effects can be a concern, there are a number of ways to manage them. These include: * Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels can help to identify any potential issues and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. * Adjusting the dosage: Adjusting the dosage of glimepiride can help to minimize side effects. * Using other medications: Using other medications, such as metformin or pioglitazone, can help to minimize side effects and improve glycemic control. * Lifestyle modifications: Making lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, can help to improve glycemic control and minimize side effects.Interactions with Other Medications
Managing Interactions
While interactions can be a concern, there are a number of ways to manage them. These include: * Monitoring blood sugar levels: Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels can help to identify any potential issues and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. * Adjusting the dosage: Adjusting the dosage of glimepiride can help to minimize interactions. * Using other medications: Using other medications, such as metformin or pioglitazone, can help to minimize interactions and improve glycemic control. * Lifestyle modifications: Making lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, can help to improve glycemic control and minimize interactions.Conclusion and Future Directions
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with glimepiride in the comments section below. Have you used glimepiride to manage your diabetes? What benefits or side effects have you experienced? Your feedback can help others who are considering using this medication.
What is glimepiride used for?
+Glimepiride is used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus. It works by stimulating the release of insulin from the pancreas, thereby helping to lower blood sugar levels.
What are the benefits of glimepiride?
+The benefits of glimepiride include lowering blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of long-term complications, and improving lipid profiles.
What are the potential side effects of glimepiride?
+The potential side effects of glimepiride include hypoglycemia, weight gain, and gastrointestinal disturbances.
Can glimepiride be used with other medications?
+Yes, glimepiride can be used with other medications, such as metformin or pioglitazone. However, it is essential to monitor blood sugar levels and adjust the dosage as necessary to minimize interactions.
How can I manage side effects and interactions with glimepiride?
+To manage side effects and interactions with glimepiride, it is essential to monitor blood sugar levels regularly, adjust the dosage as necessary, and make lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise.
