Intro
Discover what is HMO, a type of health maintenance organization, and learn about its benefits, plans, and networks, including managed care, preventive services, and healthcare providers.
The importance of understanding health insurance options cannot be overstated, especially in today's complex healthcare landscape. One type of health insurance that has been around for decades and continues to play a significant role in the healthcare system is the Health Maintenance Organization, commonly referred to as an HMO. HMOs have been a cornerstone of health insurance for many individuals and families, offering a unique approach to healthcare delivery and financing. Despite their long history, many people are still unclear about what HMOs are, how they work, and their benefits and drawbacks.
HMOs were first introduced in the 1970s as a way to control healthcare costs and improve the quality of care. The core idea behind HMOs is to provide comprehensive healthcare services to members for a fixed fee, emphasizing preventive care and early intervention to reduce the need for costly medical procedures. This approach is designed to encourage members to take an active role in their health, thereby reducing the overall cost of healthcare. Over the years, HMOs have evolved, and their structures and offerings have become more diverse, but their fundamental principle remains the same.
The mechanism by which HMOs operate is quite distinct from other types of health insurance. HMOs contract with a specific network of healthcare providers, including doctors, hospitals, and other medical facilities, to provide care to their members at a negotiated rate. Members typically pay a monthly premium and may also have a small copayment or coinsurance for certain services. In exchange, they receive access to a wide range of healthcare services, often with an emphasis on preventive care, such as routine check-ups, screenings, and health education programs. This integrated approach to healthcare is designed to foster a long-term relationship between the patient and their healthcare providers, leading to better health outcomes and more efficient use of resources.
How HMOs Work
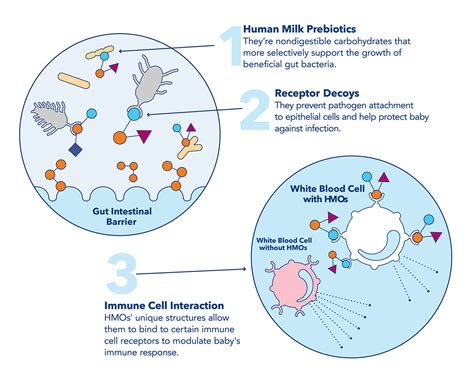
To understand how HMOs work, it's essential to delve into their operational structure and the benefits they offer to members. At the heart of every HMO is a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to provide care to HMO members at a discounted rate. Members are required to receive their medical care from providers within this network, except in emergency situations. This network approach allows HMOs to control costs more effectively and to monitor the quality of care provided to their members. HMOs also often have a primary care physician (PCP) system, where members choose a PCP from within the network who acts as their first point of contact for medical care and coordinates their healthcare needs.
Benefits of HMOs

The benefits of HMOs are multifaceted and can be significant for both individuals and families. One of the primary advantages of HMOs is their emphasis on preventive care, which can lead to better health outcomes and lower healthcare costs in the long run. HMOs often cover routine check-ups, vaccinations, and health screenings without additional cost to the member, encouraging proactive health management. Additionally, HMOs typically have lower out-of-pocket costs compared to other types of health insurance, making them an attractive option for those on a budget. The coordinated care approach, facilitated by the PCP system, also ensures that members receive comprehensive and continuous care, reducing the likelihood of medical errors and improving the overall quality of care.
Types of HMOs
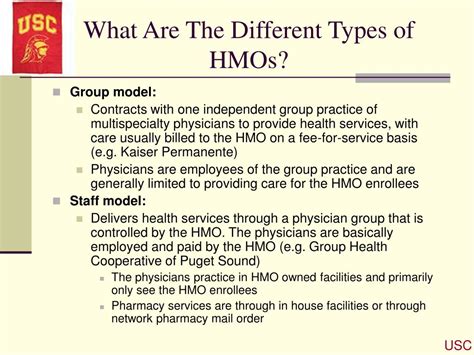
Over time, various types of HMOs have emerged, catering to different needs and preferences. The most common types include Staff Model HMOs, where the HMO employs the healthcare providers directly; Group Model HMOs, which contract with a group of physicians to provide care; Network Model HMOs, which contract with multiple groups of physicians; and Independent Practice Association (IPA) Model HMOs, where the HMO contracts with an association of independent physicians. Each type of HMO has its unique characteristics, advantages, and potential drawbacks, and the choice between them often depends on individual circumstances and priorities.
Challenges and Criticisms

Despite their benefits, HMOs have also faced criticisms and challenges. One of the main criticisms is the limited choice of healthcare providers, as members are generally restricted to receiving care from within the HMO's network. This can be particularly problematic for those who have established relationships with healthcare providers outside of the network or for individuals who require specialized care not available within the network. Additionally, the bureaucratic processes involved in HMOs, such as the need for referrals from a PCP to see specialists, can sometimes lead to delays in receiving necessary care. These limitations have led to the development of other health insurance models that offer more flexibility in terms of provider choice and access to care.
Evolution and Future of HMOs

The healthcare landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changes in consumer expectations, and regulatory reforms. HMOs have had to adapt to these changes to remain relevant and competitive. The future of HMOs likely involves a greater emphasis on personalized medicine, integration of digital health technologies to enhance patient engagement and care coordination, and innovative payment models that incentivize high-quality, cost-effective care. Additionally, there may be a shift towards more flexible network designs that balance the need for cost control with the desire for greater provider choice and accessibility.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, HMOs represent a significant component of the health insurance market, offering a unique blend of comprehensive care, cost control, and preventive focus. While they have their limitations and challenges, HMOs continue to evolve, incorporating new technologies and innovative care models to better serve their members. For individuals and families considering their health insurance options, understanding the workings and benefits of HMOs can be invaluable in making informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
As you reflect on the role of HMOs in the healthcare system, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with health insurance and managed care. Whether you are a current or former HMO member, a healthcare provider, or simply someone interested in health policy, your insights can contribute to a richer understanding of these complex issues. Please feel free to comment below, sharing your stories or asking questions about HMOs and their place in the evolving healthcare landscape.
What is the primary goal of an HMO?
+The primary goal of an HMO is to provide high-quality healthcare services to its members while controlling costs through preventive care, coordinated treatment plans, and negotiated rates with healthcare providers.
How do HMOs differ from other types of health insurance?
+HMOs differ from other types of health insurance in their emphasis on preventive care, their use of a network of contracted healthcare providers, and their requirement that members receive care from within this network, except in emergencies.
What are the benefits of choosing an HMO for health insurance?
+The benefits of choosing an HMO include lower out-of-pocket costs, comprehensive coverage for preventive care services, and the potential for better health outcomes due to the coordinated care approach and emphasis on preventive medicine.
