Intro
Discover 5 life-changing uses of insulin, from diabetes management to wound healing, and explore its role in medical treatments, hormone regulation, and cellular growth, unlocking its full potential.
The importance of insulin in the human body cannot be overstated. Insulin is a hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels, and its uses extend far beyond just treating diabetes. In this article, we will delve into the various uses of insulin, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to this vital hormone. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a patient, or simply someone interested in learning more about insulin, this article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the topic.
Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone produced by the pancreas, and its primary function is to facilitate the uptake of glucose by cells throughout the body. When we eat, our body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. Insulin helps to regulate blood sugar levels by enabling cells to take up glucose, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. Without insulin, glucose would build up in the bloodstream, leading to a range of serious health problems, including diabetes.
The discovery of insulin in the early 20th century revolutionized the treatment of diabetes, and since then, insulin has become a cornerstone of diabetes management. However, insulin's uses extend far beyond just treating diabetes. Insulin is also used in a range of other medical applications, including the treatment of certain types of cancer, the management of metabolic disorders, and even in the field of cosmetic medicine. In this article, we will explore the various uses of insulin, highlighting its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to this vital hormone.
Introduction to Insulin

How Insulin Works
Insulin works by binding to insulin receptors on the surface of cells, triggering a signaling cascade that ultimately leads to the uptake of glucose by cells. When insulin binds to its receptor, it activates a range of downstream signaling pathways, including the activation of glucose transport proteins. These proteins help to facilitate the uptake of glucose by cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. Insulin also plays a role in regulating glucose metabolism, helping to suppress the production of glucose in the liver and promoting the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen.Uses of Insulin in Diabetes Management
- Rapid-acting insulin: This type of insulin is fast-acting, taking effect within 15-30 minutes of administration. Rapid-acting insulin is often used to control blood sugar levels after meals.
- Short-acting insulin: This type of insulin takes effect within 30-60 minutes of administration and is often used to control blood sugar levels between meals.
- Intermediate-acting insulin: This type of insulin takes effect within 1-2 hours of administration and is often used to control blood sugar levels overnight.
- Long-acting insulin: This type of insulin takes effect within 2-4 hours of administration and is often used to control blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Benefits of Insulin in Diabetes Management
The benefits of insulin in diabetes management are numerous. Insulin helps to regulate blood sugar levels, preventing the complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Insulin also helps to improve quality of life, enabling people with diabetes to lead active and healthy lives. In addition, insulin can help to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications, such as blindness, amputations, and kidney failure.Uses of Insulin in Cancer Treatment
How Insulin Works in Cancer Treatment
Insulin works in cancer treatment by inhibiting the growth of cancer cells and promoting apoptosis (cell death). Insulin also helps to reduce the production of IGFs, which can stimulate the growth of cancer cells. In addition, insulin has been shown to enhance the effectiveness of other cancer therapies, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy.Uses of Insulin in Metabolic Disorders
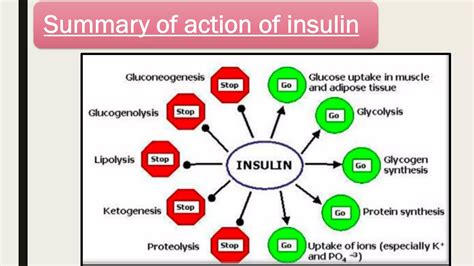
Benefits of Insulin in Metabolic Disorders
The benefits of insulin in metabolic disorders are numerous. Insulin helps to improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of complications such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Insulin also helps to regulate blood sugar levels, preventing the development of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome.Uses of Insulin in Cosmetic Medicine

How Insulin Works in Cosmetic Medicine
Insulin works in cosmetic medicine by reducing inflammation and improving skin texture. Insulin helps to regulate blood sugar levels, which can contribute to the development of acne and other skin conditions. In addition, insulin has been shown to improve collagen production, reducing the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.What is insulin and how does it work?
+Insulin is a protein hormone that is produced by the pancreas and plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin works by binding to insulin receptors on the surface of cells, triggering a signaling cascade that ultimately leads to the uptake of glucose by cells.
What are the uses of insulin in diabetes management?
+Insulin is used to treat both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent the complications associated with diabetes. There are several different types of insulin, each with its own unique characteristics and uses.
Can insulin be used to treat other medical conditions?
+Yes, insulin has been used to treat a range of other medical conditions, including certain types of cancer, metabolic disorders, and cosmetic medicine. Insulin has been shown to inhibit the growth of cancer cells, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce inflammation.
In conclusion, insulin is a vital hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and has a range of uses beyond just treating diabetes. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a patient, or simply someone interested in learning more about insulin, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the topic. We encourage you to share this article with others, and to take action to learn more about the importance of insulin in maintaining good health. By working together, we can promote a better understanding of insulin and its uses, and improve the lives of people around the world.
