Intro
Elevated urea nitrogen levels can harm your health, causing fatigue, kidney strain, and cardiovascular issues, leading to serious complications if left untreated, impacting overall well-being and quality of life.
Elevated urea nitrogen levels in the blood can be a sign of several underlying health issues, ranging from mild to severe. Urea nitrogen is a waste product that occurs in the blood when the body breaks down protein. Normally, this waste is removed by the kidneys, but when the kidneys are not functioning properly, urea nitrogen can build up to harmful levels. High urea nitrogen levels can have significant impacts on various bodily functions and overall health. Understanding the implications of elevated urea nitrogen is crucial for managing and treating the underlying causes effectively.
The presence of high urea nitrogen levels is often indicative of kidney dysfunction or disease. The kidneys play a critical role in filtering waste products, including urea, from the blood. When kidney function is impaired, the ability to filter out these waste products is compromised, leading to an accumulation of toxins in the body. This condition can result from various factors, including diabetes, high blood pressure, and kidney damage due to disease or injury. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of high urea nitrogen levels is essential for prompt medical intervention.
High urea nitrogen levels can affect multiple systems in the body, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. From neurological issues to cardiovascular problems, the impact of elevated urea nitrogen can be widespread and severe. It is vital to understand the mechanisms by which high urea nitrogen levels exert their effects and the potential consequences for long-term health. By exploring the ways in which elevated urea nitrogen hurts the body, individuals can better appreciate the importance of maintaining healthy kidney function and seeking medical care when signs of kidney distress appear.
Introduction to Urea Nitrogen

Causes of High Urea Nitrogen Levels
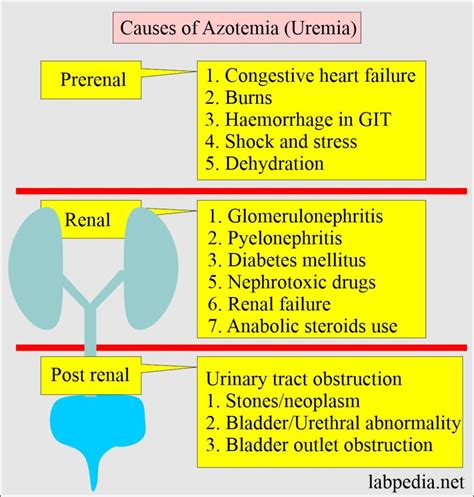
Effects on the Body
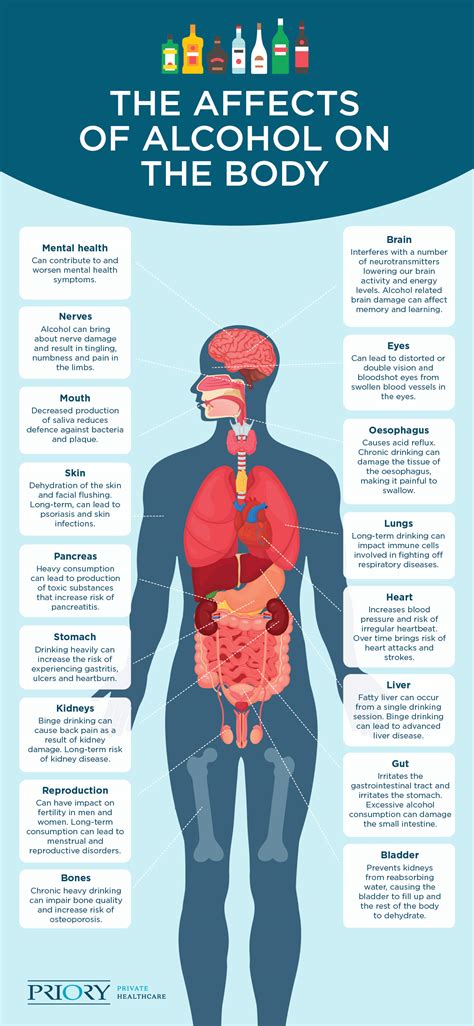
Neurological Complications
High urea nitrogen levels can affect the central nervous system, leading to a range of neurological complications. These can include: - Cognitive impairment: High levels of urea in the blood can impair cognitive function, leading to difficulties with concentration and memory. - Seizures: In severe cases, uremia can cause seizures due to the toxic effects of urea on the brain. - Peripheral neuropathy: Damage to the peripheral nerves can result in numbness, tingling, and pain in the extremities.Treatment and Management
Prevention Strategies

Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications can play a significant role in preventing and managing high urea nitrogen levels. These modifications include: - Quitting smoking: Smoking can damage the kidneys and increase the risk of kidney disease. - Limiting alcohol consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption can impair kidney function and increase the risk of kidney disease. - Engaging in regular physical activity: Exercise can help maintain healthy blood pressure and improve overall health.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about high urea nitrogen levels in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards promoting kidney health and reducing the burden of kidney disease.
What are the common symptoms of high urea nitrogen levels?
+Common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, and in severe cases, neurological symptoms such as confusion and seizures.
How is high urea nitrogen levels diagnosed?
+Diagnosis is typically made through blood tests that measure urea nitrogen levels, along with other tests to assess kidney function and identify underlying causes.
