Intro
Discover Lyme disease symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. Learn about tick-borne illness, prevention, and management of Lyme disease causes, effects, and risks.
Lyme disease is a complex and often misunderstood illness that affects thousands of people worldwide every year. It is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and is typically transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected blacklegged tick. Despite its prevalence, Lyme disease remains a topic of controversy and debate, with many people unsure of how to prevent it, diagnose it, or treat it. In this article, we will delve into the world of Lyme disease, exploring its history, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention, as well as the latest research and developments in the field.
The history of Lyme disease is fascinating, with the first reported cases dating back to the 1970s in Lyme, Connecticut. Since then, the disease has spread rapidly across the United States and Europe, with cases reported in over 60 countries worldwide. Lyme disease is often referred to as the "great imitator" due to its ability to mimic other illnesses, making diagnosis and treatment challenging. As we explore the complexities of Lyme disease, it becomes clear that education and awareness are key to preventing and managing this debilitating illness.
Lyme disease is a significant public health concern, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimating that over 300,000 cases are diagnosed in the United States each year. The disease can affect anyone, regardless of age or location, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe. From flu-like symptoms and joint pain to neurological problems and heart issues, Lyme disease is a multifaceted illness that requires a comprehensive approach to treatment and management. As we navigate the world of Lyme disease, it is essential to understand the various aspects of this complex illness and how they impact individuals and communities.
Understanding Lyme Disease
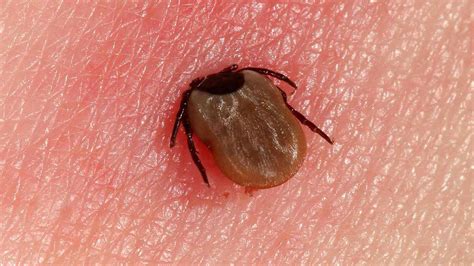
Early Localized Stage
The early localized stage of Lyme disease typically occurs within 3-30 days of the tick bite and is characterized by a distinctive rash, known as erythema migrans. The rash is usually circular or oval in shape and can expand over time, clearing in the center to form a "bull's-eye" pattern. Other symptoms during this stage may include fever, headache, and fatigue. It is essential to seek medical attention if you experience any of these symptoms, as early treatment can help prevent the disease from progressing to later stages.Symptoms and Diagnosis
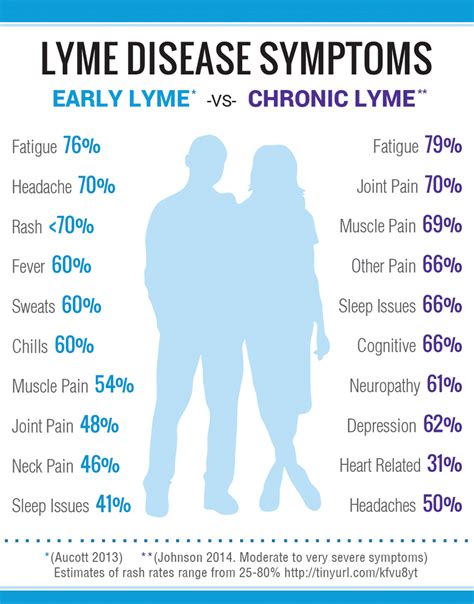
Diagnosing Lyme disease typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The most common laboratory test used to diagnose Lyme disease is the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which detects the presence of antibodies against the Borrelia burgdorferi bacterium. However, this test is not always accurate, and a Western blot test may be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment Options
Treatment for Lyme disease typically involves antibiotics, which can help eliminate the bacteria and alleviate symptoms. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics for Lyme disease are doxycycline and amoxicillin, which are usually taken for 2-4 weeks. In some cases, intravenous antibiotics may be necessary, particularly for people with neurological or heart problems. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve, to ensure that the bacteria are fully eliminated.Prevention and Management
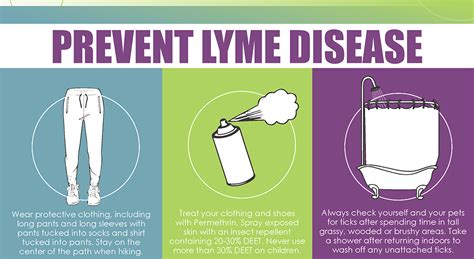
In addition to prevention, managing Lyme disease requires a comprehensive approach that includes medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and stress management. Some effective management strategies include:
- Getting plenty of rest and avoiding strenuous activities
- Eating a healthy, balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga
Current Research and Developments
Researchers are continually working to improve our understanding of Lyme disease and develop more effective treatments. Some current areas of research include: * Developing more accurate diagnostic tests, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) tests * Investigating the use of alternative antibiotics, such as azithromycin and clarithromycin * Exploring the role of coinfections, such as babesiosis and anaplasmosis, in Lyme disease * Developing vaccines to prevent Lyme diseaseChallenges and Controversies

Patient Support and Advocacy
Living with Lyme disease can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Patient support and advocacy are essential for helping people cope with the disease and navigate the healthcare system. Some effective ways to support and advocate for people with Lyme disease include: * Educating yourself and others about the disease * Joining support groups or online forums * Participating in advocacy efforts, such as fundraising and awareness campaigns * Encouraging healthcare providers to stay up-to-date with the latest research and developmentsConclusion and Future Directions

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Lyme disease in the comments below. If you or someone you know is living with Lyme disease, we encourage you to seek support and advocacy from organizations and communities dedicated to this cause. Together, we can make a difference and create a brighter future for people affected by this debilitating illness.
What are the symptoms of Lyme disease?
+The symptoms of Lyme disease can vary widely, but common symptoms include flu-like symptoms, joint pain and swelling, neurological problems, and skin rashes.
How is Lyme disease diagnosed?
+Lyme disease is typically diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as the ELISA and Western blot tests.
What is the treatment for Lyme disease?
+Treatment for Lyme disease typically involves antibiotics, such as doxycycline and amoxicillin, which can help eliminate the bacteria and alleviate symptoms.
Can Lyme disease be prevented?
+Yes, Lyme disease can be prevented by using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, conducting regular tick checks, and removing attached ticks promptly and correctly.
Is there a cure for Lyme disease?
+While there is no cure for Lyme disease, antibiotics can help eliminate the bacteria and alleviate symptoms. In some cases, people may experience persistent symptoms, which can be managed with ongoing treatment and support.
