Intro
Discover the ultimate Lisinopril Doses Guide, covering dosage forms, administration, and blood pressure management, with insights on hypertension treatment, ACE inhibitors, and cardiovascular health.
Lisinopril is a medication that belongs to a class of drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. It is primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart failure. Lisinopril works by relaxing blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood. This medication is often prescribed because it has been shown to be effective in reducing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and kidney damage due to high blood pressure and diabetes. Understanding the proper dosage of lisinopril is crucial for its safe and effective use.
The importance of managing high blood pressure cannot be overstated. Hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, which are among the leading causes of death worldwide. Effective management of blood pressure through lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication can significantly reduce the risk of these complications. Lisinopril, with its proven track record, is a commonly prescribed medication for this purpose. However, like all medications, it must be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as the appropriate dose can vary based on the individual's health status, age, and other factors.
Lisinopril's effectiveness in treating heart failure is another reason for its widespread use. Heart failure is a chronic condition where the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs for blood and oxygen. By reducing the workload on the heart and improving its efficiency, lisinopril can help manage symptoms of heart failure and improve quality of life. The medication comes in various doses, and the choice of dose depends on the specific condition being treated, as well as the patient's response to the medication.
Lisinopril Dosage Information
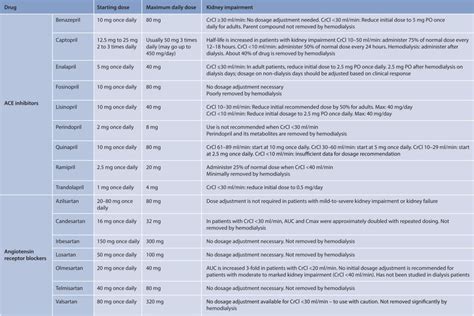
When it comes to dosing lisinopril, healthcare providers consider several factors, including the patient's age, kidney function, and the presence of other health conditions. For adults with high blood pressure, the usual starting dose is 10 mg once daily. The dose can be adjusted based on the patient's response to the medication, with a maximum dose of 80 mg per day. For heart failure, the starting dose is typically 5 mg daily, which can be increased as needed and tolerated, up to a maximum of 40 mg daily.
Factors Influencing Lisinopril Dosage
The dosage of lisinopril can be influenced by several factors, including the patient's kidney function. Since lisinopril is excreted by the kidneys, patients with impaired kidney function may require lower doses to avoid accumulation of the drug in the body. Additionally, patients over 65 years may also require lower doses due to decreased kidney function and other age-related changes. It is also important to consider potential interactions with other medications, as these can affect how lisinopril works or increase the risk of side effects.Benefits of Lisinopril

The benefits of lisinopril are well-documented. By lowering blood pressure, it reduces the strain on the heart, arteries, and kidneys, thereby decreasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. For patients with heart failure, lisinopril has been shown to improve survival and reduce hospitalizations. It is also known for its protective effects on the kidneys, particularly in patients with diabetes, by reducing proteinuria (the presence of excess proteins in the urine) and slowing the progression of kidney disease.
Common Side Effects and Precautions
Like all medications, lisinopril can cause side effects, although not everyone who takes it will experience them. Common side effects include cough, dizziness, headache, and fatigue. In some cases, lisinopril can cause more serious side effects, such as increased potassium levels, which can lead to abnormal heart rhythms. It is essential for patients to report any side effects to their healthcare provider, as adjustments in the dose or switching to a different medication may be necessary.Administration and Storage

Lisinopril should be taken exactly as prescribed by the healthcare provider. It can be taken with or without food, but it is recommended to take it at the same time every day to maintain consistent levels of the medication in the blood. The tablets should be swallowed whole and not crushed or chewed. Storage instructions typically advise keeping the medication at room temperature, away from moisture and heat.
Special Considerations
There are special considerations for certain groups of people. For pregnant women, ACE inhibitors like lisinopril are generally not recommended, especially in the second and third trimesters, due to the potential risk of harm to the fetus. Breastfeeding mothers should also consult their healthcare provider before taking lisinopril, as it is not known whether the drug passes into breast milk. Additionally, patients with a history of angioedema (a condition characterized by the rapid swelling of the skin and mucous membranes) should use lisinopril with caution.Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring is essential for patients taking lisinopril. This includes checking blood pressure regularly, as well as monitoring kidney function and electrolyte levels. Patients should also be aware of the signs of potential side effects and seek medical attention if they experience any unusual symptoms. Follow-up appointments with the healthcare provider are crucial to adjust the dose as needed, manage side effects, and ensure that the medication is working effectively.
Importance of Adherence
Adhering to the prescribed regimen is crucial for the effectiveness of lisinopril. Patients should not stop taking the medication without consulting their healthcare provider, as this can lead to a rebound effect and worsening of the condition. It is also important to keep all follow-up appointments and to inform the healthcare provider about any changes in health status or the use of other medications.Lisinopril Interactions

Lisinopril can interact with other medications, which may affect its efficacy or increase the risk of side effects. For example, diuretics can increase the risk of low blood pressure when taken with lisinopril. Potassium supplements and certain other medications can lead to high levels of potassium in the blood. It is essential for patients to provide their healthcare provider with a list of all medications, supplements, and vitamins they are taking to minimize potential interactions.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, lisinopril is a valuable medication for the management of high blood pressure and heart failure. Its effectiveness, combined with a relatively favorable side effect profile, makes it a commonly prescribed ACE inhibitor. However, like all medications, it must be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider, with careful consideration of the appropriate dose, potential side effects, and drug interactions. As research continues to uncover the benefits and limitations of lisinopril, healthcare providers and patients must work together to ensure its safe and effective use.Final Thoughts

In final thoughts, managing high blood pressure and heart failure requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medication. Lisinopril, with its proven benefits and relatively long history of use, is an important tool in this management. By understanding how to use lisinopril effectively and safely, patients can better control their condition and reduce the risk of complications.
What is the primary use of lisinopril?
+Lisinopril is primarily used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) and heart failure. It works by relaxing blood vessels, making it easier for the heart to pump blood.
How does lisinopril affect kidney function?
+Lisinopril can have protective effects on the kidneys, particularly in patients with diabetes, by reducing proteinuria and slowing the progression of kidney disease. However, it requires careful dosing in patients with impaired kidney function.
Can lisinopril be used during pregnancy?
+ACE inhibitors like lisinopril are generally not recommended during pregnancy, especially in the second and third trimesters, due to the potential risk of harm to the fetus.
We invite readers to share their experiences or ask questions about lisinopril in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this information. Your engagement and feedback are invaluable in helping us provide the most accurate and helpful content possible.
