Intro
Discover the proper Z Pack antibiotic dosage for effective treatment, including usage guidelines, side effects, and interactions, to ensure safe and successful recovery from bacterial infections.
The importance of understanding antibiotic dosages cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to commonly prescribed medications like the Z Pack. The Z Pack, also known as azithromycin, is a popular antibiotic used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory, skin, and sexually transmitted infections. With its widespread use, it's crucial for patients to comprehend the proper dosage to ensure effective treatment and minimize potential side effects. In this article, we'll delve into the world of Z Pack antibiotic dosage, exploring its benefits, working mechanisms, and key information related to its use.
As we navigate the complexities of antibiotic treatment, it's essential to recognize the significance of adhering to prescribed dosages. The Z Pack is typically prescribed in a five-day course, with the dosage varying depending on the specific infection being treated. Patients must understand that deviating from the recommended dosage can lead to reduced efficacy, increased risk of side effects, or even the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. By grasping the fundamentals of Z Pack antibiotic dosage, individuals can take an active role in their treatment, fostering a stronger partnership with their healthcare provider and promoting better health outcomes.
The Z Pack's popularity stems from its broad-spectrum antibacterial properties, which enable it to effectively combat a range of infections. From pneumonia and bronchitis to sinusitis and skin infections, azithromycin has proven to be a valuable asset in the fight against bacterial diseases. As we explore the intricacies of Z Pack antibiotic dosage, we'll examine the various factors that influence dosing, including the type and severity of the infection, patient age, weight, and renal function. By considering these factors, healthcare providers can tailor treatment regimens to meet the unique needs of each patient, optimizing the chances of successful treatment and minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Z Pack Antibiotic Dosage Information
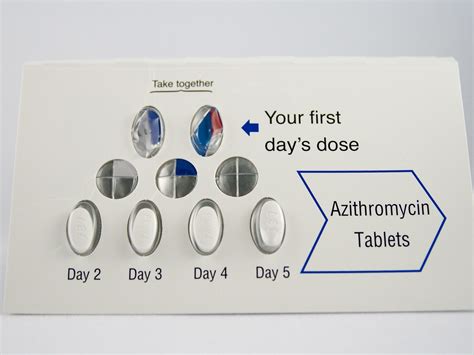
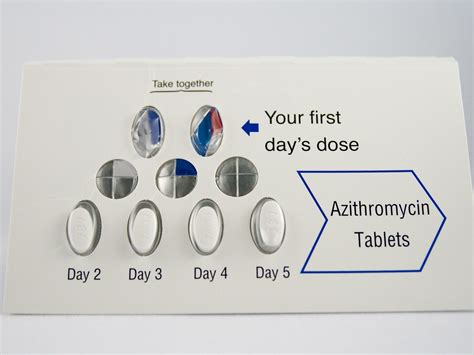
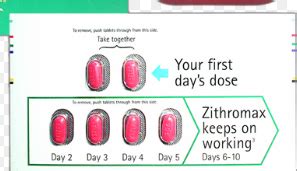
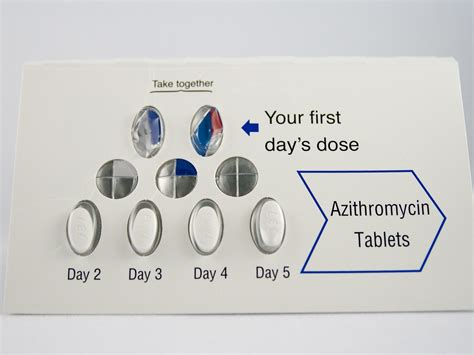
To ensure the safe and effective use of the Z Pack, it's essential to understand the recommended dosage for various infections. The typical adult dosage for azithromycin is 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg per day for the next four days. However, dosages may vary depending on the specific infection being treated. For example, patients with community-acquired pneumonia may require a higher dosage of 500 mg per day for three days. In contrast, those with uncomplicated skin infections may be prescribed a lower dosage of 250 mg per day for five days.
Factors Influencing Z Pack Dosage
When determining the optimal Z Pack dosage, healthcare providers consider several key factors, including: * Patient age and weight * Renal function and liver function * Severity of the infection * Presence of underlying medical conditions * Potential interactions with other medicationsBy taking these factors into account, healthcare providers can create personalized treatment plans that balance efficacy with safety, minimizing the risk of adverse reactions and ensuring the best possible outcomes for patients.
Z Pack Antibiotic Side Effects
While the Z Pack is generally well-tolerated, patients should be aware of potential side effects associated with its use. Common adverse reactions include:
- Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
- Headaches and dizziness
- Fatigue and weakness
- Rash and itching
In rare cases, azithromycin may cause more severe side effects, such as:
- Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis
- Cardiac arrhythmias and QT interval prolongation
- Liver damage and elevated liver enzymes
- Increased risk of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection
Patients experiencing any unusual symptoms or side effects should promptly notify their healthcare provider, as timely intervention can help mitigate potential complications.
Z Pack Interactions and Contraindications
To ensure safe and effective treatment, patients must inform their healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products they are taking. Azithromycin may interact with certain medications, including: * Warfarin and other anticoagulants * Digoxin and other cardiac glycosides * Cyclosporine and other immunosuppressants * Antacids and other medications that alter stomach pHAdditionally, patients with certain medical conditions, such as:
- Liver or kidney disease
- Heart rhythm disorders
- Myasthenia gravis
- History of allergic reactions to macrolide antibiotics
may require special consideration or alternative treatment options.
Z Pack Antibiotic Resistance
The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria poses a significant threat to public health, highlighting the need for responsible antibiotic use and stewardship. The Z Pack, like other antibiotics, can contribute to the development of resistance when used inappropriately or in excess. To mitigate this risk, healthcare providers must:
- Prescribe antibiotics judiciously, reserving them for cases where bacterial infection is confirmed or suspected
- Adhere to recommended dosages and treatment durations
- Monitor patients for signs of treatment failure or resistance
- Encourage patients to complete the full treatment course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication
By adopting these strategies, we can help preserve the effectiveness of the Z Pack and other antibiotics, ensuring their continued availability for future generations.
Z Pack Antibiotic Dosage in Special Populations
When treating patients with unique needs, such as pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, or individuals with renal impairment, healthcare providers must carefully consider the risks and benefits of Z Pack treatment. In these cases, dosages may need to be adjusted or alternative treatment options explored. For example: * Pregnant women may require lower dosages or alternative antibiotics due to potential fetal risks * Breastfeeding women may need to temporarily discontinue nursing or express and discard milk during treatment * Children may require weight-based dosing or alternative formulations, such as oral suspension * Patients with renal impairment may require dose adjustments or more frequent monitoring due to increased risk of side effectsBy tailoring treatment to the individual needs of each patient, healthcare providers can optimize outcomes while minimizing potential complications.
Z Pack Antibiotic Treatment Duration
The duration of Z Pack treatment varies depending on the specific infection being treated. Typical treatment courses range from five to seven days, although some infections may require longer or shorter treatment durations. Patients must complete the full treatment course, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication, to ensure:
- Complete eradication of the infection
- Reduced risk of treatment failure or resistance
- Prevention of relapse or recurrence
By adhering to the recommended treatment duration, patients can help ensure the best possible outcomes and minimize the risk of complications.
Z Pack Antibiotic Patient Education
To promote safe and effective treatment, patients should be educated on the proper use of the Z Pack, including: * Importance of completing the full treatment course * Potential side effects and interactions * Need for regular follow-up appointments * Signs and symptoms of treatment failure or resistanceBy empowering patients with knowledge and involving them in the treatment process, healthcare providers can foster a collaborative approach to care, leading to better health outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Z Pack Antibiotic Frequently Asked Questions
As patients navigate the complexities of Z Pack treatment, they often have questions and concerns. Some common queries include:
- What are the potential side effects of the Z Pack?
- Can I take the Z Pack with other medications?
- How long does it take for the Z Pack to start working?
- Can I stop taking the Z Pack if my symptoms improve?
By addressing these questions and providing clear, concise information, healthcare providers can help alleviate patient concerns and promote a smoother treatment experience.
Z Pack Antibiotic Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the Z Pack antibiotic dosage plays a critical role in ensuring the safe and effective treatment of various bacterial infections. By understanding the recommended dosages, potential side effects, and factors influencing treatment, patients can take an active role in their care, fostering a stronger partnership with their healthcare provider. As we move forward, it's essential to prioritize responsible antibiotic use, adopting strategies to mitigate the risk of resistance and preserve the effectiveness of the Z Pack and other antibiotics. By working together, we can promote better health outcomes, reduce the burden of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and ensure the continued availability of these life-saving medications for future generations.What is the typical dosage of the Z Pack for adults?
+The typical adult dosage for azithromycin is 500 mg on the first day, followed by 250 mg per day for the next four days.
Can I take the Z Pack with other medications?
+Azithromycin may interact with certain medications, including warfarin, digoxin, and cyclosporine. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and herbal products they are taking.
How long does it take for the Z Pack to start working?
+The Z Pack typically starts working within a few days of treatment, although the full effects may not be apparent until the treatment course is completed.
As we conclude our exploration of Z Pack antibiotic dosage, we invite you to share your thoughts, questions, and concerns. Whether you're a patient, healthcare provider, or simply an interested reader, your input can help shape the conversation around responsible antibiotic use and promote better health outcomes for all. Join the discussion, share this article with others, and let's work together to ensure the continued effectiveness of the Z Pack and other antibiotics for generations to come.
