Intro
Understand A1c levels with our comprehensive chart guide, featuring HbA1c ranges, blood sugar targets, and diabetes management insights to help monitor and control glucose levels, preventing complications and ensuring optimal health outcomes.
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as it helps prevent complications and ensures overall well-being. The A1c test is a vital tool in managing diabetes, providing a snapshot of average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. Understanding A1c levels is essential for individuals with diabetes, as well as those at risk of developing the condition. In this article, we will delve into the world of A1c levels, exploring the importance of the A1c test, how to interpret results, and strategies for achieving optimal A1c levels.
The A1c test measures the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen throughout the body. When glucose is present in the blood, it binds to hemoglobin, forming glycosylated hemoglobin, also known as A1c. The higher the A1c level, the more glucose has accumulated in the blood over time. This test is essential for diagnosing and monitoring diabetes, as well as assessing the risk of developing complications.
For individuals with diabetes, monitoring A1c levels is crucial for adjusting treatment plans and making lifestyle changes to achieve optimal blood sugar control. The American Diabetes Association recommends aiming for an A1c level below 7% for most adults, although this target may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health status, and duration of diabetes. By understanding A1c levels and how to interpret test results, individuals with diabetes can take a proactive approach to managing their condition and reducing the risk of complications.
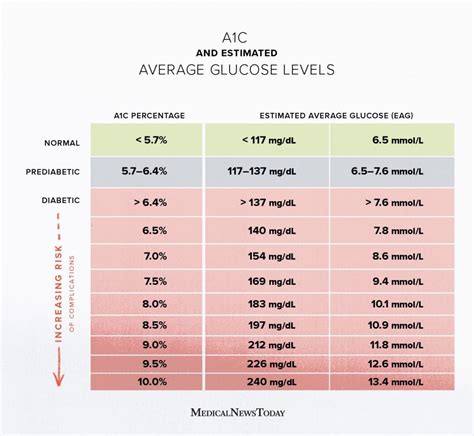
A1c Levels Chart
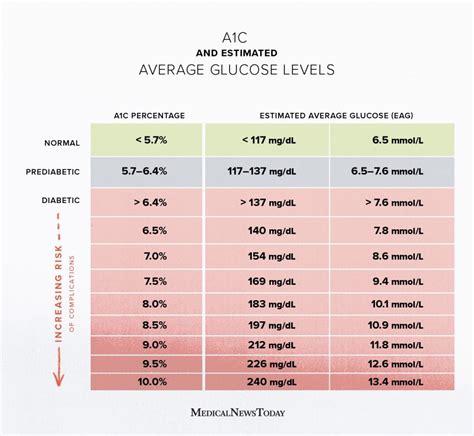
Understanding A1c Test Results

A1c Level Targets
A1c level targets may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health status, and duration of diabetes. The following A1c level targets are general guidelines: * Adults with diabetes: <7% * Children with diabetes: <7.5% * Pregnant women with diabetes: <6.5% * Older adults with diabetes: <7.5%-8%A1c Levels and Blood Sugar Control

Strategies for Lowering A1c Levels
The following strategies can help individuals with diabetes lower their A1c levels: * Increase physical activity: Engage in regular aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. * Improve diet: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods, and limit sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates. * Reduce stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. * Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.A1c Levels and Diabetes Complications
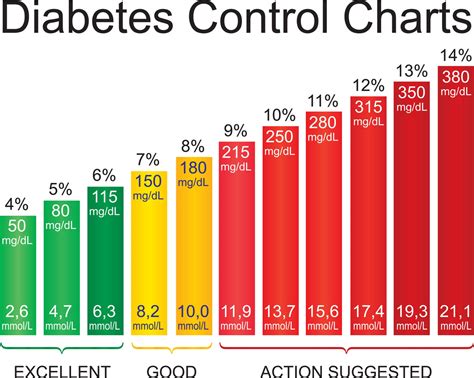
Risk Factors for Diabetes Complications
The following risk factors increase the likelihood of developing diabetes-related complications: * Duration of diabetes: The longer an individual has diabetes, the higher the risk of complications. * A1c level: High A1c levels are associated with an increased risk of complications. * Blood pressure: High blood pressure can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and kidney damage. * Cholesterol levels: High cholesterol levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease.A1c Levels and Prediabetes
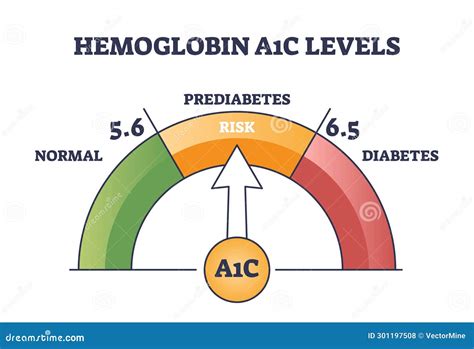
Strategies for Preventing Type 2 Diabetes
The following strategies can help individuals with prediabetes prevent the development of type 2 diabetes: * Lose weight: If overweight or obese, losing weight can help improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes. * Increase physical activity: Engage in regular aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming. * Improve diet: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods, and limit sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates. * Reduce stress: Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.A1c Levels and Pregnancy
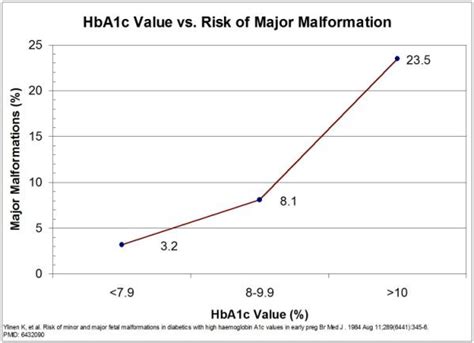
Strategies for Managing Diabetes During Pregnancy
The following strategies can help individuals with diabetes manage their condition during pregnancy: * Monitor blood glucose levels: Regularly check blood glucose levels to identify patterns and make informed decisions about diet, physical activity, and medication. * Develop a personalized meal plan: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods, and limit sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates. * Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. * Take medications as prescribed: Adhere to medication regimens and attend regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers.A1c Levels and Children
Strategies for Managing Diabetes in Children
The following strategies can help children with diabetes manage their condition: * Monitor blood glucose levels: Regularly check blood glucose levels to identify patterns and make informed decisions about diet, physical activity, and medication. * Develop a personalized meal plan: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods, and limit sugary drinks and refined carbohydrates. * Engage in regular physical activity: Aim for at least 60 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 30 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per day. * Take medications as prescribed: Adhere to medication regimens and attend regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers.What is the A1c test?
+The A1c test is a blood test that measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2-3 months.
What is the normal range for A1c levels?
+The normal range for A1c levels is 4%-5.6%.
What are the risks of high A1c levels?
+High A1c levels are associated with an increased risk of diabetes-related complications, including cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney damage, and blindness.
How can I lower my A1c levels?
+Strategies for lowering A1c levels include increasing physical activity, improving diet, reducing stress, and taking medications as prescribed.
What is the target A1c level for individuals with diabetes?
+The target A1c level for most adults with diabetes is <7%.
In conclusion, understanding A1c levels is essential for individuals with diabetes, as well as those at risk of developing the condition. By interpreting A1c test results, setting target A1c levels, and implementing strategies for achieving optimal A1c levels, individuals can take a proactive approach to managing their condition and reducing the risk of complications. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with A1c levels and diabetes management in the comments below. Additionally, please consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards better diabetes management and improved overall health.
