Intro
Discover the normal sed rate range and understand its significance in diagnosing inflammation and conditions like arthritis, lupus, and infections, with related tests and results interpretation for accurate health assessments.
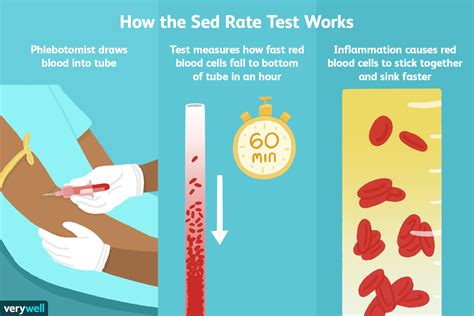
The sed rate, short for sedimentation rate, is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes (red blood cells) settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. It indirectly measures how much inflammation is in the body. The sed rate is also known as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). In this article, we will delve into the details of a normal sed rate, its significance, and what it indicates about a person's health.
A normal sed rate is typically considered to be between 0-20 mm/h for adults, but it can vary depending on age and sex. Women tend to have higher sed rates than men, and sed rates tend to increase with age. The test is often used to help diagnose and monitor various conditions, including inflammatory diseases, infections, and cancer. A sed rate that is higher than normal may indicate the presence of inflammation in the body, which can be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
The process of measuring the sed rate involves taking a blood sample from a vein, usually in the arm, and placing it in a test tube with an anticoagulant to prevent the blood from clotting. The test tube is then left to stand upright for a specified period, usually one hour, allowing the red blood cells to settle to the bottom. The distance the red blood cells have traveled is then measured and recorded as the sed rate. This test is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as the C-reactive protein (CRP) test, to get a more comprehensive picture of a person's health.
What is a Normal Sed Rate?
Factors Affecting Sed Rate
Several factors can affect the sed rate, including: * Age: Sed rates tend to increase with age * Sex: Women tend to have higher sed rates than men * Pregnancy: Sed rates can increase during pregnancy * Menstruation: Sed rates can increase during menstruation * Medications: Certain medications, such as oral contraceptives and corticosteroids, can affect sed rates * Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as anemia, can affect sed ratesHow is Sed Rate Used in Diagnosis?
Interpreting Sed Rate Results
Interpreting sed rate results requires careful consideration of various factors, including the patient's age, sex, and medical history. The following are general guidelines for interpreting sed rate results: * A sed rate of 0-20 mm/h is generally considered normal * A sed rate of 20-50 mm/h may indicate mild inflammation or infection * A sed rate of 50-100 mm/h may indicate moderate inflammation or infection * A sed rate above 100 mm/h may indicate severe inflammation or infectionWhat Does a High Sed Rate Indicate?
Treatments for High Sed Rate
Treatment for a high sed rate depends on the underlying cause of the inflammation. Some possible treatments include: * Anti-inflammatory medications, such as corticosteroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) * Antibiotics, if the cause of the inflammation is a bacterial infection * Antiviral medications, if the cause of the inflammation is a viral infection * Chemotherapy, if the cause of the inflammation is cancer * Lifestyle modifications, such as exercise and dietary changes, to help manage chronic diseasesWhat Does a Low Sed Rate Indicate?

Causes of Low Sed Rate
Some possible causes of a low sed rate include: * Medications, such as aspirin and other NSAIDs * Medical conditions, such as sickle cell anemia and polycythemia vera * Inadequate blood sample collection or handling * Laboratory errorLimitations of Sed Rate Test
Alternatives to Sed Rate Test
Some alternatives to the sed rate test include: * C-reactive protein (CRP) test: This test measures the level of CRP in the blood, which can indicate the presence of inflammation. * Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) test: This test measures the rate at which red blood cells settle to the bottom of a test tube, which can indicate the presence of inflammation. * Blood cell count: This test measures the number of red and white blood cells in the blood, which can help diagnose various medical conditions.What is a normal sed rate for adults?
+A normal sed rate for adults is typically considered to be between 0-20 mm/h, but it can vary depending on age and sex.
What does a high sed rate indicate?
+A high sed rate can indicate the presence of inflammation in the body, which can be a sign of an underlying medical condition.
What are the limitations of the sed rate test?
+The sed rate test has several limitations, including its lack of specificity and sensitivity, and its potential to be affected by various factors, such as age, sex, and medical conditions.
In conclusion, the sed rate is a blood test that measures how quickly erythrocytes settle at the bottom of a test tube containing a blood sample. A normal sed rate can vary depending on age and sex, and the test is often used to help diagnose and monitor various medical conditions. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the sed rate and its significance in medical diagnosis. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with the sed rate test, please feel free to comment below.
