Intro
Unlock the secrets of your blood health with a CBC with Differential test, analyzing white blood cell count, red blood cell count, hematocrit, and platelet count to diagnose anemia, infection, and bleeding disorders, providing valuable insights into your overall well-being.
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) with differential blood test is a crucial diagnostic tool used to evaluate various components of the blood, providing valuable insights into a person's overall health. This test is commonly ordered by healthcare providers to diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, from infections and inflammatory diseases to blood disorders and cancer. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the CBC with differential blood test, its components, and how it is used to diagnose and manage various health conditions.
The CBC with differential blood test is a comprehensive test that measures different parameters of the blood, including the levels of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin. The test also includes a differential count, which provides a detailed breakdown of the different types of white blood cells present in the blood. This information is essential for diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions, as changes in blood cell counts can indicate underlying diseases or disorders.
The importance of the CBC with differential blood test cannot be overstated. It is a vital tool for healthcare providers, allowing them to quickly and accurately diagnose a wide range of health conditions. The test is also useful for monitoring the effectiveness of treatments and detecting potential complications early on. In addition, the CBC with differential blood test is a relatively non-invasive and low-cost procedure, making it a widely used diagnostic tool in clinical practice.
CBC Components

The CBC with differential blood test includes several components, each providing valuable information about the blood. The main components of the test include:
- Red Blood Cell (RBC) count: measures the number of red blood cells in the blood
- White Blood Cell (WBC) count: measures the number of white blood cells in the blood
- Platelet count: measures the number of platelets in the blood
- Hemoglobin (Hb) level: measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood
- Hematocrit (Hct) level: measures the proportion of red blood cells in the blood
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): measures the average size of red blood cells
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH): measures the average amount of hemoglobin in red blood cells
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC): measures the average concentration of hemoglobin in red blood cells
- Differential count: provides a detailed breakdown of the different types of white blood cells present in the blood
Differential Count
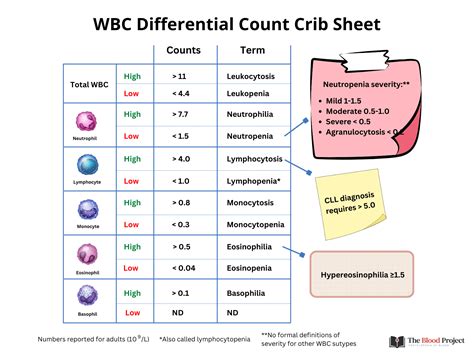
The differential count is an essential component of the CBC with differential blood test. It provides a detailed breakdown of the different types of white blood cells present in the blood, including:
- Neutrophils: the most common type of white blood cell, responsible for fighting bacterial infections
- Lymphocytes: responsible for fighting viral infections and producing antibodies
- Monocytes: mature into macrophages, which engulf and digest foreign particles and microorganisms
- Eosinophils: play a role in fighting parasitic infections and allergic reactions
- Basophils: play a role in inflammatory responses and allergic reactions
Interpreting CBC Results
Interpreting the results of the CBC with differential blood test requires a thorough understanding of the normal ranges for each component. The normal ranges for each component can vary slightly depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and other factors. Abnormal results can indicate a wide range of health conditions, from mild to severe.
For example, a low RBC count can indicate anemia, while a high WBC count can indicate infection or inflammation. A low platelet count can indicate bleeding disorders or bone marrow problems, while a high platelet count can indicate inflammation or cancer.
Clinical Applications
The CBC with differential blood test has a wide range of clinical applications, including:
- Diagnosing and monitoring anemia, blood disorders, and cancer
- Evaluating the effectiveness of treatments for various health conditions
- Detecting potential complications early on
- Monitoring patients with chronic diseases, such as diabetes and hypertension
- Evaluating patients with symptoms of infection, inflammation, or bleeding disorders
Common Health Conditions Diagnosed with CBC
The CBC with differential blood test is commonly used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions, including:
- Anemia: a condition characterized by a low RBC count or low hemoglobin level
- Infections: such as bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections
- Inflammatory diseases: such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Blood disorders: such as leukemia or lymphoma
- Bleeding disorders: such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease
Limitations and Potential Risks

While the CBC with differential blood test is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has several limitations and potential risks. For example:
- The test may not detect all types of health conditions, such as certain types of cancer or autoimmune disorders
- The test may produce false-positive or false-negative results, which can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis
- The test may require additional testing or procedures to confirm a diagnosis
- The test may cause discomfort or anxiety in some individuals, particularly those with a fear of needles or blood draws
Preparing for the Test
To prepare for the CBC with differential blood test, individuals should:
- Follow their healthcare provider's instructions for fasting or other preparations
- Avoid taking certain medications or supplements that may affect the test results
- Wear comfortable clothing and arrive early for the test
- Bring any relevant medical records or test results to the appointment
Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, the CBC with differential blood test is a vital diagnostic tool used to evaluate various components of the blood. The test provides valuable insights into a person's overall health and is commonly used to diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions. While the test has several limitations and potential risks, it remains a widely used and essential tool in clinical practice.
As medical technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see advancements in the field of hematology and the development of new diagnostic tests. For example, the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms may improve the accuracy and efficiency of blood tests, while the development of new biomarkers and molecular tests may enable earlier detection and diagnosis of various health conditions.
What is the purpose of a CBC with differential blood test?
+The purpose of a CBC with differential blood test is to evaluate various components of the blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and hemoglobin, to diagnose and monitor a wide range of health conditions.
What are the components of a CBC with differential blood test?
+The components of a CBC with differential blood test include red blood cell count, white blood cell count, platelet count, hemoglobin level, hematocrit level, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, and differential count.
What are the common health conditions diagnosed with CBC?
+Common health conditions diagnosed with CBC include anemia, infections, inflammatory diseases, blood disorders, and bleeding disorders.
How do I prepare for a CBC with differential blood test?
+To prepare for a CBC with differential blood test, individuals should follow their healthcare provider's instructions for fasting or other preparations, avoid taking certain medications or supplements, wear comfortable clothing, and arrive early for the test.
What are the limitations and potential risks of a CBC with differential blood test?
+The limitations and potential risks of a CBC with differential blood test include false-positive or false-negative results, discomfort or anxiety during the test, and the need for additional testing or procedures to confirm a diagnosis.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the CBC with differential blood test and its importance in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others.
