Intro
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue that affects both men and women, although they are more prevalent in women. However, when men do get UTIs, they can be more serious and require prompt medical attention. One of the primary treatments for UTIs, including those in men, is the use of antibiotics. Understanding the role of antibiotics in treating men's UTIs is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
UTIs occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. In men, UTIs can be categorized based on the part of the urinary tract that is affected. The most common types include cystitis (infection of the bladder) and pyelonephritis (infection of the kidneys). Symptoms of UTIs in men can include burning sensation while urinating, frequent or urgent need to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pain in the side or back.
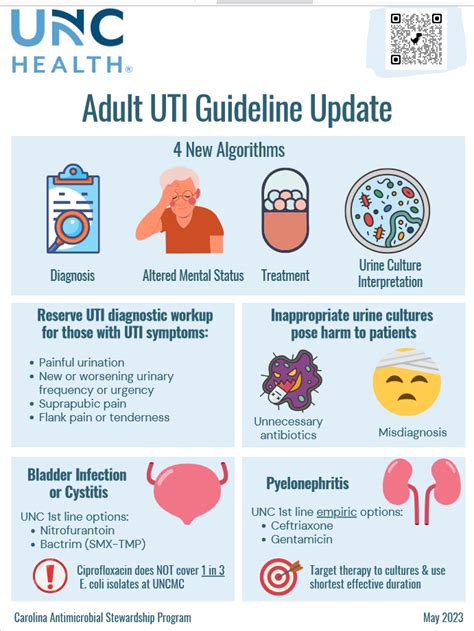
The diagnosis of a UTI typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests such as urinalysis and urine culture. The urine culture is critical in identifying the type of bacteria causing the infection, which guides the selection of the most appropriate antibiotic. Given the importance of antibiotics in treating UTIs, it is essential to use them judiciously to minimize the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Understanding Antibiotics for Men's UTI

Antibiotics are medicines that kill bacteria or stop them from multiplying. For UTIs, the choice of antibiotic depends on the severity of the infection, the type of bacteria causing the infection, and the patient's health status and medical history. Common antibiotics used for treating UTIs in men include trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and ciprofloxacin. These antibiotics are usually taken orally for a period ranging from 3 to 14 days, depending on the specific antibiotic and the severity of the infection.
Benefits of Antibiotics in Treating Men's UTI
The benefits of using antibiotics to treat UTIs in men are clear. Antibiotics can quickly eliminate the bacteria causing the infection, thereby reducing symptoms and preventing potential complications such as kidney damage. Early treatment with antibiotics can also reduce the risk of the infection spreading to other parts of the urinary tract. Furthermore, by effectively treating UTIs, antibiotics play a crucial role in improving the quality of life for men affected by these infections.Working Mechanism of Antibiotics
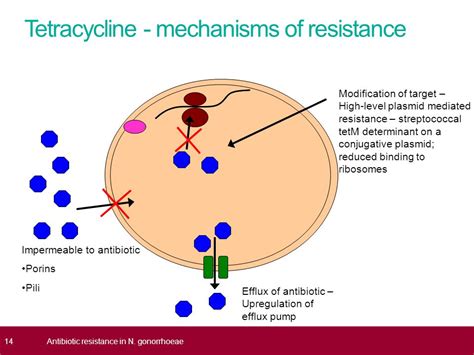
The working mechanism of antibiotics involves either killing the bacteria or inhibiting their growth. For example, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole works by inhibiting the production of folic acid, which is essential for bacterial growth and replication. Nitrofurantoin, on the other hand, damages the bacterial DNA, thereby preventing the bacteria from multiplying. Understanding how different antibiotics work is crucial for selecting the most effective treatment for a UTI.
Steps to Take Antibiotics Effectively
To ensure that antibiotics are effective in treating UTIs, men should follow their doctor's instructions carefully. This includes completing the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Stopping the antibiotic course prematurely can lead to the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Additionally, men should drink plenty of water to help flush out the bacteria from their system and reduce the concentration of the antibiotic in the urine, which can help minimize potential side effects.Practical Examples and Statistical Data
Studies have shown that the appropriate use of antibiotics can significantly reduce the duration and severity of UTI symptoms in men. For instance, a study found that men with uncomplicated UTIs who were treated with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole for 3 days had similar outcomes to those treated for 7 days, highlighting the potential for shorter treatment courses in certain cases. Statistical data also indicate that UTIs account for approximately 8 million visits to healthcare providers in the United States each year, underscoring the importance of effective treatment strategies.
Common Antibiotics Used
Some of the common antibiotics used for treating UTIs in men include: - Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole - Nitrofurantoin - Ciprofloxacin - Levofloxacin - Amoxicillin/clavulanateThese antibiotics are chosen based on their efficacy against the common bacteria causing UTIs, such as E. coli, and their safety profile.
Prevention of UTIs in Men
While antibiotics are effective in treating UTIs, prevention is also a critical aspect of managing these infections. Men can reduce their risk of developing UTIs by practicing good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back after using the bathroom, drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated, and avoiding holding urine for long periods. Additionally, men with certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or an enlarged prostate, should be particularly vigilant about UTI prevention due to their increased risk.
Complications of Untreated UTIs
Untreated UTIs can lead to serious complications, including kidney damage, recurrent infections, and in severe cases, sepsis. Therefore, it is essential for men experiencing UTI symptoms to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics can prevent these complications and ensure a full recovery.Future Perspectives on UTI Treatment
As antibiotic resistance continues to rise, there is a growing need for new and innovative approaches to treating UTIs. Research into alternative treatments, such as phage therapy and vaccines, is underway. Additionally, efforts to improve antibiotic stewardship and develop more targeted and effective antibiotics will be crucial in the future management of UTIs.
Importance of Antibiotic Stewardship
Antibiotic stewardship programs aim to promote the appropriate use of antibiotics, reduce misuse, and minimize the development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. These programs are vital in the context of UTI treatment, where the overuse or misuse of antibiotics can have significant consequences. By promoting responsible antibiotic use, we can help ensure that these lifesaving medications remain effective for generations to come.Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, antibiotics play a vital role in the treatment of UTIs in men, offering a effective way to eliminate bacterial infections and prevent complications. By understanding how antibiotics work, following treatment guidelines, and practicing prevention strategies, men can reduce their risk of UTIs and ensure prompt and effective treatment when infections do occur. As we look to the future, continued research and efforts to improve antibiotic use will be essential in managing UTIs and addressing the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance.
We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with UTIs and antibiotic treatment in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others who may benefit from this information. Together, we can promote better understanding and management of UTIs, improving health outcomes for men worldwide.
What are the symptoms of a UTI in men?
+Symptoms of a UTI in men can include a burning sensation while urinating, frequent or urgent need to urinate, cloudy or strong-smelling urine, and pain in the side or back.
How are UTIs diagnosed in men?
+UTIs are diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests such as urinalysis and urine culture.
What are the common antibiotics used to treat UTIs in men?
+Common antibiotics used to treat UTIs in men include trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and ciprofloxacin.
Can UTIs be prevented in men?
+Yes, UTIs can be prevented in men by practicing good hygiene, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding holding urine for long periods.
What are the complications of untreated UTIs in men?
+Untreated UTIs can lead to serious complications, including kidney damage, recurrent infections, and in severe cases, sepsis.
