Intro
Learn about 5 average glucose levels, normal blood sugar ranges, and managing diabetes with healthy targets, glucose monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments.
Maintaining average glucose levels is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Average glucose levels refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood, which is typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The importance of monitoring and managing average glucose levels cannot be overstated, as it plays a significant role in preventing complications and ensuring proper bodily functions.
Average glucose levels are a key indicator of how well the body is regulating blood sugar, and abnormal levels can lead to a range of health issues. For instance, high average glucose levels can cause damage to organs and tissues, increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, and lead to conditions such as diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy. On the other hand, low average glucose levels can cause symptoms like shakiness, dizziness, and confusion, and if left untreated, can lead to more severe complications.
Understanding average glucose levels and their impact on health is essential for individuals with diabetes, as well as those who are at risk of developing the condition. By monitoring and managing average glucose levels, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent complications, improve their overall health, and enhance their quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the world of average glucose levels, exploring what they are, why they are important, and how to manage them effectively.
Average Glucose Levels: What You Need to Know

Average glucose levels are typically measured using a blood test, which provides a snapshot of the amount of glucose present in the blood at a given time. The results are usually expressed as a numerical value, which can be used to determine whether average glucose levels are within a healthy range. For individuals without diabetes, average glucose levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL, while those with diabetes may have higher or lower levels, depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment.
Factors That Affect Average Glucose Levels
Several factors can affect average glucose levels, including diet, physical activity, stress, and certain medications. For example, consuming high-carbohydrate foods or drinks can cause a spike in average glucose levels, while regular physical activity can help to lower them. Stress can also impact average glucose levels, as it can cause the body to produce more cortisol, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels.Why Average Glucose Levels Matter
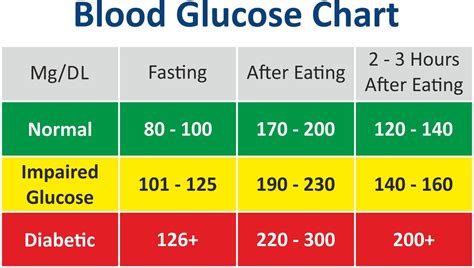
Average glucose levels play a critical role in preventing complications and ensuring proper bodily functions. High average glucose levels can cause damage to organs and tissues, increase the risk of heart disease and stroke, and lead to conditions such as diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy. On the other hand, low average glucose levels can cause symptoms like shakiness, dizziness, and confusion, and if left untreated, can lead to more severe complications.
The Risks of Unmanaged Average Glucose Levels
Unmanaged average glucose levels can lead to a range of health issues, including cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage. For example, high average glucose levels can cause the blood vessels to become damaged, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Similarly, unmanaged average glucose levels can cause kidney damage, leading to conditions such as diabetic nephropathy.Managing Average Glucose Levels

Managing average glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates diet, physical activity, stress management, and medication (if necessary). For individuals with diabetes, working with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan is essential. This may involve monitoring average glucose levels regularly, adjusting diet and physical activity, and taking medication to regulate blood sugar levels.
Strategies for Managing Average Glucose Levels
There are several strategies that can help to manage average glucose levels, including: * Eating a balanced diet that is low in carbohydrates and added sugars * Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming * Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga * Monitoring average glucose levels regularly and adjusting treatment as needed * Taking medication as prescribed by a healthcare providerAverage Glucose Levels and Diet
Diet plays a critical role in managing average glucose levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Eating a balanced diet that is low in carbohydrates and added sugars can help to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent spikes in average glucose levels. Foods that are rich in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can also help to slow the absorption of sugar and reduce the risk of complications.
Foods That Can Help to Manage Average Glucose Levels
There are several foods that can help to manage average glucose levels, including: * Leafy green vegetables, such as spinach and kale * Berries, such as blueberries and strawberries * Nuts and seeds, such as almonds and chia seeds * Fatty fish, such as salmon and tuna * Whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoaAverage Glucose Levels and Physical Activity
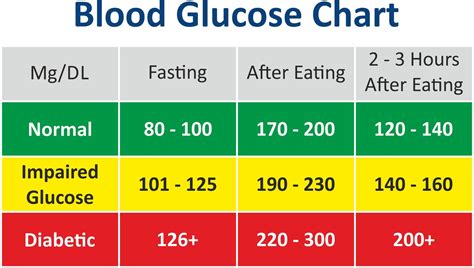
Physical activity is also essential for managing average glucose levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Regular physical activity can help to lower average glucose levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of complications. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent options, as they are low-impact and can be modified to suit individual fitness levels.
Benefits of Physical Activity for Average Glucose Levels
There are several benefits of physical activity for average glucose levels, including: * Lowering average glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity * Reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke * Improving mental health and reducing stress * Enhancing overall physical fitness and mobilityAverage Glucose Levels and Stress Management

Stress management is also essential for managing average glucose levels, particularly for individuals with diabetes. Stress can cause the body to produce more cortisol, a hormone that raises blood sugar levels. Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help to lower average glucose levels and reduce the risk of complications.
Techniques for Managing Stress and Average Glucose Levels
There are several techniques that can help to manage stress and average glucose levels, including: * Meditation and mindfulness * Yoga and tai chi * Deep breathing exercises * Progressive muscle relaxation * Journaling and expressive writingWhat are average glucose levels?
+Average glucose levels refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood, typically measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
Why are average glucose levels important?
+Average glucose levels play a critical role in preventing complications and ensuring proper bodily functions, particularly for individuals with diabetes.
How can I manage my average glucose levels?
+Managing average glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates diet, physical activity, stress management, and medication (if necessary), as well as regular monitoring and adjustments to treatment as needed.
In conclusion, managing average glucose levels is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By understanding the importance of average glucose levels, incorporating strategies for management, and working with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent complications, improve their overall health, and enhance their quality of life. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with managing average glucose levels, and to take action by consulting with a healthcare provider or making lifestyle changes to improve your overall health.
