Intro
Learn about 5 blood sugar levels, normal range, and fluctuations. Understand blood glucose monitoring, diabetes management, and healthy targets to control glucose levels effectively.
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as it affects the body's ability to function properly. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body's cells. When blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it can lead to various health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, and nerve damage. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood sugar levels, exploring the importance of maintaining healthy levels, the factors that affect blood sugar, and the ways to manage and regulate blood sugar levels.
The importance of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels cannot be overstated. When blood sugar levels are within the normal range, the body can function efficiently, and the risk of developing chronic diseases is reduced. On the other hand, high or low blood sugar levels can lead to a range of symptoms, including fatigue, blurred vision, and increased thirst and urination. In severe cases, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to life-threatening complications, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemic coma. Therefore, it is essential to understand the factors that affect blood sugar levels and take steps to maintain healthy levels.
Blood sugar levels are influenced by a combination of factors, including diet, physical activity, stress, and genetics. The food we eat plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar levels, with carbohydrates having the most significant impact. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during digestion, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream, causing blood sugar levels to rise. The type and amount of carbohydrates consumed can affect blood sugar levels, with simple carbohydrates, such as sugary drinks and refined grains, causing a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are digested more slowly, resulting in a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Levels: What's Normal?

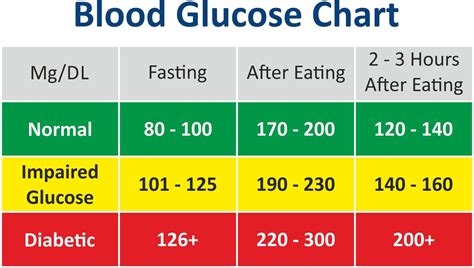
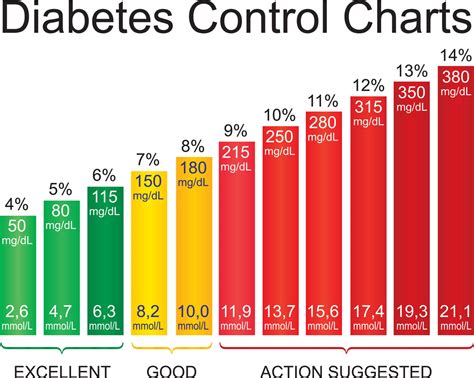
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as meal times and physical activity. In general, a normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70 and 99 mg/dL, while a normal postprandial (after meal) blood sugar level is less than 140 mg/dL. Blood sugar levels that are consistently above or below these ranges can indicate an underlying health problem, such as diabetes or hypoglycemia. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to determine the optimal blood sugar range for individual needs.
Factors That Affect Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can affect blood sugar levels, including: * Diet: Carbohydrates have the most significant impact on blood sugar levels, with simple carbohydrates causing a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. * Physical activity: Regular physical activity can help regulate blood sugar levels, while a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to high blood sugar levels. * Stress: Stress can cause blood sugar levels to rise, as the body releases stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline, which stimulate the release of glucose from stored energy sources. * Genetics: Family history can play a role in the development of diabetes and other blood sugar-related disorders. * Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation, leading to high blood sugar levels. * Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain psychiatric medications, can affect blood sugar levels.Managing Blood Sugar Levels

Managing blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates dietary changes, regular physical activity, stress management, and, if necessary, medication. Here are some tips for managing blood sugar levels:
- Eat a balanced diet that is rich in whole, unprocessed foods, such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Choose complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which are digested more slowly and result in a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels.
- Incorporate regular physical activity into daily routines, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get enough sleep each night, aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly, using a glucose meter or continuous glucose monitor.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Blood sugar monitoring is an essential tool for managing blood sugar levels. There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including: * Fasting blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast. * Postprandial blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels after a meal. * Random blood sugar test: This test measures blood sugar levels at any time of day. * Continuous glucose monitoring: This involves wearing a small device that continuously monitors blood sugar levels throughout the day.Blood Sugar Levels and Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. There are several types of diabetes, including:
- Type 1 diabetes: This is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes: This is a metabolic disorder in which the body becomes resistant to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Gestational diabetes: This is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester.
- Prediabetes: This is a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes.
Diabetes Treatment
Treatment for diabetes depends on the type and severity of the condition. Here are some common treatments for diabetes: * Medications: Oral medications or insulin injections may be prescribed to help regulate blood sugar levels. * Lifestyle changes: Dietary changes, regular physical activity, and stress management can help manage blood sugar levels. * Monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring is essential for managing diabetes and preventing complications.Blood Sugar Levels and Heart Health

High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease, as they can damage blood vessels and nerves that control the heart. Here are some ways in which blood sugar levels can affect heart health:
- High blood pressure: High blood sugar levels can lead to high blood pressure, which can increase the risk of heart disease.
- Atherosclerosis: High blood sugar levels can contribute to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition in which plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to hardening and narrowing of the arteries.
- Heart failure: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart failure, a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs.
Heart Health Tips
Here are some tips for maintaining heart health: * Eat a balanced diet that is low in saturated and trans fats, added sugars, and sodium. * Incorporate regular physical activity into daily routines, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. * Manage stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. * Get enough sleep each night, aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep. * Monitor blood pressure and cholesterol levels regularly.Blood Sugar Levels and Nerve Health
High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to a range of symptoms, including numbness, tingling, and pain. Here are some ways in which blood sugar levels can affect nerve health:
- Neuropathy: High blood sugar levels can contribute to the development of neuropathy, a condition in which nerves are damaged, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain.
- Autonomic neuropathy: High blood sugar levels can damage the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary functions, such as heart rate and digestion.
Nerve Health Tips
Here are some tips for maintaining nerve health: * Eat a balanced diet that is rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly B vitamins, which are essential for nerve health. * Incorporate regular physical activity into daily routines, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming. * Manage stress through techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. * Get enough sleep each night, aiming for 7-9 hours of sleep. * Monitor blood sugar levels regularly and work with a healthcare provider to manage diabetes and prevent complications.What are normal blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as meal times and physical activity. In general, a normal fasting blood sugar level is between 70 and 99 mg/dL, while a normal postprandial (after meal) blood sugar level is less than 140 mg/dL.
How can I manage my blood sugar levels?
+Managing blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates dietary changes, regular physical activity, stress management, and, if necessary, medication. Eat a balanced diet, choose complex carbohydrates, incorporate regular physical activity, practice stress-reducing techniques, and get enough sleep each night.
What are the risks of high blood sugar levels?
+High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease, nerve damage, and other complications. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to life-threatening conditions, such as diabetic ketoacidosis or hypoglycemic coma.
In
