Intro
Discover causes of high cardiac enzymes, including heart attacks, myocarditis, and coronary artery disease, and learn about related conditions like cardiac arrhythmias and heart failure.
Cardiac enzymes, also known as cardiac biomarkers, are proteins that are released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle is damaged. High levels of these enzymes can indicate a heart attack or other cardiac conditions. The most common cardiac enzymes measured are troponin, creatine kinase (CK), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Understanding the causes of high cardiac enzymes is crucial for timely and effective treatment.
The importance of monitoring cardiac enzymes cannot be overstated. Elevated levels of these enzymes can signal a range of cardiac issues, from mild to severe. For instance, a slight elevation in troponin levels might indicate minor cardiac stress, while significantly elevated levels could point to a full-blown heart attack. The ability to accurately diagnose and treat cardiac conditions based on enzyme levels has revolutionized cardiovascular care, saving countless lives and improving patient outcomes.
The detection of high cardiac enzymes often prompts immediate medical attention. Doctors use these enzyme levels, alongside symptoms and other diagnostic tests, to determine the best course of action. This might include administering medications to reduce cardiac workload, performing emergency surgeries, or implementing lifestyle changes to mitigate future risk. The nuances of cardiac enzyme interpretation require a deep understanding of both the enzymes themselves and the broader context of the patient's health.
Understanding Cardiac Enzymes

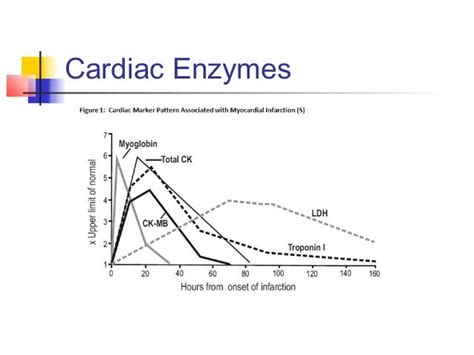
Troponin
Troponin is highly specific to the heart muscle and is considered the most sensitive indicator of heart damage. Elevated troponin levels are a key diagnostic criterion for myocardial infarction (heart attack). The level of troponin in the blood can also give clues about the severity of the heart attack and the amount of heart muscle that has been damaged.Creatine Kinase (CK)
CK is found in various muscles, including the heart. While not as specific to the heart as troponin, CK levels can still indicate heart damage, particularly when measured in conjunction with other enzymes. There are different types of CK, with CK-MB being the most relevant to heart health.Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
LDH is an enzyme found in many body tissues, including the heart. While it is not as specific for heart damage as troponin or CK-MB, elevated LDH levels can indicate tissue damage, including that of the heart.Causes of High Cardiac Enzymes
- Cardiac Contusion: A bruise of the heart muscle, often resulting from a blunt trauma to the chest.
- Myocarditis: Inflammation of the heart muscle, usually caused by a viral infection.
- Cardiomyopathy: Diseases of the heart muscle that make it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body.
- Coronary Artery Spasm: A temporary, sudden narrowing of one of the coronary arteries, which can cause chest pain (angina) and potentially lead to a heart attack.
Other Factors Influencing Cardiac Enzyme Levels
Several factors can influence cardiac enzyme levels, including: - **Age:** Older adults may have slightly higher levels of certain enzymes. - **Sex:** Some studies suggest minor differences in enzyme levels between men and women. - **Physical Activity:** Strenuous exercise can cause minor elevations in certain cardiac enzymes. - **Medications:** Certain drugs can affect cardiac enzyme levels.Diagnosis and Treatment
Prevention
Preventing high cardiac enzymes and the conditions they indicate involves reducing cardiovascular risk factors. Key strategies include: - **Maintaining a Healthy Diet:** Eating a diet low in saturated fats, cholesterol, and sodium, and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. - **Regular Physical Activity:** Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercises or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercises or a combination of both, per week. - **Not Smoking:** Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke. - **Managing Stress:** Engaging in stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises. - **Monitoring and Managing Health Conditions:** Keeping blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and diabetes under control through lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication.Managing High Cardiac Enzymes

Lifestyle Adjustments
Making lifestyle adjustments is crucial for managing high cardiac enzymes and preventing further heart damage. This includes dietary changes, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and managing stress.Medication Adherence
For many conditions causing high cardiac enzymes, medication is a critical component of treatment. Adhering to a prescribed medication regimen can help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and prevent complications.Future Directions

Personalized Medicine
The future of cardiac care may involve more personalized approaches, with treatments tailored to an individual's specific genetic profile, medical history, and lifestyle. This personalized medicine approach could lead to more effective treatments and better patient outcomes.Public Awareness
Raising public awareness about the importance of cardiac health, the signs of heart attack, and the role of cardiac enzymes in diagnosis is critical. Educated individuals are more likely to recognize symptoms early and seek timely medical attention, potentially saving lives.What are the most common symptoms of a heart attack?
+Chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, pain or discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach, feeling weak, light-headed, or faint, and cold sweats are common symptoms.
How are high cardiac enzymes diagnosed?
+Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure enzyme levels, alongside clinical evaluation, ECG, and imaging studies like echocardiography or cardiac MRI.
Can high cardiac enzymes be prevented?
+Yes, by reducing cardiovascular risk factors such as maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, not smoking, managing stress, and monitoring and managing health conditions like hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
What is the prognosis for individuals with high cardiac enzymes?
+The prognosis depends on the underlying cause, the severity of the condition, and how promptly and effectively treatment is initiated. With appropriate management, many individuals can achieve a full recovery or significant improvement in their condition.
How often should cardiac enzyme levels be checked?
+The frequency of checking cardiac enzyme levels depends on the individual's condition and the doctor's recommendations. For some, this may involve regular monitoring, while for others, it may be part of an emergency evaluation.
In conclusion, understanding the causes and implications of high cardiac enzymes is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions. By recognizing the signs of heart damage, adopting preventive measures, and seeking timely medical attention when necessary, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of cardiac complications and improve their overall heart health. We invite you to share your thoughts on this critical topic, ask questions, and explore ways to promote heart health in your community. Together, we can work towards a future where cardiac care is more personalized, effective, and accessible to all.
