Intro
Discover the causes of low sodium levels, including dehydration, medication, and underlying conditions like hyponatremia, adrenal insufficiency, and kidney disease, and learn how to manage and treat sodium deficiency symptoms.
Low sodium levels, also known as hyponatremia, is a condition where the concentration of sodium in the blood falls below 135 mmol/L. Sodium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, such as regulating water balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions. Low sodium levels can have severe consequences, including seizures, coma, and even death. Understanding the causes of low sodium levels is crucial for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
The human body is composed of approximately 60% water, and sodium helps regulate the amount of water in the body. When sodium levels are low, the body may retain excess water, leading to swelling of brain and potentially life-threatening complications. Low sodium levels can be caused by various factors, including dietary habits, medical conditions, and certain medications. It is essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of low sodium levels, such as headache, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue, to seek medical attention promptly.
Low sodium levels can be acute or chronic, and the underlying causes may vary. In some cases, low sodium levels may be a symptom of an underlying medical condition, such as heart failure, liver disease, or kidney disease. In other cases, low sodium levels may be caused by excessive sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting, which can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances. Understanding the causes of low sodium levels is critical for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Causes of Low Sodium Levels
Low sodium levels can be caused by various factors, including:
- Dehydration: Excessive sweating, diarrhea, or vomiting can lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, causing low sodium levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as diuretics, can cause low sodium levels as a side effect.
- Heart failure: Heart failure can lead to low sodium levels due to the accumulation of fluid in the body.
- Liver disease: Liver disease, such as cirrhosis, can cause low sodium levels due to the accumulation of fluid in the body.
- Kidney disease: Kidney disease, such as nephrotic syndrome, can cause low sodium levels due to the loss of sodium in the urine.
Types of Hyponatremia
There are three types of hyponatremia, including: * Euvolemic hyponatremia: This type of hyponatremia occurs when the body has a normal amount of fluid, but the sodium levels are low. * Hypovolemic hyponatremia: This type of hyponatremia occurs when the body has a low amount of fluid, and the sodium levels are low. * Hypervolemic hyponatremia: This type of hyponatremia occurs when the body has an excess amount of fluid, and the sodium levels are low.Symptoms of Low Sodium Levels
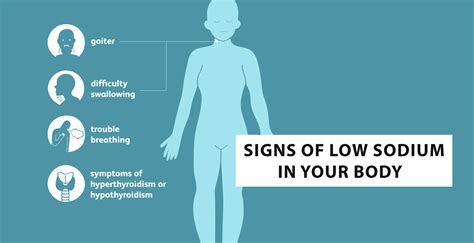
The symptoms of low sodium levels can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Mild cases of hyponatremia may not exhibit any symptoms, while severe cases can be life-threatening. Common symptoms of low sodium levels include:
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Seizures
- Coma
Diagnosis of Low Sodium Levels
Diagnosing low sodium levels typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. The doctor may perform a blood test to measure the sodium levels in the blood. Other tests, such as urine tests and imaging studies, may be ordered to determine the underlying cause of low sodium levels.Treatment of Low Sodium Levels

The treatment of low sodium levels depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases of hyponatremia may be treated with dietary changes, such as increasing sodium intake. Severe cases may require hospitalization and intravenous administration of sodium supplements. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to treat the underlying cause of low sodium levels.
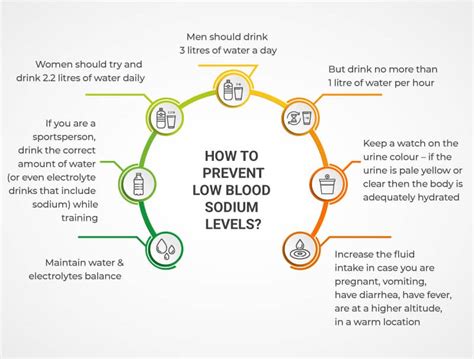
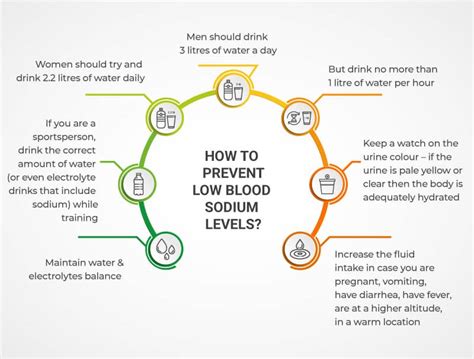
Prevention of Low Sodium Levels
Preventing low sodium levels involves maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions. It is essential to consume adequate amounts of sodium, approximately 1,500-2,300 milligrams per day. Avoiding excessive sweating, diarrhea, and vomiting can also help prevent low sodium levels.Complications of Low Sodium Levels
Low sodium levels can lead to severe complications, including:
- Seizures
- Coma
- Brain damage
- Death
Management of Low Sodium Levels
Managing low sodium levels involves monitoring sodium levels, treating underlying medical conditions, and preventing complications. It is essential to work with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, low sodium levels are a serious medical condition that requires prompt attention. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for preventing and managing low sodium levels. Future research should focus on developing effective prevention and treatment strategies, as well as improving our understanding of the underlying mechanisms of low sodium levels.
Final Thoughts
Low sodium levels can have severe consequences, and it is essential to take proactive steps to prevent and manage the condition. By maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions, individuals can reduce their risk of developing low sodium levels. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of low sodium levels, seek medical attention promptly.What are the symptoms of low sodium levels?
+The symptoms of low sodium levels can vary depending on the severity of the condition, but common symptoms include headache, nausea and vomiting, fatigue, muscle weakness, seizures, and coma.
How is low sodium levels diagnosed?
+Diagnosing low sodium levels typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as a blood test to measure sodium levels in the blood.
Can low sodium levels be prevented?
+Yes, low sodium levels can be prevented by maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and managing underlying medical conditions. It is essential to consume adequate amounts of sodium and avoid excessive sweating, diarrhea, and vomiting.
What are the complications of low sodium levels?
+Low sodium levels can lead to severe complications, including seizures, coma, brain damage, and death. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if symptoms of low sodium levels occur.
How is low sodium levels treated?
+The treatment of low sodium levels depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases may be treated with dietary changes, while severe cases may require hospitalization and intravenous administration of sodium supplements.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of low sodium levels, including the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. By working together, we can raise awareness and promote education about this critical medical condition.
