Intro
Learn about 5 CBC normal values, including white blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelet count, and mean corpuscular volume, to understand complete blood count results and diagnose health conditions like anemia, infection, or blood disorders.
Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in medicine to assess various components of the blood, providing valuable insights into the body's overall health. The CBC test measures different parameters, including red blood cell count, white blood cell count, platelet count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, among others. Understanding the normal values of these components is crucial for diagnosing and managing various health conditions.
A CBC test is often performed as part of a routine medical examination or when a healthcare provider suspects a patient might have a blood-related disorder. It's a quick and relatively inexpensive test that can reveal a wealth of information about the body's condition. For instance, abnormalities in the CBC results can indicate conditions such as anemia, infection, or blood cancers. Therefore, knowing the normal ranges for each component of the CBC is essential for healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans.
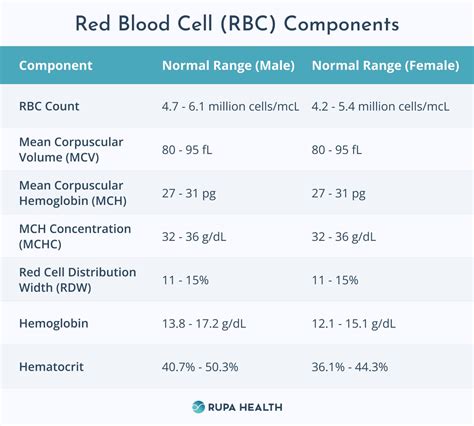
The importance of CBC normal values cannot be overstated, as they serve as a baseline for comparison when evaluating patients' health. These values can vary slightly depending on the laboratory conducting the test, but general ranges have been established. For adults, the normal ranges are typically as follows: red blood cell count (4.32-5.72 million cells per microliter for men and 3.90-5.30 million cells per microliter for women), white blood cell count (3,500-10,500 cells per microliter), platelet count (150,000-450,000 platelets per microliter), hemoglobin (13.5-17.5 grams per deciliter for men and 12-16 grams per deciliter for women), and hematocrit (40.7-50.3% for men and 36.1-48.3% for women).
Introduction to CBC Components

To delve deeper into the world of CBC, it's essential to understand each component and its significance. The red blood cell count, for example, is crucial for assessing the body's ability to transport oxygen to tissues. A decrease in red blood cell count can lead to anemia, characterized by fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. On the other hand, an elevated count can indicate dehydration or polycythemia, a condition where the body produces too many red blood cells.
Red Blood Cell Parameters
The red blood cell parameters include not just the count but also the hemoglobin and hematocrit levels. Hemoglobin is a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen, and its levels are critical for maintaining adequate oxygen delivery to tissues. Hematocrit, which measures the proportion of blood volume made up of red blood cells, can indicate the body's capacity for transporting oxygen. Abnormalities in these parameters can signal underlying health issues that require medical attention.Understanding White Blood Cell Count
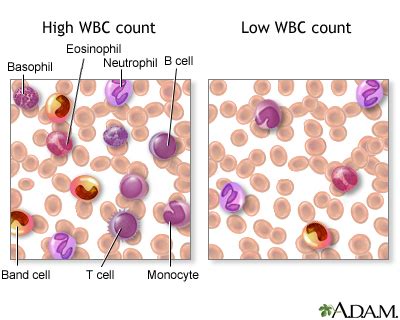
The white blood cell count is another vital component of the CBC, reflecting the body's immune response. An elevated white blood cell count can indicate the presence of an infection or inflammation, while a decreased count can signal a weakened immune system, potentially due to conditions such as leukemia or an autoimmune disorder. The differential count, which categorizes white blood cells into different types (neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils), provides further insight into the specific nature of the immune response.
Differential Count Significance
Each type of white blood cell has a distinct function in the immune system. Neutrophils, for instance, are crucial for fighting bacterial infections, while lymphocytes play a key role in viral infections and immune memory. An increase in eosinophils can indicate a parasitic infection or an allergic reaction. Understanding the differential count is essential for diagnosing and treating infections effectively.Platelet Count and Its Implications
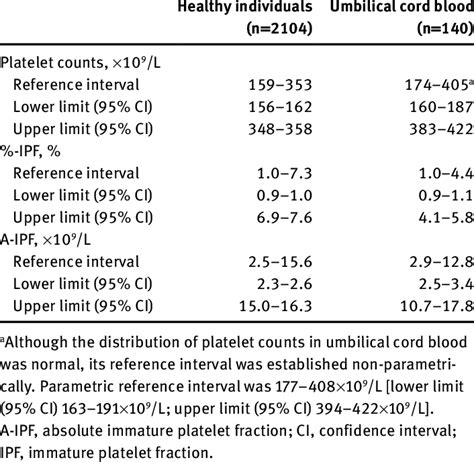
Platelets are tiny blood cells that play a critical role in blood clotting. A normal platelet count ranges from 150,000 to 450,000 platelets per microliter. Both low (thrombocytopenia) and high (thrombocytosis) platelet counts can be associated with significant health risks. Thrombocytopenia can lead to an increased risk of bleeding, while thrombocytosis can increase the risk of blood clots. Understanding the platelet count is vital for managing conditions related to bleeding or clotting disorders.
Blood Clotting Disorders
Blood clotting disorders, such as hemophilia or von Willebrand disease, can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. These conditions often require lifelong management, including regular monitoring of platelet counts and clotting factors. Advances in medical science have led to the development of various treatments, including clotting factor concentrates and antifibrinolytic agents, which can help manage bleeding episodes and improve outcomes for patients with these disorders.CBC in Disease Diagnosis
The CBC is a versatile diagnostic tool that can aid in the diagnosis of a wide range of diseases, from anemia and infections to blood cancers. For instance, a significantly elevated white blood cell count can be indicative of leukemia, a type of blood cancer characterized by the uncontrolled proliferation of white blood cells. Similarly, abnormalities in red blood cell parameters can suggest conditions such as iron-deficiency anemia or sickle cell disease.
Leukemia and Lymphoma
Leukemia and lymphoma are types of blood cancers that affect the blood and bone marrow. Leukemia is characterized by the abnormal growth of white blood cells, while lymphoma affects the immune system, specifically the lymphatic system. Early diagnosis through CBC and other diagnostic tests is crucial for effective treatment and management of these conditions. Treatment options include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and stem cell transplantation, depending on the type and stage of the disease.Interpreting CBC Results
Interpreting CBC results requires a comprehensive understanding of the normal ranges and how they relate to different health conditions. Healthcare providers consider the patient's medical history, physical examination, and other diagnostic tests when interpreting CBC results. For example, a mild increase in white blood cell count might not be significant in an otherwise healthy individual but could be indicative of an underlying infection in someone with symptoms such as fever or cough.
CBC and Other Diagnostic Tests
The CBC is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tests to provide a more complete picture of a patient's health. For instance, in cases of suspected anemia, a CBC might be ordered alongside iron studies or a reticulocyte count to assess the body's iron stores and the production of new red blood cells. Similarly, in cases of infection, a CBC might be accompanied by blood cultures or other microbiological tests to identify the causative organism.CBC in Monitoring Health
Regular CBC tests can be an essential part of health monitoring, especially for individuals with chronic health conditions or those undergoing treatments that can affect blood cell counts. For example, patients on chemotherapy require regular CBCs to monitor the effects of treatment on their blood cells and to adjust the treatment plan as necessary. Similarly, individuals with chronic anemia or other blood disorders may need periodic CBCs to assess the effectiveness of their treatment and make any necessary adjustments.
Chronic Disease Management
Managing chronic diseases often involves a multidisciplinary approach, including lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. The CBC is a valuable tool in this context, providing insights into the body's response to treatment and helping healthcare providers make informed decisions. By closely monitoring CBC results, healthcare providers can identify potential issues early, preventing complications and improving patient outcomes.Future of CBC Testing

The future of CBC testing is promising, with advancements in technology and diagnostic techniques offering the potential for more precise and rapid results. Automated analyzers can now perform CBC tests quickly and accurately, reducing the turnaround time and allowing for more timely interventions. Furthermore, research into new biomarkers and diagnostic parameters may expand the utility of the CBC, enabling healthcare providers to diagnose and manage a broader range of conditions more effectively.
Advances in Diagnostic Technology
Advances in diagnostic technology are continuously improving the field of medicine, enabling healthcare providers to diagnose and treat conditions more effectively. The development of point-of-care testing devices, for example, allows for rapid CBC testing in outpatient settings, enhancing patient care and convenience. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into diagnostic systems may help in identifying patterns and anomalies in CBC results, potentially leading to earlier diagnosis and better patient outcomes.What is a complete blood count (CBC) test?
+A complete blood count (CBC) test is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate various components of the blood, including red blood cell count, white blood cell count, platelet count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, among others.
What are the normal values for a CBC test?
+Normal values for a CBC test can vary slightly depending on the laboratory but generally include: red blood cell count (4.32-5.72 million cells per microliter for men and 3.90-5.30 million cells per microliter for women), white blood cell count (3,500-10,500 cells per microliter), platelet count (150,000-450,000 platelets per microliter), hemoglobin (13.5-17.5 grams per deciliter for men and 12-16 grams per deciliter for women), and hematocrit (40.7-50.3% for men and 36.1-48.3% for women).
Why is it important to understand CBC normal values?
+Understanding CBC normal values is crucial for diagnosing and managing various health conditions. Abnormalities in CBC results can indicate conditions such as anemia, infection, or blood cancers, and knowing the normal ranges allows healthcare providers to make accurate diagnoses and develop appropriate treatment plans.
In conclusion, the CBC is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides valuable insights into the body's overall health. By understanding the normal values of the various components of the CBC and how they relate to different health conditions, healthcare providers can diagnose and manage a wide range of diseases more effectively. As technology continues to advance, the future of CBC testing holds promise for even more precise and rapid results, potentially leading to better patient outcomes. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with CBC testing, and we hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the importance and utility of the CBC in modern medicine.
