Intro
Wound care is a critical aspect of healthcare, as it directly impacts the recovery and well-being of patients. Debridement, the process of removing dead tissue, bacteria, and other contaminants from wounds, is a crucial step in promoting healing and preventing infection. Effective debridement can significantly improve patient outcomes, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster recovery times. In this article, we will explore the importance of debridement, its benefits, and various methods used to debride wounds.
Debridement is essential for creating an environment conducive to healing. Dead tissue and bacteria can impede the healing process, leading to prolonged recovery times, increased risk of infection, and potentially life-threatening complications. By removing these contaminants, healthcare professionals can promote the growth of new tissue, reduce the risk of infection, and improve patient outcomes. Furthermore, debridement can also help reduce the financial burden associated with prolonged hospital stays and repeated treatments.
The benefits of debridement are numerous, and its importance cannot be overstated. Not only does it promote healing and reduce the risk of infection, but it also improves patient comfort and quality of life. By removing dead tissue and bacteria, healthcare professionals can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, which can contribute to pain, swelling, and other symptoms. Additionally, debridement can also help reduce the risk of antibiotic resistance, as it can help prevent the overuse of antibiotics.
Introduction to Debridement Methods
Surgical Debridement
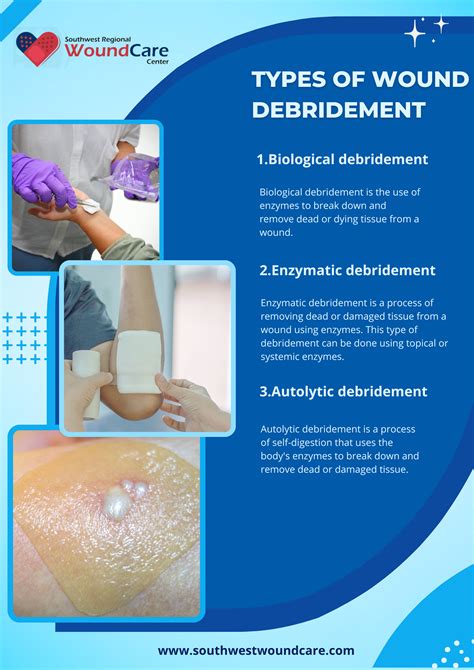
Surgical debridement is a method that involves the surgical removal of dead tissue and contaminants from the wound. This method is typically used for large or deep wounds, or those that are heavily contaminated. Surgical debridement can be performed under local or general anesthesia, depending on the size and location of the wound. The procedure involves the use of surgical instruments, such as scalpels and forceps, to remove dead tissue and contaminants. Surgical debridement is an effective method, but it can be painful and may require repeated procedures.Autolytic Debridement

Enzymatic Debridement
Enzymatic debridement is a method that involves the use of enzymes to break down dead tissue and contaminants. This method is typically used for small to medium-sized wounds, or those that are not heavily contaminated. Enzymatic debridement involves the application of a topical enzyme, such as papain or collagenase, to the wound. The enzyme breaks down the dead tissue, allowing it to be easily removed. Enzymatic debridement is a gentle and non-invasive method, but it can be slow and may require repeated applications.Mechanical Debridement

Biosurgical Debridement
Biosurgical debridement is a method that involves the use of living organisms, such as maggots, to break down dead tissue and contaminants. This method is typically used for small to medium-sized wounds, or those that are not heavily contaminated. Biosurgical debridement involves the application of maggots to the wound, which break down the dead tissue and contaminants. Biosurgical debridement is a gentle and non-invasive method, but it can be slow and may require repeated applications.Benefits of Debridement
Steps Involved in Debridement
The steps involved in debridement vary depending on the method used. However, some common steps include: 1. Assessment of the wound: The wound is assessed to determine the size, depth, and location, as well as the presence of any underlying conditions. 2. Preparation of the wound: The wound is prepared for debridement by cleaning and disinfecting the area. 3. Application of the debridement method: The chosen debridement method is applied to the wound, such as surgical debridement, autolytic debridement, or enzymatic debridement. 4. Removal of dead tissue: The dead tissue and contaminants are removed from the wound, either through surgical excision or autolytic breakdown. 5. Dressing and aftercare: The wound is dressed and aftercare is provided to promote healing and prevent infection.Practical Examples of Debridement
Statistical Data on Debridement
Statistical data on debridement highlights its importance in wound care. According to recent studies, debridement can reduce the risk of infection by up to 50%, and promote healing by up to 30%. Additionally, debridement can also reduce the financial burden associated with prolonged hospital stays and repeated treatments by up to 20%.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
Debridement is a complex and multifaceted topic, and its importance cannot be overstated. By understanding the benefits and methods of debridement, healthcare professionals can provide better care for their patients, promoting healing, reducing the risk of infection, and improving patient outcomes. Whether through surgical, autolytic, enzymatic, mechanical, or biosurgical debridement, the goal of debridement remains the same: to promote healing, reduce the risk of infection, and improve patient comfort and quality of life.What is debridement?
+Debridement is the process of removing dead tissue, bacteria, and other contaminants from wounds to promote healing and prevent infection.
What are the benefits of debridement?
+The benefits of debridement include promoting healing, reducing the risk of infection, improving patient comfort and quality of life, and reducing the financial burden associated with prolonged hospital stays and repeated treatments.
What are the different methods of debridement?
+The different methods of debridement include surgical debridement, autolytic debridement, enzymatic debridement, mechanical debridement, and biosurgical debridement.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of debridement and its importance in wound care. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about debridement, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others. Additionally, if you have any personal experiences with debridement or wound care, we would love to hear about them. By working together, we can promote better wound care and improve patient outcomes.
