Intro
Understand your Fasting Sugar Test results with our comprehensive guide, covering normal ranges, high blood sugar implications, and low sugar levels, to help manage diabetes and glucose metabolism effectively.
The importance of monitoring blood sugar levels cannot be overstated, particularly for individuals diagnosed with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. One of the most common methods for checking blood sugar levels is through a fasting sugar test, also known as a fasting blood glucose test. This test measures the level of glucose in the blood after an overnight fast, typically lasting at least 8 hours. Understanding the results of a fasting sugar test is crucial for managing diabetes, making informed lifestyle choices, and preventing complications associated with high blood sugar levels.
For individuals who have been advised to take a fasting sugar test, it is essential to follow the instructions provided by their healthcare provider to ensure accurate results. This may involve avoiding food and drink, except for water, for a specified period before the test. The test itself is relatively straightforward, involving a blood sample taken from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The results of the test can provide valuable insights into how the body is managing blood sugar levels, helping to diagnose diabetes, prediabetes, or other conditions that may be affecting glucose metabolism.
The fasting sugar test is a critical diagnostic tool because it offers a snapshot of how the body regulates blood glucose levels when it is not influenced by recent food intake. By assessing the body's ability to manage glucose during a fasting state, healthcare providers can better understand an individual's risk of developing diabetes or related conditions. Moreover, for those already diagnosed with diabetes, regular fasting sugar tests are vital for monitoring the effectiveness of their treatment plan, making adjustments as necessary to maintain blood sugar levels within a healthy range. This proactive approach to diabetes management can significantly reduce the risk of long-term complications, such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Understanding Fasting Sugar Test Results

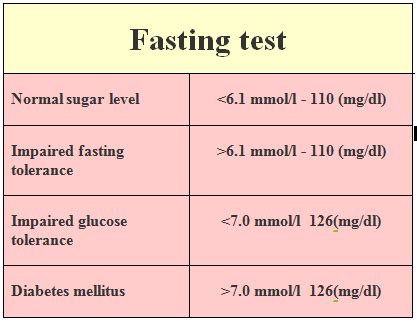
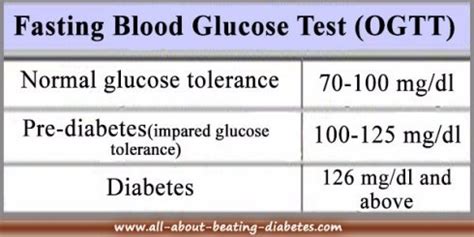
Interpreting the results of a fasting sugar test requires an understanding of the different levels of blood glucose and what they signify. The results are typically categorized into several ranges, each indicating a different status regarding glucose metabolism. For individuals without diabetes, a normal fasting blood glucose level is usually below 100 mg/dL. Levels between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL may indicate prediabetes, a condition where blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. A fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher is often used as a criterion for diagnosing diabetes.
Normal Fasting Blood Glucose Levels
Normal fasting blood glucose levels are crucial for maintaining overall health. They indicate that the body is effectively regulating blood sugar levels, utilizing insulin efficiently to facilitate the entry of glucose into cells. For most adults, a normal fasting blood glucose level is less than 100 mg/dL. However, it's essential to note that these values can slightly vary depending on the laboratory conducting the test and the specific criteria used by healthcare providers.Prediabetes and Fasting Sugar Test Results

Prediabetes is a condition characterized by blood glucose levels that are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. The fasting sugar test plays a pivotal role in identifying individuals with prediabetes, as it can detect impaired fasting glucose (IFG), a condition where fasting blood glucose levels are between 100 mg/dL and 125 mg/dL. Recognizing prediabetes is critical because it presents an opportunity for intervention, potentially preventing the progression to type 2 diabetes through lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, and weight loss.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prediabetes
For individuals diagnosed with prediabetes, adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Key strategies include: - **Dietary Changes:** Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reducing the intake of sugary drinks, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates is also beneficial. - **Physical Activity:** Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, for at least 150 minutes per week can improve insulin sensitivity and help manage weight. - **Weight Loss:** For individuals who are overweight or obese, losing 5-10% of their body weight can substantially reduce the risk of progressing to diabetes.Diabetes Diagnosis and Fasting Sugar Test Results

A fasting blood glucose level of 126 mg/dL or higher is commonly used as a diagnostic criterion for diabetes. This threshold indicates that the body is not effectively managing blood glucose levels, either due to insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance. Upon receiving a diabetes diagnosis, individuals should work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive management plan, which may include medication, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring of blood glucose levels to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Management of Diabetes
Effective management of diabetes involves a multifaceted approach, including: - **Medication:** Depending on the type of diabetes and the individual's health status, medication may be prescribed to help lower blood glucose levels. - **Lifestyle Modifications:** Similar to those recommended for prediabetes, adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight are crucial for managing diabetes. - **Monitoring Blood Glucose:** Regularly checking blood glucose levels helps individuals with diabetes understand how different factors, such as food, physical activity, and medication, affect their blood sugar levels, enabling them to make informed decisions about their care.Gestational Diabetes and Fasting Sugar Test Results
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, typically in the second or third trimester. The fasting sugar test is part of the screening process for gestational diabetes, which also includes an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). The criteria for diagnosing gestational diabetes may vary slightly from those for other types of diabetes, but the principle of using fasting and postprandial glucose measurements to assess glucose metabolism remains the same. Managing gestational diabetes is crucial to prevent complications for both the mother and the baby, such as excessive birth weight, premature birth, and increased risk of cesarean delivery.
Screening for Gestational Diabetes
Screening for gestational diabetes usually occurs between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy. The process typically involves: - **Initial Screening:** An oral glucose challenge test (OGCT) is conducted, where the woman drinks a sugary solution and has her blood glucose level checked after one hour. - **Follow-Up Testing:** If the initial screening indicates a high risk, a follow-up test, such as a 100-gram OGTT, may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.Implications of Fasting Sugar Test Results for Health and Lifestyle
The implications of fasting sugar test results extend beyond the diagnosis of diabetes or prediabetes, influencing various aspects of health and lifestyle. Understanding these implications can motivate individuals to make positive changes, whether it's adopting healthier eating habits, increasing physical activity, or managing stress more effectively. For those with abnormal fasting sugar test results, working with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan can lead to improved glucose control, reduced risk of complications, and an enhanced overall quality of life.
Psychological Impact of Diabetes Diagnosis
Receiving a diagnosis of diabetes or prediabetes can have a significant psychological impact, leading to feelings of anxiety, denial, or overwhelm. It's essential for individuals to seek support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends. Joining a diabetes support group or seeking counseling can also provide valuable coping strategies and help individuals come to terms with their condition, facilitating a smoother transition to a diabetes management routine.Future Directions in Diabetes Management and Fasting Sugar Test Results

The field of diabetes management is continuously evolving, with advancements in technology, medication, and our understanding of glucose metabolism. Future directions may include more personalized approaches to diabetes care, leveraging genetic information, and innovative technologies such as continuous glucose monitoring systems and insulin pumps. These developments aim to improve the accuracy of diabetes diagnosis, enhance the effectiveness of treatment plans, and ultimately lead to better health outcomes for individuals with diabetes.
Emerging Technologies in Diabetes Care
Emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize diabetes care, offering more precise glucose monitoring, automated insulin delivery, and personalized advice based on real-time data analysis. Some of the promising areas include: - **Artificial Intelligence (AI):** AI can help analyze glucose data, predict blood glucose levels, and provide personalized recommendations for diet and exercise. - **Wearable Devices:** Wearable glucose monitors and smart insulin pens can make tracking glucose levels and insulin dosing more convenient and accurate.As we move forward in the management and diagnosis of diabetes, it's clear that fasting sugar test results will remain a cornerstone of care, providing critical information that guides treatment decisions and helps individuals manage their condition effectively. By staying informed about the latest developments in diabetes care and the implications of fasting sugar test results, individuals can take a proactive role in their health, working towards a future where diabetes is managed with greater ease and effectiveness.
What is the normal range for fasting blood glucose levels?
+Normal fasting blood glucose levels are typically below 100 mg/dL for individuals without diabetes.
How often should I get a fasting sugar test if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of fasting sugar tests for individuals with diabetes can vary depending on the type of diabetes, the effectiveness of the current treatment plan, and the presence of any complications. It's best to follow the advice of your healthcare provider.
Can lifestyle changes alone manage prediabetes and prevent the development of type 2 diabetes?
+Yes, adopting healthy lifestyle habits such as a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and maintaining a healthy weight can significantly reduce the risk of progressing from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes.
What are the risks associated with gestational diabetes if left untreated?
+Untreated gestational diabetes can lead to complications for both the mother and the baby, including excessive birth weight, premature birth, and an increased risk of cesarean delivery.
How can I lower my fasting blood glucose levels naturally?
+Natural ways to lower fasting blood glucose levels include increasing physical activity, losing weight if necessary, and following a diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates and high in fiber and whole foods.
In conclusion, understanding fasting sugar test results is a vital component of diabetes management and prevention. By recognizing the implications of these results and taking proactive steps towards healthier living, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. We invite you to share your experiences, ask questions, or seek further information on managing blood sugar levels and the role of fasting sugar tests in diabetes care. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of diabetes and strive for improved health outcomes for all.
