Intro
Discover the Glycemic Scale Food Guide, managing blood sugar with low glycemic index foods, healthy eating, and balanced diets for optimal nutrition and weight management.
The importance of managing blood sugar levels cannot be overstated, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. One effective way to achieve this is by understanding the glycemic scale and incorporating it into daily meal planning. The glycemic scale, also known as the glycemic index (GI), is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating a more rapid increase in blood sugar. By choosing foods with a lower GI, individuals can better manage their blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of related health complications.
Understanding the glycemic scale is crucial for maintaining good health, as it helps individuals make informed decisions about their diet. Foods with a high GI, such as white bread and sugary snacks, can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels, followed by a crash, leaving individuals feeling lethargic and hungry. On the other hand, foods with a low GI, such as whole grains and non-starchy vegetables, are digested more slowly, resulting in a gradual increase in blood sugar levels and a feeling of fullness and satisfaction. By incorporating more low-GI foods into their diet, individuals can improve their overall health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and certain types of cancer.
In addition to its health benefits, the glycemic scale can also be a useful tool for weight management. Foods with a low GI tend to be more filling and satisfying, making it easier to stick to a healthy eating plan and avoid overeating. Furthermore, the glycemic scale can help individuals identify which foods are likely to cause cravings and energy crashes, allowing them to make more informed choices and develop healthier eating habits. With the rising prevalence of obesity and related health conditions, understanding the glycemic scale and incorporating it into daily meal planning is more important than ever.
Glycemic Index Food Guide
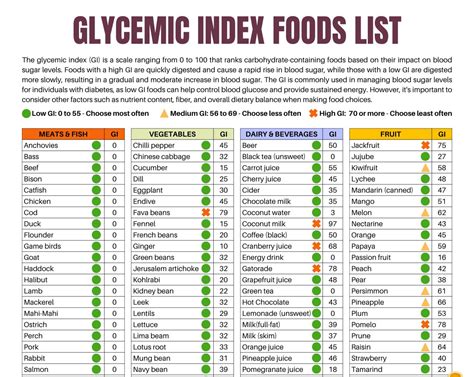
The glycemic index food guide is a comprehensive resource that provides information on the GI values of various foods. The guide is divided into three categories: low GI (0-55), medium GI (56-69), and high GI (70-100). Foods with a low GI are typically rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats, which slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, resulting in a gradual increase in blood sugar levels. Examples of low-GI foods include whole grains, such as brown rice and quinoa, non-starchy vegetables, such as broccoli and spinach, and lean protein sources, such as chicken and fish.
Low GI Foods
Low GI foods are ideal for individuals with diabetes or those who want to manage their blood sugar levels. These foods are rich in nutrients and fiber, making them filling and satisfying. Some examples of low GI foods include: * Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread * Non-starchy vegetables, such as broccoli, spinach, and bell peppers * Lean protein sources, such as chicken, fish, and tofu * Healthy fats, such as avocado, nuts, and seeds * Legumes, such as lentils, chickpeas, and black beansMedium GI Foods
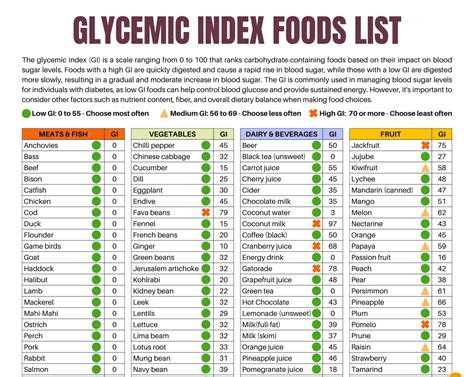
Medium GI foods have a GI value between 56 and 69. These foods can be part of a healthy diet, but it's essential to consume them in moderation. Examples of medium GI foods include:
- Whole grain pasta
- Sweet potatoes
- Corn
- Peas
- Fruit, such as apples and bananas
High GI Foods
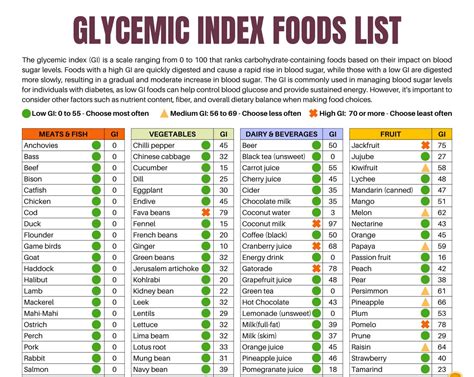
High GI foods have a GI value of 70 or higher. These foods can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels and should be consumed in limited amounts. Examples of high GI foods include: * White bread * Sugary snacks, such as candy and cookies * Refined grains, such as white rice and sugary cereals * Starchy vegetables, such as potatoes and corn * Fruit juice and sugary drinksGlycemic Load
The glycemic load (GL) is a measure of the total amount of carbohydrate in a food and its GI value. The GL takes into account the serving size of the food, making it a more accurate measure of the food's impact on blood sugar levels. Foods with a high GL can cause a more significant increase in blood sugar levels, even if they have a low GI. For example, a large serving of brown rice may have a high GL, even though it has a low GI.
Calculating Glycemic Load
To calculate the GL of a food, you need to know the GI value and the amount of carbohydrate in the food. The formula for calculating GL is: GL = (GI x carbohydrate content) / 100 For example, if a food has a GI value of 50 and contains 30 grams of carbohydrate, the GL would be: GL = (50 x 30) / 100 = 15Practical Tips for Managing Blood Sugar Levels

Managing blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Here are some practical tips for managing blood sugar levels:
- Eat regular meals to maintain stable blood sugar levels
- Choose low GI foods, such as whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and lean protein sources
- Avoid high GI foods, such as sugary snacks and refined grains
- Drink plenty of water to stay hydrated
- Exercise regularly, such as walking or jogging, to improve insulin sensitivity
- Get enough sleep, aiming for 7-8 hours per night, to help regulate blood sugar levels
Meal Planning
Meal planning is an essential aspect of managing blood sugar levels. Here are some tips for planning healthy meals: * Plan your meals in advance to ensure you have healthy ingredients on hand * Shop for whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains * Avoid processed and packaged foods, which tend to be high in added sugars and unhealthy fats * Cook at home using healthy cooking methods, such as grilling and roasting * Pack healthy snacks, such as fruits and nuts, to avoid relying on convenience foodsBenefits of Managing Blood Sugar Levels

Managing blood sugar levels has numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as heart disease and certain types of cancer
- Improved energy levels and reduced fatigue
- Enhanced cognitive function and reduced risk of dementia
- Healthy weight management and reduced risk of obesity
- Improved overall health and well-being
Reducing the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Here are some ways that managing blood sugar levels can help: * Reduce the risk of heart disease by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation * Reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer, by regulating blood sugar levels * Reduce the risk of dementia and cognitive decline by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing inflammation * Reduce the risk of kidney disease and kidney failure by managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetic nephropathyCommon Mistakes to Avoid

When managing blood sugar levels, there are several common mistakes to avoid. Here are some of the most common mistakes:
- Not eating regular meals, leading to unstable blood sugar levels
- Consuming high GI foods, such as sugary snacks and refined grains
- Not drinking enough water, leading to dehydration and unstable blood sugar levels
- Not exercising regularly, leading to reduced insulin sensitivity and unstable blood sugar levels
- Not getting enough sleep, leading to unstable blood sugar levels and reduced insulin sensitivity
Avoiding High GI Foods
Avoiding high GI foods is essential for managing blood sugar levels. Here are some tips for avoiding high GI foods: * Read food labels carefully to identify added sugars and refined grains * Avoid processed and packaged foods, which tend to be high in added sugars and unhealthy fats * Choose whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains * Cook at home using healthy cooking methods, such as grilling and roasting * Pack healthy snacks, such as fruits and nuts, to avoid relying on convenience foodsWhat is the glycemic index?
+The glycemic index is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating a more rapid increase in blood sugar.
How can I manage my blood sugar levels?
+Managing blood sugar levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Eat regular meals, choose low GI foods, avoid high GI foods, drink plenty of water, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep.
What are the benefits of managing blood sugar levels?
+Managing blood sugar levels has numerous benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases, improved energy levels, enhanced cognitive function, healthy weight management, and improved overall health and well-being.
In conclusion, managing blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining good health and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. By understanding the glycemic scale and incorporating it into daily meal planning, individuals can make informed decisions about their diet and develop healthier eating habits. Remember to eat regular meals, choose low GI foods, avoid high GI foods, drink plenty of water, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. By following these tips and avoiding common mistakes, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels and improve their overall health and well-being. We invite you to share your experiences and tips for managing blood sugar levels in the comments below.
