Intro
Discover 7 heart medications, including beta blockers, statins, and ACE inhibitors, to manage cardiovascular health, lower blood pressure, and reduce heart disease risk, with expert insights on medication interactions and side effects.
The heart is a vital organ that plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of an individual. It pumps blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to various tissues and organs. However, the heart can be affected by various diseases and conditions, such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease, and heart failure, which can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Fortunately, there are various medications available that can help manage and treat these conditions. In this article, we will discuss 7 heart medications that are commonly used to treat various heart-related conditions.
The importance of heart medications cannot be overstated. These medications can help reduce the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events, improving overall survival rates and quality of life. Moreover, they can also help manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and prevent complications. With the advancement of medical science, new and innovative heart medications are being developed, offering hope to individuals affected by heart diseases. In the following sections, we will delve into the details of 7 heart medications, their mechanisms of action, benefits, and potential side effects.
The use of heart medications has become increasingly common, and it is essential to understand how they work and their potential benefits and risks. By educating oneself about these medications, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options and work closely with their healthcare providers to manage their condition effectively. Furthermore, a comprehensive understanding of heart medications can also help individuals take preventive measures to reduce their risk of developing heart diseases. In the subsequent sections, we will explore the 7 heart medications in detail, including their indications, dosages, and potential interactions.
Introduction to Heart Medications
Types of Heart Medications
There are several types of heart medications available, each with its specific indications and uses. Some of the most common types of heart medications include: * Beta blockers: These medications slow the heart rate and reduce blood pressure, making them useful for treating conditions such as hypertension, angina, and heart failure. * ACE inhibitors: These medications relax blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and improving blood flow to the heart, making them useful for treating conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and coronary artery disease. * Statins: These medications lower cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of heart attacks and strokes, making them useful for treating conditions such as high cholesterol and coronary artery disease. * Diuretics: These medications remove excess fluid from the body, reducing blood pressure and improving symptoms of heart failure, making them useful for treating conditions such as hypertension, heart failure, and edema.7 Heart Medications
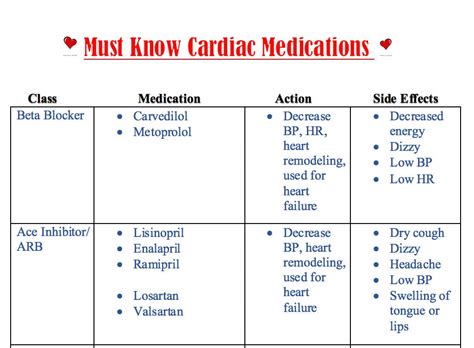
Benefits and Risks of Heart Medications
While heart medications can be highly effective in managing and treating heart-related conditions, they can also have potential benefits and risks. Some of the benefits of heart medications include: * Reduced risk of heart attacks and strokes * Improved symptoms of heart failure * Lower blood pressure * Improved quality of life However, heart medications can also have potential side effects, such as: * Dizziness and lightheadedness * Nausea and vomiting * Headaches and dizziness * Fatigue and weakness * Increased risk of bleeding and bruisingManaging Heart Medications
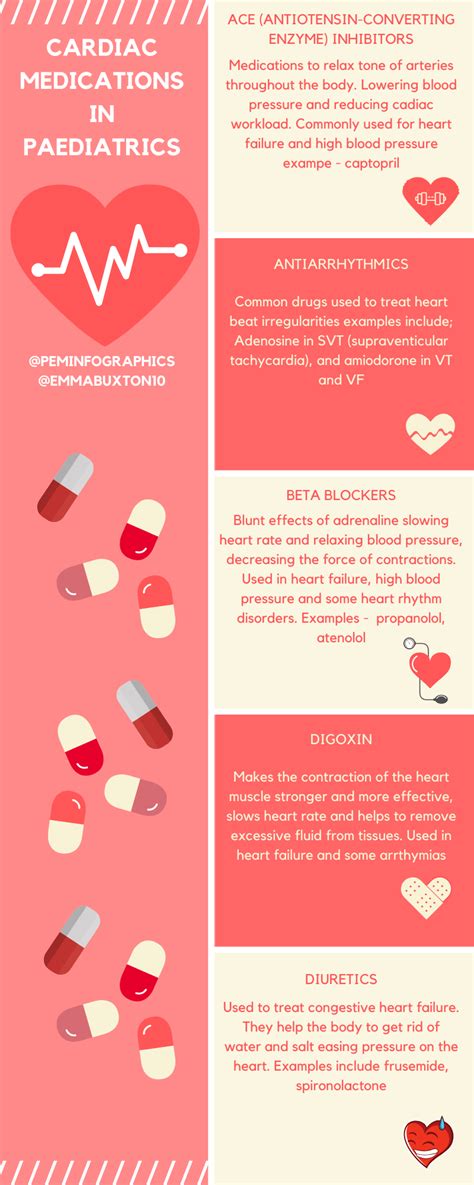
Interactions with Other Medications
Heart medications can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter medications, herbal supplements, and prescription medications. Some potential interactions include: * Aspirin and warfarin: Increased risk of bleeding and bruising * Metoprolol and lisinopril: Increased risk of hypotension and dizziness * Atorvastatin and digoxin: Increased risk of digitalis toxicity * Furosemide and warfarin: Increased risk of bleeding and bruisingConclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
Heart medications are a crucial aspect of cardiovascular care, and their proper use can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by heart diseases. By staying informed and up-to-date on the latest developments in heart medication research, individuals can take a proactive approach to their cardiovascular health and work towards a healthier and more fulfilling life.What are the most common types of heart medications?
+The most common types of heart medications include beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, statins, diuretics, and anti-coagulants.
How do I manage my heart medications effectively?
+To manage your heart medications effectively, take your medications as directed by your healthcare provider, keep track of your medication schedule and dosages, and monitor your blood pressure and heart rate regularly.
What are the potential side effects of heart medications?
+The potential side effects of heart medications include dizziness and lightheadedness, nausea and vomiting, headaches and dizziness, fatigue and weakness, and increased risk of bleeding and bruising.
Can I take heart medications with other medications?
+It is essential to consult with your healthcare provider before taking heart medications with other medications, as some interactions can be potentially hazardous.
How can I reduce my risk of heart disease?
+To reduce your risk of heart disease, maintain a healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity, manage stress, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of 7 heart medications and their role in managing and treating heart-related conditions. If you have any questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to your healthcare provider. Additionally, we invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with heart medications in the comments section below. By working together, we can promote greater awareness and understanding of cardiovascular health and improve outcomes for individuals affected by heart diseases.
