Intro
Discover 5 ways to reduce alt text errors, improving image accessibility and SEO with optimized alt tags, descriptive text, and semantic HTML for better search engine rankings and user experience.
Reducing altitude, or the effects of high altitude, is crucial for individuals who live, work, or travel to high-elevation areas. High altitudes can cause a range of health issues, from mild discomfort to life-threatening conditions, due to the lower oxygen levels in the air. Understanding how to mitigate these effects is essential for maintaining health and safety.
The human body adapts to high altitudes through a process called acclimatization, where it increases red blood cell production to carry more oxygen to the body's tissues. However, this process takes time, and immediate measures can be taken to reduce the impact of altitude sickness. These measures not only help in preventing severe health issues but also ensure that individuals can perform their daily activities without significant hindrance.
High-altitude environments pose unique challenges, and being prepared is key to enjoying or working in these conditions safely. Whether you are an adventurer, an athlete, or someone who has relocated to a high-altitude area, knowing how to reduce the effects of altitude is vital. This knowledge enables individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining their health and well-being in environments that are naturally challenging due to lower oxygen levels.
Understanding Altitude Sickness
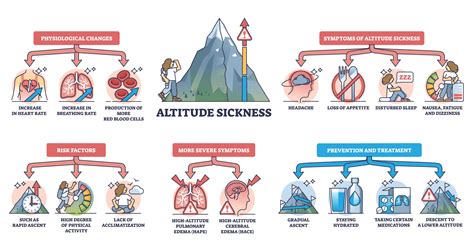
Altitude sickness, also known as acute mountain sickness (AMS), occurs when the body cannot adapt well to high elevations, leading to a lack of oxygen in the bloodstream. Symptoms can range from headaches and nausea to more severe conditions like high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) and high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE), which are life-threatening and require immediate medical attention. Understanding the symptoms and taking preventive measures are crucial for safe travel or living in high-altitude areas.
Recognizing Symptoms
The first step in managing altitude sickness is recognizing its symptoms. These can include: - Headaches - Fatigue - Nausea and vomiting - Dizziness or lightheadedness - Loss of appetite - Insomnia - Shortness of breathMethods to Reduce Altitude Sickness

Several methods can help reduce the effects of altitude sickness, including gradual ascent, hydration, medication, dietary changes, and rest. Each of these methods plays a critical role in helping the body adapt to higher elevations more efficiently.
Gradual Ascent
Gradual ascent is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of altitude sickness. By giving the body time to acclimatize, individuals can significantly lower their risk of experiencing severe symptoms. A general rule of thumb is not to ascend more than 1,000 feet per day once above 8,000 feet. This gradual increase allows the body to produce more red blood cells and adapt to the lower oxygen levels.Hydration and Nutrition

Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet are essential for overall health and can also play a role in reducing the effects of altitude sickness. Drinking plenty of water helps in preventing dehydration, which can exacerbate altitude sickness symptoms. A diet rich in carbohydrates can help provide energy, as the body may have difficulty digesting fats and proteins at high altitudes.
Dietary Adjustments
Dietary adjustments can support the body's adaptation to high altitudes. Foods high in antioxidants and iron can be beneficial, as they help in reducing oxidative stress and supporting the production of red blood cells. Additionally, consuming foods that are easy to digest can help manage nausea and other gastrointestinal symptoms associated with altitude sickness.Medication and Supplements

Certain medications and supplements can help prevent or alleviate altitude sickness symptoms. Acetazolamide is a commonly prescribed medication that helps the body acclimatize to high altitudes by increasing urine production, which in turn helps reduce fluid buildup in the body and improves oxygen delivery to the tissues. Supplements like ginkgo biloba and vitamin C may also offer some benefits, although their effectiveness can vary from person to person.
Rest and Recovery
Rest and recovery are crucial when ascending to high altitudes. Allowing the body time to rest can help in the acclimatization process. Avoiding strenuous activities, especially in the initial days after ascending, can reduce the risk of developing severe altitude sickness. Listening to the body and taking rest days as needed can make a significant difference in how well an individual adapts to the high-altitude environment.Technological Aids

Technological advancements have led to the development of various devices and equipment that can aid in reducing the effects of altitude sickness. Portable oxygen generators, for example, can provide supplemental oxygen, which can be particularly useful for individuals who need to ascend rapidly or have pre-existing health conditions that make them more susceptible to altitude sickness.
Oxygen Therapy
Oxygen therapy can be highly effective in managing altitude sickness, especially in severe cases. By increasing the oxygen levels in the blood, oxygen therapy can help alleviate symptoms and support the body's recovery. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who experience severe shortness of breath or other critical symptoms of altitude sickness.Preparation and Planning

Preparation and planning are key to safely traveling to or living in high-altitude areas. Researching the destination, understanding the risks associated with altitude sickness, and consulting with healthcare professionals can provide valuable insights and recommendations tailored to an individual's health status and travel plans.
Health Consultations
Consulting with a healthcare professional before traveling to high-altitude areas is essential, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice, prescribe medications if necessary, and recommend specific preventive measures based on an individual's health history and the nature of their travel or relocation.Community and Support

Having a supportive community and access to resources can make a significant difference for individuals adapting to high-altitude environments. Sharing experiences, advice, and support with others who have undergone similar adaptations can provide valuable insights and emotional support, making the transition smoother and less isolating.
Education and Awareness
Education and awareness about altitude sickness, its symptoms, and preventive measures are crucial for individuals who spend time in high-altitude areas. By understanding the risks and taking proactive steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing severe altitude sickness, ensuring a safer and more enjoyable experience in these environments.What are the primary symptoms of altitude sickness?
+The primary symptoms of altitude sickness include headaches, fatigue, nausea, dizziness, and shortness of breath. In severe cases, it can lead to high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) and high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE), which are life-threatening conditions.
How can I prevent altitude sickness?
+Preventing altitude sickness involves gradual ascent, staying hydrated, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding strenuous activities, and considering medication or supplements as advised by healthcare professionals. It's also crucial to recognize the symptoms early and take appropriate action.
What role does acclimatization play in reducing altitude sickness?
+Acclimatization is the body's natural process of adapting to higher elevations. It involves the production of more red blood cells to carry oxygen more efficiently. Allowing the body time to acclimatize through gradual ascent is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of altitude sickness.
In conclusion, managing and reducing the effects of altitude sickness requires a comprehensive approach that includes understanding the condition, recognizing its symptoms, and taking proactive measures such as gradual ascent, hydration, dietary adjustments, medication, and rest. By being informed and prepared, individuals can safely enjoy high-altitude environments, whether for adventure, work, or residence. We invite you to share your experiences and tips on managing altitude sickness, and we look forward to your comments and questions on this critical topic.
