Intro
Stay protected with a timely Tetanus Shot Schedule, including booster shots and vaccination guidelines, to prevent tetanus infection and lockjaw, ensuring a healthy immune system and preventing disease outbreaks.
The importance of vaccinations cannot be overstated, and one of the most critical vaccines is the tetanus shot. Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is a serious bacterial infection that can lead to severe muscle stiffness, spasms, and even death. The tetanus shot schedule is designed to provide protection against this deadly disease, and it's essential to understand the schedule and its significance. In this article, we'll delve into the world of tetanus shots, exploring the schedule, benefits, and everything you need to know to stay protected.
Tetanus is a bacterial infection caused by Clostridium tetani, which is commonly found in soil, dust, and the gastrointestinal tracts of animals. The bacteria can enter the body through cuts, wounds, or other injuries, and if left untreated, can lead to severe complications. The tetanus shot, also known as the tetanus vaccine, is a highly effective way to prevent the disease. The vaccine works by introducing a small, harmless piece of the bacteria to the body, which triggers an immune response and produces antibodies to fight the infection.
The tetanus shot schedule is typically recommended for individuals of all ages, from infants to adults. The schedule may vary depending on factors such as age, health status, and occupation, but the general guidelines are as follows: infants and young children receive a series of tetanus shots as part of their routine vaccinations, while adults may need booster shots every 10 years to maintain protection. It's crucial to follow the recommended schedule to ensure maximum protection against tetanus.
Tetanus Shot Schedule for Infants and Children
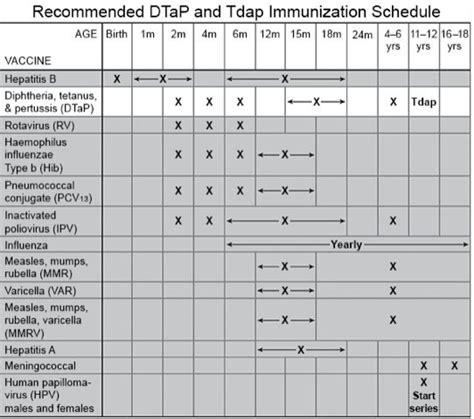
Benefits of the Tetanus Shot Schedule for Infants and Children
The benefits of the tetanus shot schedule for infants and children are numerous. The vaccine provides protection against a serious and potentially life-threatening disease, and it also helps to prevent the spread of tetanus in the community. Additionally, the tetanus shot schedule helps to build a strong immune system in children, which can provide long-term protection against other diseases. Some of the key benefits of the tetanus shot schedule for infants and children include: * Protection against tetanus and other diseases * Prevention of serious complications and death * Building a strong immune system * Reduced risk of transmission to others * Peace of mind for parents and caregiversTetanus Shot Schedule for Adults
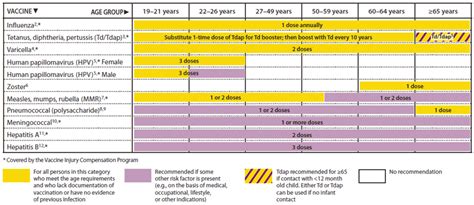
Benefits of the Tetanus Shot Schedule for Adults
The benefits of the tetanus shot schedule for adults are similar to those for infants and children. The vaccine provides protection against tetanus and other diseases, and it also helps to prevent the spread of tetanus in the community. Some of the key benefits of the tetanus shot schedule for adults include: * Protection against tetanus and other diseases * Prevention of serious complications and death * Reduced risk of transmission to others * Peace of mind for individuals and their loved ones * Compliance with occupational health and safety regulationsTetanus Shot Side Effects
Managing Tetanus Shot Side Effects
Most side effects of the tetanus shot are mild and temporary, and they can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers or antihistamines. However, if you experience any severe or persistent side effects, it's essential to seek medical attention immediately. Some tips for managing tetanus shot side effects include: * Applying a cold compress to the injection site to reduce swelling * Taking over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen * Resting and staying hydrated to reduce fatigue and weakness * Avoiding strenuous activities or exercise to reduce muscle painTetanus Shot Interactions

Managing Tetanus Shot Interactions
If you have any concerns about potential interactions with the tetanus shot, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider. They can provide personalized advice and guidance to minimize the risk of interactions and ensure safe and effective vaccination. Some tips for managing tetanus shot interactions include: * Informing your healthcare provider about any medications or medical conditions * Avoiding certain medications or activities that may interact with the vaccine * Monitoring for signs of interactions, such as increased side effects or reduced efficacyTetanus Shot Effectiveness

Factors Affecting Tetanus Shot Effectiveness
Some factors that can affect the effectiveness of the tetanus shot include: * Age: The vaccine is most effective in individuals under 65 years of age. * Health status: Individuals with weakened immune systems or certain medical conditions may not respond as well to the vaccine. * Occupation: Individuals who work in high-risk occupations, such as construction or healthcare, may require more frequent booster shots to maintain protection. * Compliance: Failure to follow the recommended vaccination schedule can reduce the effectiveness of the vaccine.Tetanus Shot Recommendations
Special Considerations
Some individuals may require special considerations when it comes to the tetanus shot. For example: * Pregnant women: The tetanus shot is safe and recommended for pregnant women, especially if they are at high risk of exposure to tetanus. * Breastfeeding women: The tetanus shot is safe and recommended for breastfeeding women, especially if they are at high risk of exposure to tetanus. * Individuals with weakened immune systems: The tetanus shot may not be as effective in individuals with weakened immune systems, and they may require more frequent booster shots.What is the tetanus shot schedule for infants and children?
+The tetanus shot schedule for infants and children typically begins at 2 months of age, with subsequent doses given at 4, 6, and 15-18 months. A booster shot is then given at 4-6 years of age, and another booster shot is recommended at 11-12 years of age.
How often do adults need to get a tetanus shot?
+Adults typically need to get a tetanus shot every 10 years, although this may vary depending on individual circumstances.
What are the potential side effects of the tetanus shot?
+Common side effects of the tetanus shot include redness, swelling, or pain at the injection site, fatigue or weakness, headache or muscle pain, nausea or vomiting, fever or chills, and allergic reactions.
In summary, the tetanus shot schedule is an essential part of maintaining protection against tetanus and other diseases. By following the recommended schedule and taking steps to manage potential side effects and interactions, individuals can ensure they are protected against this serious and potentially life-threatening disease. We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions about the tetanus shot schedule in the comments below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and to take the necessary steps to stay protected against tetanus.
