Intro
Discover high blood glucose level symptoms, including hyperglycemia signs, diabetes warning signs, and blood sugar symptoms, to manage blood glucose levels and prevent complications.
High blood glucose levels, also known as hyperglycemia, can have severe consequences on the body if left untreated. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of high blood glucose levels to take prompt action and prevent long-term damage. The importance of monitoring blood glucose levels cannot be overstated, as it plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the world of high blood glucose level symptoms, exploring the causes, effects, and management strategies to help individuals lead a healthier life.
The human body relies on insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas, to regulate blood glucose levels. When we consume food, our body breaks down the carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. Insulin helps to facilitate the entry of glucose into cells, providing them with the necessary energy to function properly. However, when the body is unable to produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to its effects, blood glucose levels can rise, leading to a range of symptoms. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial, as it enables individuals to seek medical attention and prevent complications.
High blood glucose levels can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or background. It is a prevalent condition that requires attention and care to manage effectively. The symptoms of high blood glucose levels can vary from person to person, but there are common signs that individuals should be aware of. By understanding these symptoms and taking proactive steps, individuals can reduce their risk of developing complications and improve their overall quality of life.
Understanding High Blood Glucose Levels
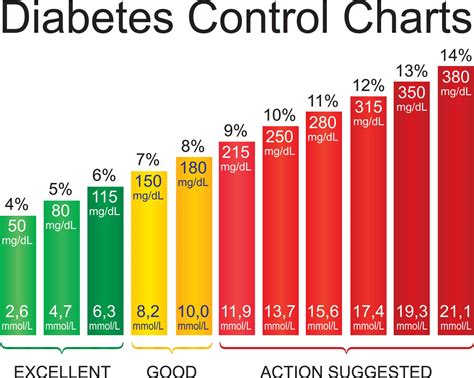
Causes of High Blood Glucose Levels
The causes of high blood glucose levels can be broadly classified into two categories: genetic and lifestyle-related factors. Genetic factors, such as a family history of diabetes, can increase an individual's risk of developing high blood glucose levels. Lifestyle-related factors, including a poor diet, lack of physical activity, and obesity, can also contribute to the development of hyperglycemia. Other factors, such as certain medications, stress, and sleep deprivation, can also affect blood glucose levels.Common Symptoms of High Blood Glucose Levels

Diagnosing High Blood Glucose Levels
Diagnosing high blood glucose levels typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. A healthcare provider may perform a physical examination to look for signs of hyperglycemia, such as dry skin, slow healing wounds, and blurred vision. They may also ask questions about the individual's medical history, including their family history, diet, and physical activity level. Laboratory tests, such as a fasting blood glucose test or an oral glucose tolerance test, can help to confirm the diagnosis.Managing High Blood Glucose Levels
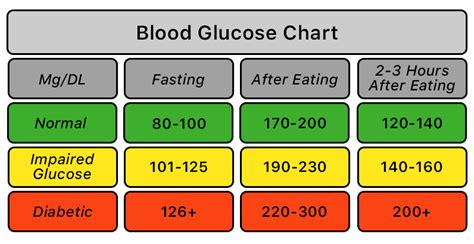
Lifestyle Modifications for Managing High Blood Glucose Levels
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing high blood glucose levels. A healthy diet that is low in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats can help to reduce blood glucose levels and improve overall health. Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can help to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels. Weight loss, if necessary, can also help to improve blood glucose control and reduce the risk of complications.Complications of High Blood Glucose Levels
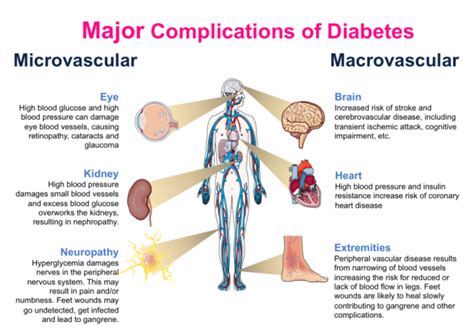
Preventing Complications of High Blood Glucose Levels
Preventing complications of high blood glucose levels requires a proactive approach that includes regular monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and medication. Regular monitoring can help to track blood glucose levels and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular physical activity, can help to reduce blood glucose levels and improve overall health. Medications, such as metformin or insulin, may be prescribed to help regulate blood glucose levels and prevent complications.Conclusion and Next Steps

We encourage readers to share their experiences and ask questions in the comments section below. If you found this article helpful, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. By working together, we can raise awareness about the importance of managing high blood glucose levels and improve the health and well-being of individuals around the world.
What are the common symptoms of high blood glucose levels?
+The common symptoms of high blood glucose levels include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet.
How can I manage high blood glucose levels?
+Managing high blood glucose levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring. Lifestyle modifications, such as a healthy diet and regular physical activity, can help to reduce blood glucose levels and improve overall health.
What are the complications of high blood glucose levels?
+The complications of high blood glucose levels include heart disease, kidney disease, vision loss, and nerve damage. Chronic high blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of these complications.









