Intro
Identify 7 high blood symptoms, including headaches and dizziness, to manage hypertension and prevent cardiovascular diseases, heart attacks, and strokes, with lifestyle changes and medical treatments.
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a serious medical condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. It is essential to recognize the symptoms of high blood pressure to take prompt action and prevent long-term damage to the body. High blood pressure can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, or lifestyle, making it crucial to be aware of the warning signs. In this article, we will delve into the importance of recognizing high blood pressure symptoms and explore the various aspects of this condition.
High blood pressure is often referred to as the "silent killer" because it can go unnoticed for years, causing damage to the blood vessels, heart, and other organs. The American Heart Association estimates that nearly 108 million adults in the United States have high blood pressure, with many more cases going undiagnosed. The consequences of untreated high blood pressure can be devastating, including heart attacks, strokes, and kidney disease. Therefore, it is vital to be aware of the symptoms and take proactive steps to manage blood pressure.
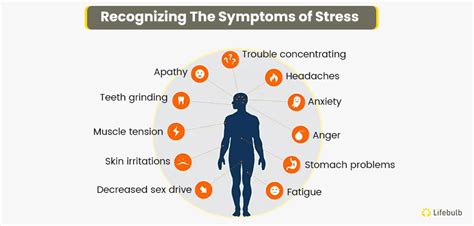
Recognizing the symptoms of high blood pressure is not always easy, as they can be subtle and may not appear until the condition has advanced. However, being informed about the potential warning signs can help individuals take control of their health and seek medical attention if necessary. Some common symptoms of high blood pressure include headaches, dizziness, and nosebleeds, although these can also be caused by other conditions. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to discuss the best course of treatment.
Understanding High Blood Pressure

Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of high blood pressure are complex and multifaceted, involving a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some of the key risk factors include: * Family history: Individuals with a family history of high blood pressure are more likely to develop the condition. * Age: Blood pressure tends to increase with age, with most people developing high blood pressure by the age of 60. * Obesity: Excess weight can increase blood pressure, as well as the risk of developing other health conditions. * Physical inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to high blood pressure, as well as other health problems. * Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and increase blood pressure. * Diet: A diet high in salt, sugar, and saturated fat can contribute to high blood pressure.Recognizing the Symptoms
Diagnosing High Blood Pressure
Diagnosing high blood pressure typically involves a physical exam, medical history, and blood pressure readings. A healthcare professional will use a blood pressure monitor to take multiple readings, usually at different times of the day. The American Heart Association recommends the following blood pressure categories: * Normal blood pressure: Less than 120/80 mmHg * Elevated blood pressure: 120-129/80 mmHg * Stage 1 hypertension: 130-139/80-89 mmHg * Stage 2 hypertension: 140 or higher/90 or higher mmHgManaging High Blood Pressure

Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes can be challenging, but it is essential in managing high blood pressure. Some additional lifestyle changes that can help include: * Reducing stress: Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga, can help lower blood pressure. * Getting enough sleep: Aiming for 7-8 hours of sleep per night can help regulate blood pressure. * Limiting caffeine intake: Consuming too much caffeine can increase blood pressure, so it is essential to limit intake to moderate levels. * Monitoring blood pressure: Regularly monitoring blood pressure can help identify any changes or trends, allowing for prompt intervention.Treatment Options
Medication
Medication is often necessary to manage high blood pressure, particularly if lifestyle changes are not enough to lower blood pressure. Some common medications used to treat high blood pressure include: * Diuretics: Help remove excess fluid from the body, reducing blood pressure. * Beta blockers: Slow the heart rate, reducing blood pressure. * ACE inhibitors: Relax blood vessels, reducing blood pressure.Complications of High Blood Pressure
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications of high blood pressure requires prompt treatment and lifestyle changes. Some ways to prevent complications include: * Monitoring blood pressure: Regularly monitoring blood pressure can help identify any changes or trends, allowing for prompt intervention. * Maintaining a healthy lifestyle: Engaging in regular physical activity, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress can help lower blood pressure. * Seeking medical attention: If symptoms persist or worsen, seeking medical attention is essential to prevent long-term damage.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with high blood pressure in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from this information. Take the first step towards managing your blood pressure and reducing the risk of complications – consult a healthcare professional today.
What are the common symptoms of high blood pressure?
+Common symptoms of high blood pressure include headaches, dizziness, and nosebleeds, although these can also be caused by other conditions.
How can I manage my high blood pressure?
+Managing high blood pressure requires a comprehensive approach, involving lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring. Some effective ways to manage high blood pressure include maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, eating a balanced diet, and reducing sodium intake.
What are the complications of high blood pressure?
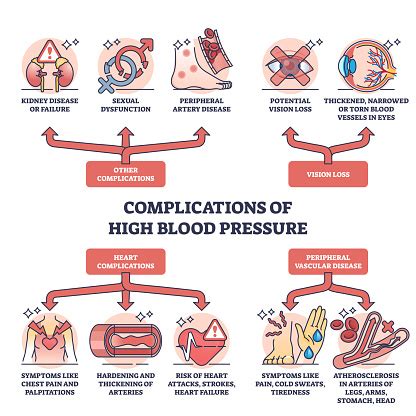
+If left untreated, high blood pressure can lead to a range of complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, and vision loss. Preventing complications requires prompt treatment and lifestyle changes.
