Intro
Discover Clonidines mechanism of action, an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, and its effects on blood pressure, anxiety, and ADHD, through its sympatholytic and anxiolytic properties.
Clonidine is a medication that has been widely used for several decades to treat various medical conditions, including high blood pressure, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and certain pain disorders. Despite its widespread use, many people are not aware of the mechanism of action of clonidine, which is essential to understanding how it works and its potential benefits and risks. In this article, we will delve into the details of clonidine's mechanism of action, its effects on the body, and its uses in different medical conditions.
Clonidine is an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist, which means that it works by stimulating certain receptors in the brain and other parts of the body. These receptors are responsible for regulating various physiological processes, including blood pressure, heart rate, and the transmission of pain signals. By activating these receptors, clonidine can produce a range of effects, including lowering blood pressure, reducing pain, and improving attention and focus. The exact mechanism of action of clonidine is complex and involves multiple pathways and receptors, but it is generally understood to involve the stimulation of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
The effects of clonidine on the body are numerous and can vary depending on the individual and the condition being treated. In general, clonidine can produce a range of benefits, including lowering blood pressure, reducing pain, and improving attention and focus. It can also produce some side effects, such as drowsiness, dry mouth, and constipation, although these are typically mild and temporary. Overall, clonidine is a versatile medication that has been shown to be effective in treating a range of medical conditions, and its mechanism of action is an important aspect of its therapeutic effects.
Introduction to Clonidine

How Clonidine Works
Clonidine works by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body. These receptors are responsible for regulating various physiological processes, including blood pressure, heart rate, and the transmission of pain signals. By activating these receptors, clonidine can produce a range of effects, including lowering blood pressure, reducing pain, and improving attention and focus. The exact mechanism of action of clonidine is complex and involves multiple pathways and receptors, but it is generally understood to involve the stimulation of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.Benefits of Clonidine

Some of the benefits of clonidine include:
- Lowering blood pressure: Clonidine can help to lower blood pressure by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
- Reducing pain: Clonidine can help to reduce pain by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
- Improving attention and focus: Clonidine can help to improve attention and focus by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
- Treating ADHD: Clonidine can help to treat ADHD by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
Clonidine Uses
Clonidine is used to treat a range of medical conditions, including high blood pressure, ADHD, and certain pain disorders. It is widely used to lower blood pressure, reduce pain, and improve attention and focus. Clonidine can also be used to treat other conditions, such as anxiety and insomnia, although these uses are typically off-label.Some of the uses of clonidine include:
- High blood pressure: Clonidine can help to lower blood pressure by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
- ADHD: Clonidine can help to treat ADHD by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
- Pain disorders: Clonidine can help to reduce pain by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
- Anxiety: Clonidine can help to treat anxiety by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
- Insomnia: Clonidine can help to treat insomnia by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body.
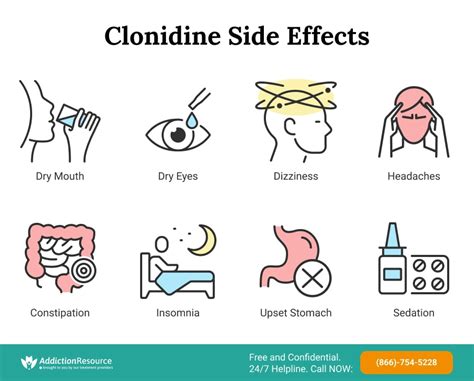
Side Effects of Clonidine
Clonidine Interactions
Clonidine can interact with other medications, including beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, and ACE inhibitors. These interactions can increase the risk of side effects and reduce the effectiveness of clonidine. It is essential to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking before starting clonidine.Some of the medications that can interact with clonidine include:
- Beta blockers: Clonidine can interact with beta blockers, which can increase the risk of side effects and reduce the effectiveness of clonidine.
- Calcium channel blockers: Clonidine can interact with calcium channel blockers, which can increase the risk of side effects and reduce the effectiveness of clonidine.
- ACE inhibitors: Clonidine can interact with ACE inhibitors, which can increase the risk of side effects and reduce the effectiveness of clonidine.
- Other medications: Clonidine can interact with other medications, including antidepressants, antipsychotics, and anti-anxiety medications.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

If you are considering taking clonidine, it is essential to consult with your doctor to discuss the potential benefits and risks of the medication. Your doctor can help you determine whether clonidine is right for you and monitor you for any side effects or interactions.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of clonidine and its mechanism of action. If you have any questions or comments, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We would be happy to hear from you and provide any additional information you may need.
What is clonidine used for?
+Clonidine is used to treat high blood pressure, ADHD, and certain pain disorders. It can also be used to treat other conditions, such as anxiety and insomnia.
How does clonidine work?
+Clonidine works by stimulating alpha-2 adrenergic receptors in the brain and other parts of the body. This can produce a range of effects, including lowering blood pressure, reducing pain, and improving attention and focus.
What are the side effects of clonidine?
+Clonidine can produce some side effects, including drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, headache, and fatigue. These side effects are typically mild and temporary, but it is essential to inform your doctor if you experience any of them.
