Intro
Discover the truth about breads nutritional value, exploring whole grain benefits, refined flour drawbacks, and healthy alternatives to make informed choices about your diet and wellbeing.
Bread has been a staple food in many cultures for thousands of years, providing sustenance and energy for people of all ages. However, with the rise of modern diets and nutritional awareness, many have begun to question whether bread is truly healthy. Some argue that bread is a source of empty calories, while others claim that it is a nutritious food that provides essential vitamins and minerals. In this article, we will delve into the world of bread and explore its nutritional value, benefits, and drawbacks.
The importance of bread in our diets cannot be overstated. It is a versatile food that can be consumed at any time of day, whether as a breakfast toast, a lunchtime sandwich, or a dinner accompaniment. Bread is also a significant source of carbohydrates, which are the body's primary source of energy. However, with the increasing prevalence of diet-related diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease, many have begun to scrutinize the nutritional content of bread. Some have even gone so far as to label bread as "unhealthy" or "toxic," citing its high glycemic index and potential for causing inflammation.
Despite these claims, bread can be a healthy part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. Whole grain bread, in particular, is rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, making it a nutritious choice for those looking to improve their overall health. Furthermore, bread can be a valuable source of sustenance for people with certain dietary needs, such as those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease. In this article, we will explore the nutritional benefits and drawbacks of bread, as well as provide guidance on how to make healthier bread choices.
Understanding the Nutritional Content of Bread

To understand the nutritional content of bread, it is essential to examine its macronutrient composition. Bread is primarily composed of carbohydrates, with smaller amounts of protein and fat. The exact nutritional content of bread can vary depending on the type of flour used, the presence of additives, and the baking process. Whole grain bread, for example, is higher in fiber and nutrients compared to refined white bread. Some of the key nutrients found in bread include:
- Carbohydrates: Bread is primarily composed of carbohydrates, which are the body's primary source of energy.
- Fiber: Whole grain bread is a rich source of dietary fiber, which can help promote digestive health and support healthy blood sugar levels.
- Protein: Bread contains small amounts of protein, which is essential for building and repairing tissues in the body.
- Vitamins and minerals: Bread can be a good source of various vitamins and minerals, including iron, B vitamins, and selenium.
Types of Bread and Their Nutritional Content
The nutritional content of bread can vary significantly depending on the type of flour used and the presence of additives. Some common types of bread include:- Whole grain bread: Made from whole grains, this type of bread is higher in fiber and nutrients compared to refined white bread.
- White bread: Made from refined flour, white bread is lower in fiber and nutrients compared to whole grain bread.
- Sourdough bread: Made using a natural starter culture, sourdough bread has a higher pH level and may be easier to digest for some individuals.
- Gluten-free bread: Made from gluten-free flours, this type of bread is suitable for individuals with gluten intolerance or celiac disease.
The Benefits of Bread in a Healthy Diet
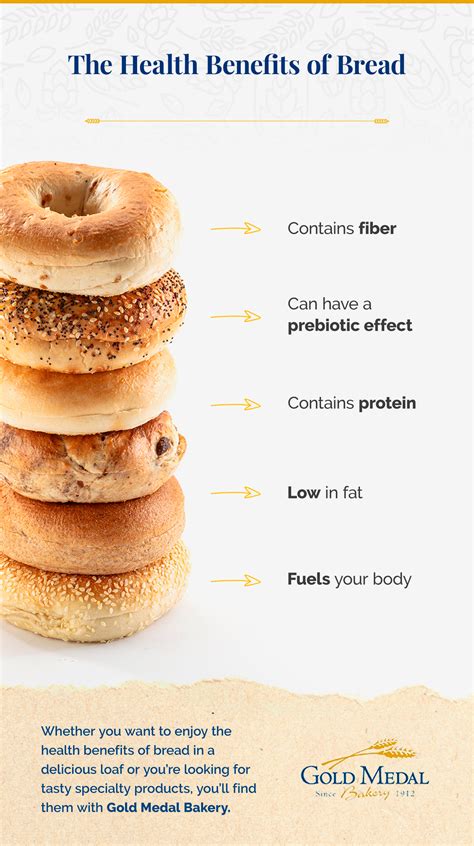
Despite the negative publicity surrounding bread, it can be a healthy part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. Some of the benefits of bread include:
- Providing energy: Bread is a rich source of carbohydrates, which are the body's primary source of energy.
- Supporting digestive health: Whole grain bread is high in fiber, which can help promote digestive health and support healthy blood sugar levels.
- Offering essential nutrients: Bread can be a good source of various vitamins and minerals, including iron, B vitamins, and selenium.
- Being versatile: Bread can be consumed at any time of day, whether as a breakfast toast, a lunchtime sandwich, or a dinner accompaniment.
How to Make Healthier Bread Choices
To make healthier bread choices, consider the following tips:- Choose whole grain bread: Whole grain bread is higher in fiber and nutrients compared to refined white bread.
- Opt for bread with fewer additives: Some breads may contain additives such as preservatives, artificial flavorings, and colorings.
- Consider gluten-free bread: If you have gluten intolerance or celiac disease, consider choosing gluten-free bread made from gluten-free flours.
- Be mindful of portion sizes: Bread can be high in calories, so be mindful of portion sizes to maintain a healthy weight.
The Drawbacks of Bread in a Healthy Diet

While bread can be a healthy part of a balanced diet, there are also some drawbacks to consider. Some of the drawbacks of bread include:
- Being high in calories: Bread can be high in calories, particularly if consumed in excess.
- Having a high glycemic index: Some types of bread, such as white bread, have a high glycemic index, which can cause a spike in blood sugar levels.
- Containing additives: Some breads may contain additives such as preservatives, artificial flavorings, and colorings.
- Being a potential allergen: Some individuals may be allergic to gluten or other ingredients found in bread.
Common Bread-Related Health Concerns
Some common health concerns related to bread consumption include:- Gluten intolerance: Some individuals may experience symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea after consuming gluten.
- Celiac disease: A chronic autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to react to gluten, leading to damage in the small intestine.
- Wheat allergy: A rare but potentially life-threatening allergy that can cause symptoms such as hives, itching, and difficulty breathing.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts

In conclusion, bread can be a healthy part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. While there are some drawbacks to consider, the benefits of bread, including providing energy, supporting digestive health, and offering essential nutrients, make it a valuable food for many individuals. By choosing whole grain bread, being mindful of portion sizes, and opting for bread with fewer additives, you can make healthier bread choices and enjoy the nutritional benefits of this versatile food.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the health benefits and drawbacks of bread in the comments below. Have you experienced any health benefits or concerns related to bread consumption? Do you have any favorite bread recipes or tips for making healthier bread choices? Share your experiences and join the conversation.
Is whole grain bread healthier than white bread?
+Yes, whole grain bread is generally considered healthier than white bread due to its higher fiber and nutrient content.
Can bread be a part of a weight loss diet?
+Yes, bread can be part of a weight loss diet when consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced meal plan.
What are some common bread-related health concerns?
+Common bread-related health concerns include gluten intolerance, celiac disease, and wheat allergy.
