Intro
Discover how Metoprolol works to treat hypertension, angina, and heart failure through its beta-blocking effects, reducing heart rate, and lowering blood pressure, while also exploring its role in cardiovascular health and management of cardiac conditions.
Metoprolol is a widely prescribed medication that belongs to the class of beta-blockers. It is primarily used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions. Understanding how metoprolol works is crucial for patients who are prescribed this medication, as it can help them manage their conditions more effectively and minimize potential side effects. The importance of metoprolol lies in its ability to reduce the heart's workload, thereby lowering blood pressure and alleviating symptoms associated with heart disease.
The mechanism of action of metoprolol is complex and involves several pathways. At its core, metoprolol works by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and by slowing the heart rate. This dual action reduces the force of the heart's contractions and the heart rate, which in turn lowers blood pressure. Furthermore, metoprolol has been shown to reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes in patients with high blood pressure or heart disease. Its benefits extend beyond just lowering blood pressure; it also improves survival rates in patients who have had a heart attack.
The use of metoprolol has become increasingly common due to its effectiveness in managing a range of cardiovascular conditions. As research continues to uncover the full potential of beta-blockers like metoprolol, it is essential for healthcare providers and patients to stay informed about the latest developments and guidelines. By understanding the ways in which metoprolol works, individuals can better navigate their treatment plans and make informed decisions about their health. Whether you are a patient considering metoprolol as part of your treatment or simply interested in learning more about cardiovascular health, delving into the specifics of how metoprolol functions can provide valuable insights.
Introduction to Metoprolol

Benefits of Metoprolol
The benefits of metoprolol are multifaceted, ranging from the reduction of blood pressure and heart rate to the improvement of survival rates post-myocardial infarction (heart attack). By decreasing the heart's demand for oxygen, metoprolol can help alleviate symptoms of angina, such as chest pain, and reduce the frequency of angina attacks. Furthermore, metoprolol's ability to slow the heart rate can be beneficial in certain arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms), helping to restore a more normal heart rhythm.How Metoprolol Lowers Blood Pressure
Metoprolol's Impact on the Heart
Metoprolol's impact on the heart is significant, particularly in patients with existing heart disease. By reducing the heart's workload, metoprolol can decrease the size of the heart in conditions where the heart is enlarged, a condition known as hypertrophy. This reduction in heart size can improve the heart's efficiency and reduce the risk of complications such as heart failure. Moreover, metoprolol's ability to reduce the frequency and severity of arrhythmias can improve the quality of life for patients with irregular heartbeats.Side Effects of Metoprolol
Interactions with Other Medications
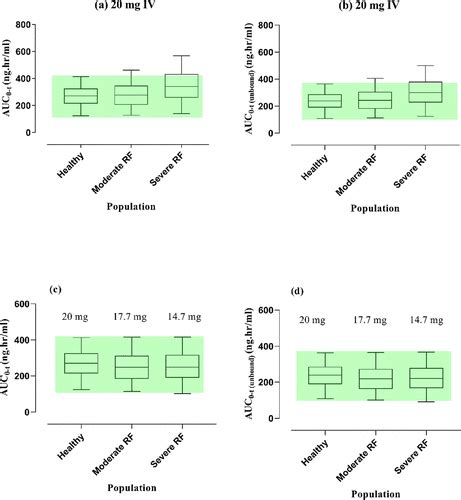
Metoprolol can interact with other medications, either enhancing or reducing its effects. For example, when taken with certain antidepressants, the levels of metoprolol in the blood can increase, potentially leading to increased side effects. Conversely, metoprolol can also affect the levels of other medications in the body, such as digoxin, used to treat heart failure and arrhythmias. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and supplements, they are taking to avoid potential interactions.Metoprolol in Special Populations
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Patients taking metoprolol should have regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider to monitor the effectiveness of the medication and to check for any side effects. This may involve regular blood pressure checks, heart rate monitoring, and periodic blood tests to assess kidney function and check for any electrolyte imbalances. Adherence to the prescribed treatment regimen is crucial for maximizing the benefits of metoprolol and minimizing the risk of complications.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
For individuals considering metoprolol as part of their treatment plan, it is essential to maintain open communication with healthcare providers, ask questions, and seek clarification on any concerns. By doing so, patients can navigate their treatment journey with confidence, leveraging the full potential of metoprolol to improve their heart health and overall well-being.What is metoprolol used for?
+Metoprolol is used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain (angina), and certain heart-related conditions. It belongs to the class of beta-blockers and works by reducing the heart's workload and lowering blood pressure.
How long does it take for metoprolol to start working?
+The effects of metoprolol can be seen within a few hours of taking the first dose, but it may take several weeks to achieve its full blood pressure-lowering effect.
Can metoprolol be stopped abruptly?
+No, metoprolol should not be stopped abruptly. Stopping the medication suddenly can lead to a rebound effect, where blood pressure increases rapidly, potentially leading to heart attack or stroke. The dosage should be tapered off under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
We hope this comprehensive overview of metoprolol has provided you with a deeper understanding of its uses, benefits, and potential side effects. Whether you are a patient, a caregiver, or simply interested in cardiovascular health, we invite you to share your thoughts, ask questions, or explore further resources on this topic. Your engagement is invaluable in fostering a community that prioritizes heart health and well-being.
