Intro
Learn 5 effective ways to treat burns, including minor and severe burn care, using natural remedies, topical creams, and medical treatments to promote wound healing, reduce scarring, and alleviate burn pain.
Burns are a common type of injury that can occur in various situations, from accidents at home to workplace incidents. They can be caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, or radiation, and can range from mild to severe. Treating burns promptly and properly is essential to promote healing, prevent infection, and minimize scarring. In this article, we will explore the different types of burns, their symptoms, and most importantly, the various ways to treat them.
Burns can be classified into three main categories: first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree. First-degree burns affect only the outer layer of the skin, causing redness, swelling, and pain. Second-degree burns extend to the middle layer of the skin, leading to blisters, redness, and swelling. Third-degree burns, also known as full-thickness burns, destroy both layers of the skin and can reach underlying tissues, causing charred skin, numbness, and little to no pain. Understanding the type and severity of a burn is crucial for determining the best course of treatment.
The importance of proper burn treatment cannot be overstated. Inadequate care can lead to infection, scarring, and even long-term damage to the skin and underlying tissues. Moreover, severe burns can be life-threatening if not treated promptly and effectively. With the right approach, however, it is possible to manage the symptoms, facilitate healing, and reduce the risk of complications. In the following sections, we will delve into the different methods for treating burns, including home remedies, medical treatments, and preventive measures.
Introduction to Burn Treatment
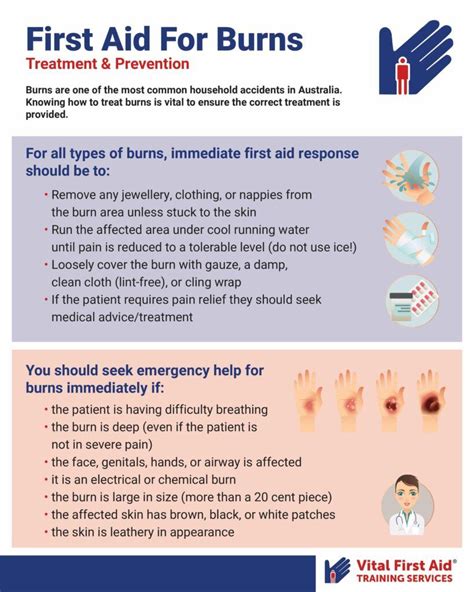
Burn treatment depends on the severity and type of burn. For minor burns, such as first-degree burns, home remedies and self-care measures may be sufficient. These include cooling the burn with cool water, applying topical creams or gels, and covering the burn with a non-stick dressing. For more severe burns, medical attention is necessary. This may involve debridement (removing dead skin), wound dressing, and the administration of antibiotics to prevent infection.
Types of Burns and Their Treatment
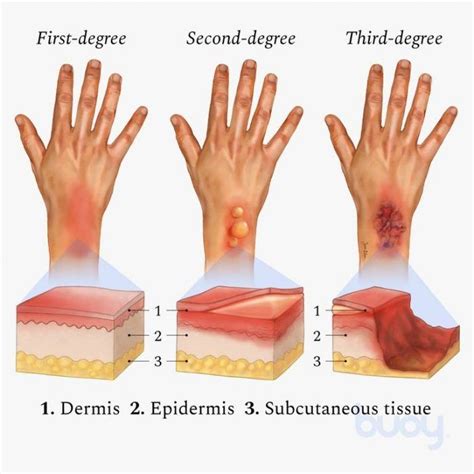
Each type of burn requires a specific approach to treatment. First-degree burns can often be treated at home with cool compresses, topical creams, and over-the-counter pain relievers. Second-degree burns may require medical attention, especially if they cover a large area or are deep. Treatment for second-degree burns includes wound cleaning, application of antibiotic ointment, and dressing. Third-degree burns are medical emergencies that require immediate hospitalization. Treatment involves fluid replacement, wound debridement, and possibly skin grafting.
First-Degree Burns Treatment
First-degree burns are the mildest form of burns and can be managed with basic first aid. The initial step is to stop the burning process by removing the source of heat or flame. Then, the burn should be cooled with cool tap water for about 10 minutes to reduce the temperature of the skin and ease the pain. Never use ice or ice water, as this can cause further damage. After cooling, the burn can be covered with a non-stick dressing to protect it from further irritation and infection.Second-Degree Burns Treatment
Second-degree burns are more serious and require more thorough care. In addition to cooling the burn, it's essential to clean the wound with mild soap and lukewarm water to prevent infection. Apply an antibiotic ointment to the burn and cover it with a non-stick dressing. For pain management, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used. It's crucial to monitor the burn for signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or pus, and seek medical attention if these symptoms occur.Home Remedies for Burns

Several home remedies can help in the healing process of minor burns. Aloe vera gel is known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties, making it an effective remedy for minor burns. Honey has antibacterial properties that can help prevent infection and promote healing. Cool milk can be used as a compress to cool the burn and provide relief. Tea tree oil, due to its antiseptic properties, can be applied to the burn after it has cooled to prevent infection, but it should be diluted with water as it can be harsh on the skin.
Natural Remedies for Burn Relief
Natural remedies can provide relief and aid in the healing process. Coconut oil, rich in fatty acids, can help soothe and moisturize the skin, reducing the risk of infection. Vitamin E oil can be applied to the burn once it has started to heal to reduce the appearance of scars. Oatmeal baths can help relieve itching and irritation associated with burns. It's essential to note that while these remedies can be beneficial, they should not replace medical treatment for severe burns.Medical Treatment for Severe Burns

Severe burns require immediate medical attention. The primary goal of medical treatment is to prevent infection, facilitate healing, and minimize scarring. Debridement, the removal of dead skin, is often necessary to promote healing and prevent infection. Wound dressings are used to protect the wound and keep it moist, promoting a conducive environment for healing. In some cases, skin grafting may be required to cover large areas of burned skin. Intravenous antibiotics may be administered to prevent or treat infections.
Surgical Interventions for Burns
Surgical interventions may be necessary for severe burns. Skin grafting involves taking healthy skin from another part of the body and transplanting it to the burned area. This procedure can help cover large wounds, promote healing, and minimize scarring. In cases where the burn is deep and extensive, reconstructive surgery may be required to repair damaged tissues and restore function and appearance.Prevention and Safety Measures

Preventing burns is always better than treating them. Several safety measures can be taken to reduce the risk of burns. In the kitchen, never leave cooking unattended, and keep a fire extinguisher nearby. Ensure that electrical appliances are kept away from water, and avoid overloading electrical outlets. In the workplace, follow all safety protocols, especially when working with hazardous materials or equipment. At home, install smoke detectors and keep emergency phone numbers handy.
Fire Safety and Burn Prevention
Fire safety is crucial in preventing burns. Ensure that all family members know what to do in case of a fire, including escape routes and a meeting point outside the home. Keep flammable materials away from heat sources, and never smoke near flammable substances. Regularly inspect electrical cords and appliances for damage, and replace them if necessary. Teaching children about fire safety and the dangers of playing with fire can also help prevent burns.Conclusion and Future Directions

In conclusion, treating burns effectively requires understanding the type and severity of the burn, as well as the appropriate treatment options. From home remedies for minor burns to medical interventions for severe ones, the key to successful treatment is prompt action and proper care. As research continues to advance, new treatments and technologies are being developed to improve burn care, including stem cell therapy, nanotechnology, and advanced wound dressings. By staying informed and taking preventive measures, we can reduce the incidence and impact of burns.
Looking Ahead: Advances in Burn Treatment
The future of burn treatment holds much promise. Advances in stem cell research may lead to new methods for regenerating damaged skin. Nanotechnology could provide innovative solutions for wound healing, such as nanofibers that mimic the structure of skin. Furthermore, telemedicine is becoming increasingly important, allowing for remote consultations and monitoring, which can be especially beneficial for patients in remote areas or with limited mobility. As these technologies evolve, they are likely to play a significant role in improving outcomes for burn patients.What are the common causes of burns?
+Burns can be caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, or radiation. Common causes include fires, scalds from hot liquids, electrical accidents, and chemical spills.
How can I prevent burns at home?
+To prevent burns at home, ensure that all electrical appliances are kept away from water, never leave cooking unattended, and keep emergency phone numbers handy. Installing smoke detectors and teaching children about fire safety are also important preventive measures.
What should I do immediately after a burn occurs?
+Immediately after a burn occurs, stop the burning process, cool the burn with cool water for about 10 minutes, and remove any clothing or jewelry near the burned area. For severe burns, seek medical attention immediately.
We hope this comprehensive guide to treating burns has been informative and helpful. Whether you're looking to understand the basics of burn treatment, explore home remedies, or learn about the latest medical interventions, this article has covered it all. Remember, prevention is key, and by taking the necessary safety measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of burns. If you have any further questions or would like to share your experiences with burn treatment, please don't hesitate to comment below. Sharing this article with others can also help spread awareness and potentially save lives. Let's work together to create a safer, more informed community.
