Intro
Learn how to treat ear infections with effective remedies, alleviating symptoms like earache, hearing loss, and tinnitus, using antibiotics, ear drops, and home treatments.
Ear infections are a common health issue that can affect people of all ages, but they are most prevalent among children. The infection occurs when bacteria or viruses enter the middle ear, causing inflammation and fluid buildup. This can lead to symptoms such as ear pain, fever, and difficulty hearing. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ear infections is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
Ear infections can be caused by a variety of factors, including upper respiratory tract infections, allergies, and anatomical issues such as a narrow Eustachian tube. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat and plays a crucial role in regulating air pressure and draining fluid from the ear. When the tube is blocked or dysfunctional, fluid can accumulate in the middle ear, creating an environment conducive to bacterial or viral growth.
The symptoms of an ear infection can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the infection. Common symptoms include ear pain or discomfort, fever, difficulty hearing, and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear. In some cases, the infection can cause discharge or fluid to drain from the ear, which may be yellow or green in color. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as untreated ear infections can lead to complications such as hearing loss, balance problems, and speech development issues in children.
Understanding Ear Infections
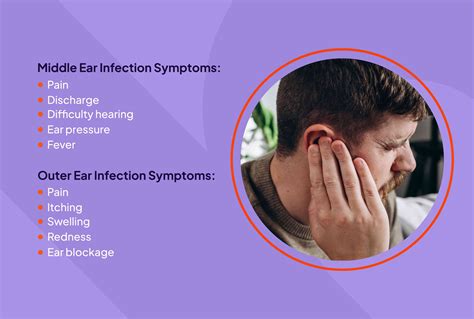
Ear infections are typically classified into three categories: acute otitis media (AOM), otitis media with effusion (OME), and chronic otitis media. AOM is the most common type and is characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms, including ear pain, fever, and fluid buildup in the middle ear. OME is a condition where fluid accumulates in the middle ear, but there are no signs of infection. Chronic otitis media is a persistent or recurring infection that can cause long-term damage to the ear.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes and risk factors for ear infections are diverse and can include upper respiratory tract infections, allergies, colds, and flu. Anatomical issues such as a narrow Eustachian tube or enlarged adenoids can also contribute to the development of ear infections. Additionally, exposure to cigarette smoke, attending daycare, and having a family history of ear infections can increase an individual's risk of developing the condition.Treatment Options for Ear Infections
The treatment for ear infections depends on the severity and type of infection, as well as the individual's overall health. Mild cases of AOM may be treated with watchful waiting, where the doctor monitors the individual's symptoms and prescribes antibiotics if the condition worsens or does not improve within 48 to 72 hours. In more severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help clear the infection. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
For individuals with recurring ear infections or chronic otitis media, surgical intervention may be necessary. A myringotomy, which involves making a small incision in the eardrum to drain fluid, may be performed to relieve pressure and improve hearing. In some cases, ear tubes may be inserted to help ventilate the middle ear and prevent future infections.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
In addition to medical treatment, there are several home remedies and self-care strategies that can help alleviate symptoms and support recovery. Applying a warm compress to the affected ear can help reduce pain and discomfort. Over-the-counter pain medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can also be used to manage pain and fever. It is essential to follow the recommended dosage and consult with a doctor before giving medication to children.Getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, and using a humidifier to add moisture to the air can also help relieve symptoms. Avoiding close contact with others, especially during the first few days of illness, can help prevent the spread of infection. Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding sharing utensils or personal items, can also reduce the risk of transmission.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing ear infections requires a combination of good hygiene practices, lifestyle modifications, and environmental changes. Avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke, both in utero and after birth, can significantly reduce the risk of ear infections. Breastfeeding, especially exclusively for the first six months, can also provide protection against ear infections.
Practicing good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and avoiding close contact with others when ill, can help prevent the spread of infection. Keeping children home from daycare or school when they are sick can also reduce the risk of transmission. Avoiding bottle-feeding when lying down and using pacifiers judiciously can also help reduce the risk of ear infections.
Vaccinations and Immunizations
Vaccinations and immunizations play a critical role in preventing ear infections. The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) and the influenza vaccine can help protect against infections that can lead to ear infections. The PCV vaccine is recommended for all children under the age of two, while the influenza vaccine is recommended for individuals of all ages, especially during flu season.Complications and Long-Term Effects
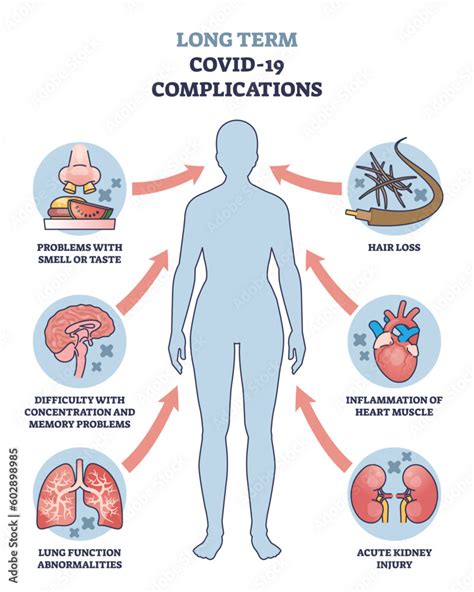
Untreated or recurring ear infections can lead to complications and long-term effects, especially in children. Hearing loss, either temporary or permanent, can occur due to damage to the eardrum or middle ear. Delayed speech development and language skills can also be affected, especially if the infection occurs during critical periods of language development.
Balance problems and dizziness can occur due to damage to the vestibular system, which is responsible for balance and equilibrium. In rare cases, ear infections can spread to other parts of the body, such as the brain or meningitis, which can be life-threatening.
Seeking Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms of an ear infection persist or worsen over time. A doctor can diagnose an ear infection by performing a physical examination and using an otoscope to visualize the eardrum. In some cases, a tympanometry test may be performed to assess the movement of the eardrum and the conduction of sound.If you or your child is experiencing symptoms of an ear infection, do not hesitate to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and promote recovery. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for ear infections, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent future occurrences.
Conclusion and Next Steps

In conclusion, ear infections are a common health issue that requires prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and prevent future occurrences. If you or your child is experiencing symptoms of an ear infection, do not hesitate to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and promote recovery.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable information and insights into ear infections. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to reach out to us. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be experiencing similar issues and to take proactive steps to protect your hearing health.
What are the common symptoms of an ear infection?
+Common symptoms of an ear infection include ear pain or discomfort, fever, difficulty hearing, and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
How can I prevent ear infections?
+Preventing ear infections requires a combination of good hygiene practices, lifestyle modifications, and environmental changes, such as avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke, breastfeeding, and practicing good hygiene.
What are the potential complications of untreated ear infections?
+Untreated or recurring ear infections can lead to complications and long-term effects, such as hearing loss, delayed speech development, balance problems, and dizziness.
How can I treat an ear infection at home?
+In addition to medical treatment, home remedies and self-care strategies can help alleviate symptoms and support recovery, such as applying a warm compress, taking over-the-counter pain medications, and getting plenty of rest.
When should I seek medical attention for an ear infection?
+It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms of an ear infection persist or worsen over time, or if you experience severe symptoms such as severe ear pain, fever, or difficulty hearing.
