Intro
Iodine is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in maintaining good health, particularly in the production of thyroid hormones. These hormones are crucial for regulating metabolism, growth, and development. Despite its importance, many people are unaware of the significance of iodine and the various food sources that provide this vital nutrient. In this article, we will delve into the world of iodine, exploring its benefits, food sources, and the consequences of iodine deficiency.
Iodine deficiency is a significant public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. It is estimated that over 2 billion people suffer from iodine deficiency, with the majority residing in developing countries. Iodine deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including thyroid disorders, cretinism, and cognitive impairment. In severe cases, it can even cause stillbirths and miscarriages. The good news is that iodine deficiency can be easily prevented by consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of iodine-rich foods.
The importance of iodine cannot be overstated, and it is essential to understand the various ways it benefits our health. Iodine is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, energy production, and growth. It also plays a crucial role in the development of the brain and nervous system, particularly during fetal development and early childhood. Furthermore, iodine has been shown to have antioxidant properties, helping to protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
Iodine Benefits
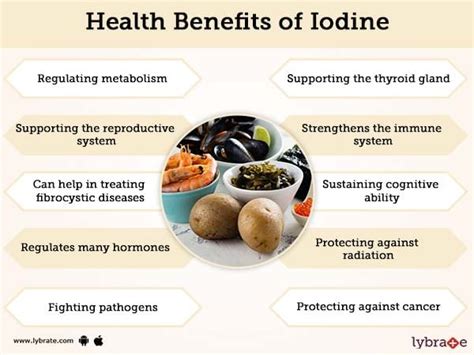
Iodine and Thyroid Function
Iodine is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, energy production, and growth. The thyroid gland uses iodine to produce two primary hormones: triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones play a crucial role in maintaining healthy cells, tissues, and organs. Without sufficient iodine, the thyroid gland cannot produce these hormones, leading to a range of health problems.Iodine-Rich Foods

It is essential to note that the iodine content of foods can vary depending on factors such as the soil quality, climate, and cooking methods. For example, seafood that is caught in areas with high levels of iodine in the water will generally have higher iodine content than seafood caught in areas with low iodine levels.
Iodine Supplementation
While it is possible to get enough iodine from food sources, some people may require supplementation, particularly those who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Iodine supplements are available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and liquid solutions. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as excessive iodine consumption can lead to adverse health effects.Iodine Deficiency

Iodine deficiency can be caused by a range of factors, including a lack of iodine in the diet, poor soil quality, and limited access to iodized salt. In some cases, iodine deficiency can also be caused by certain medical conditions, such as thyroid disorders or gastrointestinal problems.
Iodine Deficiency Symptoms
The symptoms of iodine deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency and the individual's overall health. Some common symptoms of iodine deficiency include: * Fatigue and weakness * Weight gain * Dry skin and hair * Cold intolerance * Depression and anxietyIf left untreated, iodine deficiency can lead to more severe health problems, including thyroid disorders and cognitive impairment. It is essential to seek medical attention if you are experiencing any of these symptoms, as early treatment can help prevent long-term health consequences.
Iodine and Pregnancy

Some of the best sources of iodine for pregnant women include:
- Iodized salt
- Seafood, such as cod and shrimp
- Dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- Eggs
- Prenatal vitamins that contain iodine
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as excessive iodine consumption can lead to adverse health effects.
Iodine and Breastfeeding
Iodine is also essential for breastfeeding women, as it helps to support the production of milk and ensures that the baby receives adequate amounts of iodine. Breastfeeding women require higher amounts of iodine than non-breastfeeding women, and it is essential to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of iodine-rich foods.Some of the best sources of iodine for breastfeeding women include:
- Iodized salt
- Seafood, such as cod and shrimp
- Dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- Eggs
- Breastfeeding supplements that contain iodine
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements, as excessive iodine consumption can lead to adverse health effects.
Iodine and Cognitive Function
Some of the best sources of iodine for cognitive function include:
- Iodized salt
- Seafood, such as cod and shrimp
- Dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- Eggs
- Fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries and cranberries
It is essential to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of iodine-rich foods to support cognitive function and overall health.
Iodine and Mental Health
Iodine has also been linked to mental health, with some studies suggesting that it may help reduce the risk of depression and anxiety. Iodine deficiency has been linked to a range of mental health problems, including: * Depression * Anxiety * Bipolar disorder * SchizophreniaSome of the best sources of iodine for mental health include:
- Iodized salt
- Seafood, such as cod and shrimp
- Dairy products, such as milk and cheese
- Eggs
- Fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries and cranberries
It is essential to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of iodine-rich foods to support mental health and overall well-being.
What are the symptoms of iodine deficiency?
+The symptoms of iodine deficiency can vary depending on the severity of the deficiency and the individual's overall health. Some common symptoms of iodine deficiency include fatigue and weakness, weight gain, dry skin and hair, cold intolerance, and depression and anxiety.
What are the best sources of iodine?
+Some of the best sources of iodine include iodized salt, seafood, such as cod and shrimp, dairy products, such as milk and cheese, eggs, and fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries and cranberries.
Can iodine deficiency be prevented?
+Yes, iodine deficiency can be prevented by consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of iodine-rich foods. It is also essential to use iodized salt and to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.
What are the consequences of iodine deficiency?
+The consequences of iodine deficiency can be severe, particularly for pregnant women and young children. Some of the most common health problems associated with iodine deficiency include hypothyroidism, goiter, cretinism, cognitive impairment, and stillbirths and miscarriages.
How can I ensure I am getting enough iodine?
+To ensure you are getting enough iodine, it is essential to consume a balanced diet that includes a variety of iodine-rich foods. You can also consult with a healthcare professional to determine if you need to take any supplements.
In conclusion, iodine is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in maintaining good health. It is necessary for the production of thyroid hormones, which regulate metabolism, energy production, and growth. Iodine deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including thyroid disorders, cretinism, and cognitive impairment. Fortunately, iodine deficiency can be easily prevented by consuming a balanced diet that includes a variety of iodine-rich foods. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the importance of iodine and the various ways it benefits our health. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with your friends and family.
