Intro
Discover the causes and symptoms of low globulin levels, a condition affecting blood protein balance, and learn about hypogammaglobulinemia, immunodeficiency, and treatment options for optimal health.
Globulins are a type of protein found in the blood, playing a crucial role in the immune system, blood clotting, and the transportation of various substances throughout the body. They are an essential component of the blood's protein composition, making up approximately 36% of the total protein in the blood. The remaining 64% consists of albumin, another type of protein. Low globulin levels can indicate a range of health issues, from mild to severe, and understanding the causes, symptoms, and implications of low globulin levels is vital for maintaining overall health and well-being.
The importance of globulins cannot be overstated. They are involved in the production of antibodies, which are critical for fighting off infections and diseases. Globulins also play a role in blood clotting, helping to prevent excessive bleeding when an injury occurs. Furthermore, they transport hormones, lipids, and other substances throughout the body, facilitating various physiological processes. Given their multifaceted role, abnormalities in globulin levels can have significant consequences on the body's functioning.
Abnormal globulin levels, particularly low levels, can be indicative of underlying health issues. These may include liver disease, as the liver is responsible for producing many of the globulins in the blood. Nephrotic syndrome, a condition characterized by excessive loss of protein in the urine, can also lead to low globulin levels. Additionally, certain autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, and severe infections can cause a decrease in globulin production. Understanding the causes and symptoms of low globulin levels is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment of the underlying condition.
What are Globulins?
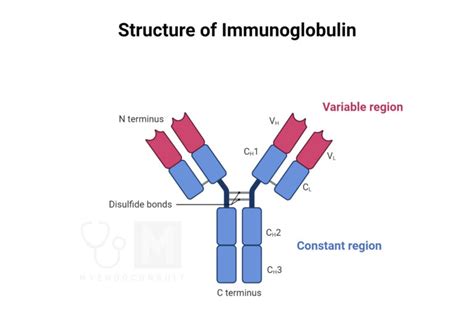
Functions of Globulins
The functions of globulins are diverse and critical for various bodily processes. They include: - **Immune Response:** Gamma globulins, in particular, are key players in the immune system, producing antibodies to combat pathogens. - **Blood Clotting:** Certain globulins are involved in the coagulation cascade, helping to form blood clots and prevent excessive bleeding. - **Transportation:** Globulins can bind and transport hormones, lipids, and other substances, facilitating their distribution throughout the body. - **Inflammation:** Some globulins are acute-phase proteins, which increase in response to inflammation, helping to manage and resolve inflammatory processes.Causes of Low Globulin Levels

Symptoms of Low Globulin Levels
Symptoms can vary widely depending on the underlying cause and the specific type of globulin that is low. Common symptoms include: - **Increased Infections:** Due to impaired immune function. - **Edema:** Swelling can occur due to decreased oncotic pressure from low protein levels. - **Bleeding Disorders:** Impaired blood clotting can lead to easy bruising or bleeding. - **Fatigue and Weakness:** General feeling of being unwell.Diagnosis of Low Globulin Levels
Treatment of Low Globulin Levels
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. It may involve: - **Addressing Underlying Conditions:** Treating liver disease, managing autoimmune disorders, or resolving infections. - **Nutritional Support:** Ensuring adequate nutrition to support protein production. - **Immunoglobulin Replacement Therapy:** In cases of severe immune deficiency. - **Monitoring:** Regular follow-up to assess the effectiveness of treatment and adjust as necessary.Complications of Untreated Low Globulin Levels

Prevention and Management
Preventing low globulin levels involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, and managing chronic conditions effectively. Regular health check-ups can help in early detection and treatment of underlying causes.Conclusion and Future Directions

Final Thoughts
Low globulin levels underscore the importance of preventive care, early diagnosis, and comprehensive management of underlying conditions. By staying informed and proactive about health, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall quality of life.What are the common symptoms of low globulin levels?
+Common symptoms include increased susceptibility to infections, edema, bleeding disorders, and general feelings of fatigue and weakness.
How are low globulin levels diagnosed?
+Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to measure total protein and albumin levels, followed by calculations to determine globulin levels. Additional tests may be necessary to identify the underlying cause.
What are the potential complications of untreated low globulin levels?
+Untreated low globulin levels can lead to recurrent infections, organ damage, and malnutrition, among other complications.
We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, or seek advice on managing low globulin levels. Your engagement is valuable in creating a supportive community that fosters health awareness and promotes well-being. Feel free to comment below or share this article with others who might benefit from this information. Together, we can work towards a healthier and more informed community.
