Intro
Discover the significance of Low Globulin Protein, its effects on immune function, and related conditions like Hypogammaglobulinemia, exploring symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for optimal health management.
The importance of protein in our diet cannot be overstated, as it plays a critical role in maintaining overall health and well-being. Among the various types of proteins, globulin protein is a crucial component that helps to support immune function, transport nutrients, and facilitate various bodily processes. However, for some individuals, low globulin protein levels can be a cause for concern, potentially leading to a range of health issues. In this article, we will delve into the world of globulin protein, exploring its functions, benefits, and the implications of low globulin protein levels.
Globulin protein is a type of protein found in the blood, making up approximately 30-40% of the total protein in the body. It is produced by the liver and plays a vital role in maintaining immune function, as it helps to produce antibodies that fight off infections and diseases. Additionally, globulin protein is involved in the transport of nutrients, hormones, and other essential substances throughout the body. With its wide range of functions, it is essential to maintain healthy globulin protein levels to ensure overall well-being.
A low globulin protein level can be caused by various factors, including liver disease, kidney disease, and certain nutritional deficiencies. For instance, individuals with liver disease may experience a decline in globulin protein production, leading to low levels. Similarly, those with kidney disease may experience a loss of protein in the urine, resulting in low globulin protein levels. Furthermore, a diet lacking essential nutrients, such as protein, vitamins, and minerals, can also contribute to low globulin protein levels. Understanding the causes of low globulin protein is crucial in developing effective treatment and prevention strategies.
Understanding Globulin Protein
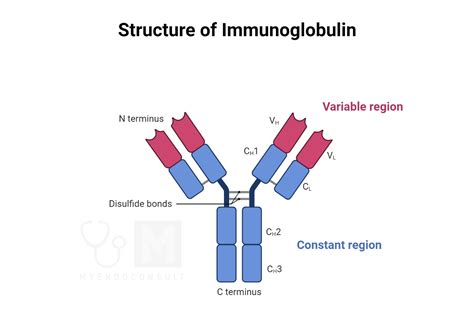
Functions of Globulin Protein
The functions of globulin protein are diverse and critical to maintaining overall health. Some of the key functions include: * Immune function: Globulin protein helps to produce antibodies that fight off infections and diseases. * Nutrient transport: Globulin protein is involved in the transport of nutrients, hormones, and other essential substances throughout the body. * Regulation of blood sugar levels: Beta-globulin helps to regulate blood sugar levels by transporting lipids and other nutrients. * Hormone transport: Alpha-globulin is involved in the transport of hormones, ensuring that they reach their target cells and tissues.Causes of Low Globulin Protein
Symptoms of Low Globulin Protein
The symptoms of low globulin protein levels can vary depending on the underlying cause. Some common symptoms include: * Fatigue and weakness * Recurrent infections * Poor wound healing * Edema and swelling * Abnormal blood sugar levelsDiagnosis and Treatment
Treatment for low globulin protein levels depends on the underlying cause. Some common treatment strategies include:
- Medications to manage underlying conditions, such as liver or kidney disease
- Nutritional supplements to address nutritional deficiencies
- Immunoglobulin replacement therapy to boost immune function
- Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and stress management
Prevention Strategies
Preventing low globulin protein levels involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle and addressing underlying conditions. Some effective prevention strategies include: * Eating a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals * Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation and yoga * Getting regular exercise to maintain overall health and well-being * Avoiding exposure to toxins and environmental pollutants * Getting regular health check-ups to monitor globulin protein levels and address any underlying conditionsComplications of Low Globulin Protein

Managing Complications
Managing complications of low globulin protein levels involves addressing the underlying cause and implementing effective treatment strategies. Some effective management strategies include: * Medications to manage underlying conditions, such as liver or kidney disease * Nutritional supplements to address nutritional deficiencies * Immunoglobulin replacement therapy to boost immune function * Lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and stress managementConclusion and Future Directions
What is globulin protein?
+Globulin protein is a type of protein found in the blood, making up approximately 30-40% of the total protein in the body. It plays a vital role in maintaining immune function, transporting nutrients, and facilitating various bodily processes.
What are the symptoms of low globulin protein levels?
+The symptoms of low globulin protein levels can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include fatigue and weakness, recurrent infections, poor wound healing, edema and swelling, and abnormal blood sugar levels.
How is low globulin protein levels diagnosed?
+Diagnosing low globulin protein levels typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, such as serum protein electrophoresis (SPEP), urine protein electrophoresis (UPEP), immunoglobulin tests, liver function tests, and kidney function tests.
What are the treatment options for low globulin protein levels?
+Treatment for low globulin protein levels depends on the underlying cause, but common treatment strategies include medications to manage underlying conditions, nutritional supplements to address nutritional deficiencies, immunoglobulin replacement therapy to boost immune function, and lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and stress management.
Can low globulin protein levels be prevented?
+Yes, low globulin protein levels can be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, addressing underlying conditions, and implementing effective prevention strategies, such as eating a balanced diet, managing stress, getting regular exercise, avoiding exposure to toxins, and getting regular health check-ups.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of low globulin protein levels, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below. Share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of globulin protein in maintaining overall health and well-being.
