Intro
Discover the Rh blood type system, including Rh positive and Rh negative factors, and understand its impact on pregnancy, blood transfusions, and overall health, exploring Rh incompatibility and its effects.
The Rh blood type system is one of the most important blood group systems in human medicine, and understanding it is crucial for transfusion medicine and prenatal care. The Rh system is named after the Rhesus monkey, in which it was first identified. It is a complex system with multiple antigens, but the most significant one is the RhD antigen. The presence or absence of this antigen determines whether an individual has Rh-positive or Rh-negative blood.
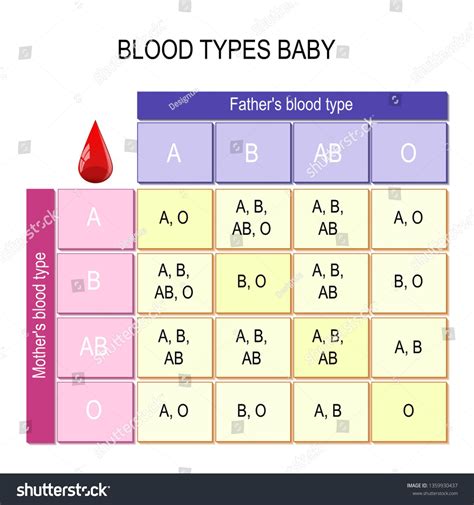
The Rh blood type system is essential because it can cause severe reactions during blood transfusions if incompatible blood is used. For example, if an individual with Rh-negative blood receives Rh-positive blood, their immune system may react to the foreign antigen and produce antibodies against it. This can lead to a severe hemolytic reaction, which can be life-threatening. Similarly, during pregnancy, an Rh-negative mother carrying an Rh-positive fetus can produce antibodies against the RhD antigen, which can cross the placenta and destroy the fetus's red blood cells.
The Rh blood type system has several antigens, but the most important ones are RhD and RhCE. These antigens are encoded by two adjacent genes, RHD and RHCE, which are located on chromosome 1. The RhD antigen is the most significant one, and its presence or absence determines the Rh blood type. Individuals with the RhD antigen are considered Rh-positive, while those without it are considered Rh-negative. The RhCE antigen is also important, as it can influence the expression of the RhD antigen.
Rh Blood Type Classification
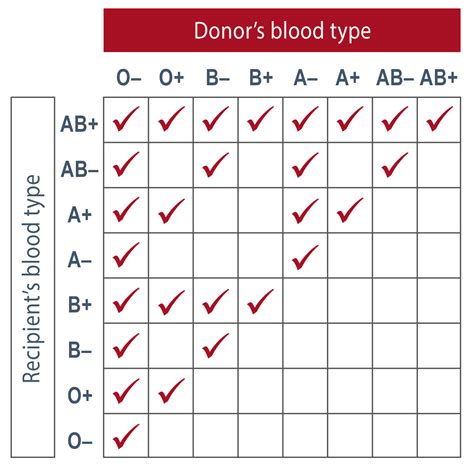
The Rh blood type system classifies blood into several groups based on the presence or absence of the RhD and RhCE antigens. The main Rh blood types are Rh-positive (Rh+) and Rh-negative (Rh-). Rh-positive individuals can be further classified into several subgroups based on the presence or absence of other Rh antigens, such as RhC, RhE, and RhG. Rh-negative individuals, on the other hand, can be classified into several subgroups based on the presence or absence of the RhCE antigen.
Rh Blood Type and Pregnancy
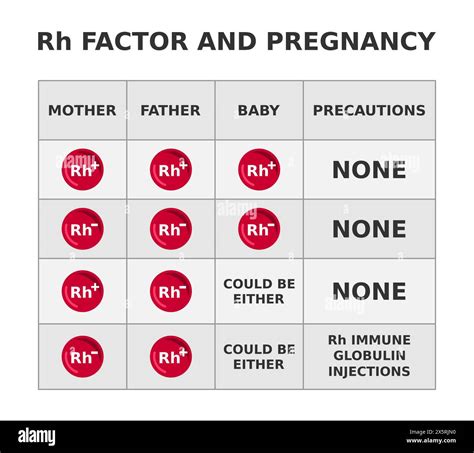
The Rh blood type system is crucial during pregnancy, especially if the mother is Rh-negative and the father is Rh-positive. In such cases, the mother's immune system may produce antibodies against the RhD antigen, which can cross the placenta and destroy the fetus's red blood cells. This can lead to a condition called hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN), which can be severe and even life-threatening. To prevent HDN, Rh-negative mothers are given Rh immune globulin (RhIg) during pregnancy, which prevents the production of antibodies against the RhD antigen.
Rh Blood Type and Transfusion Medicine
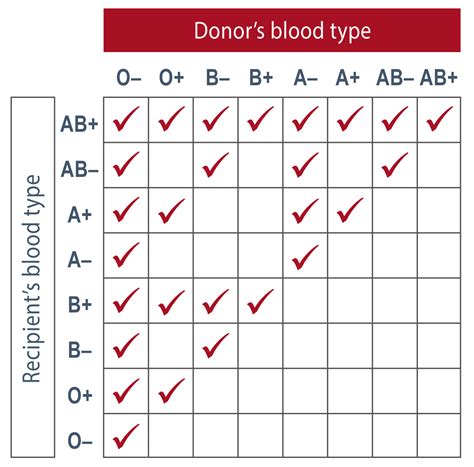
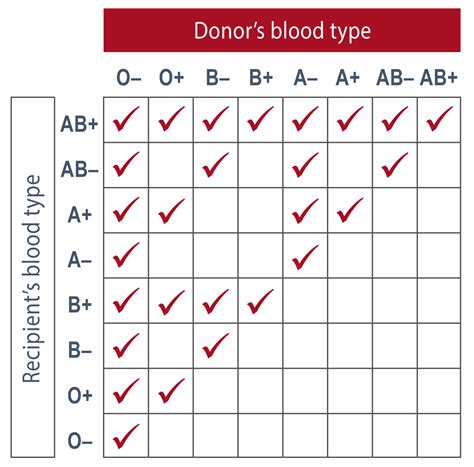
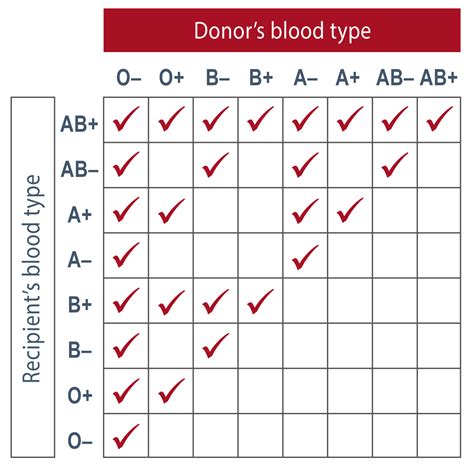
The Rh blood type system is also essential in transfusion medicine, as incompatible blood can cause severe reactions. For example, if an individual with Rh-negative blood receives Rh-positive blood, their immune system may react to the foreign antigen and produce antibodies against it. This can lead to a severe hemolytic reaction, which can be life-threatening. To prevent such reactions, blood banks carefully match the blood type of the donor and the recipient, taking into account the Rh blood type and other blood group systems.
Rh Blood Type and Health Implications
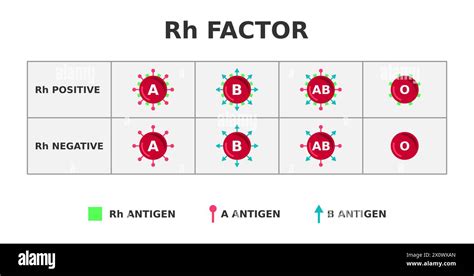
The Rh blood type system has several health implications, particularly for individuals with Rh-negative blood. For example, Rh-negative individuals may be more susceptible to certain diseases, such as autoimmune disorders and allergies. Additionally, Rh-negative individuals may be more likely to experience complications during pregnancy, such as placental abruption and premature birth. However, it is essential to note that the Rh blood type system is just one of many factors that can influence an individual's health, and other genetic and environmental factors also play a significant role.
Rh Blood Type and Genetics
The Rh blood type system is determined by two adjacent genes, RHD and RHCE, which are located on chromosome 1. The RHD gene encodes the RhD antigen, while the RHCE gene encodes the RhCE antigen. The Rh blood type is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that a single copy of the RHD gene is enough to produce the RhD antigen and determine the Rh-positive blood type. The Rh-negative blood type, on the other hand, is recessive and requires the absence of the RHD gene.
Rh Blood Type and Evolution
The Rh blood type system has evolved over time, and its distribution varies across different populations. The Rh-positive blood type is more common in populations of European and Asian descent, while the Rh-negative blood type is more common in populations of African descent. The evolution of the Rh blood type system is thought to have been influenced by various factors, including genetic drift, natural selection, and gene flow.
Rh Blood Type and Anthropology

The Rh blood type system has been used in anthropology to study human migration and population dynamics. By analyzing the distribution of Rh blood types across different populations, researchers can infer the migration patterns and genetic relationships between populations. For example, the presence of Rh-negative blood in certain populations may indicate a common ancestry or genetic exchange between populations.
Rh Blood Type and Medical Research
The Rh blood type system has been the subject of extensive medical research, particularly in the fields of transfusion medicine and prenatal care. Researchers have developed various techniques to detect and prevent Rh incompatibility, including Rh immune globulin and fetal Rh typing. Additionally, researchers have explored the potential applications of the Rh blood type system in other fields, such as cancer treatment and gene therapy.
What is the Rh blood type system?
+The Rh blood type system is a complex system of antigens on red blood cells that can cause severe reactions during blood transfusions or pregnancy if incompatible blood is used.
What are the main Rh blood types?
+The main Rh blood types are Rh-positive (Rh+) and Rh-negative (Rh-), which are determined by the presence or absence of the RhD antigen.
Why is the Rh blood type system important during pregnancy?
+The Rh blood type system is important during pregnancy because an Rh-negative mother carrying an Rh-positive fetus can produce antibodies against the RhD antigen, which can cross the placenta and destroy the fetus's red blood cells.
Can the Rh blood type system affect my health?
+The Rh blood type system can have several health implications, particularly for individuals with Rh-negative blood, who may be more susceptible to certain diseases or complications during pregnancy.
How is the Rh blood type system inherited?
+The Rh blood type system is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning that a single copy of the RHD gene is enough to produce the RhD antigen and determine the Rh-positive blood type.
In conclusion, the Rh blood type system is a complex and essential system in human medicine, with significant implications for transfusion medicine, prenatal care, and overall health. By understanding the Rh blood type system and its importance, individuals can take steps to ensure their health and well-being, particularly during pregnancy or when receiving blood transfusions. We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about the Rh blood type system in the comments below, and to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about this fascinating topic.
