Intro
Discover common 5 Shingles vaccine reactions, including side effects, symptoms, and complications, to make informed decisions about vaccination, mitigating risks and ensuring herpes zoster protection.
The shingles vaccine has been a game-changer in preventing the onset of shingles, a painful and debilitating condition caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus. However, like any vaccine, it can cause reactions in some individuals. Understanding these reactions is crucial for making informed decisions about vaccination. In this article, we will delve into the world of shingles vaccine reactions, exploring their causes, symptoms, and management.
The importance of the shingles vaccine cannot be overstated. Shingles affects millions of people worldwide, causing significant discomfort, pain, and even long-term complications such as postherpetic neuralgia. The vaccine has been shown to reduce the risk of developing shingles by approximately 50%, making it a vital tool in the prevention of this condition. Despite its benefits, some individuals may experience reactions to the vaccine, which can range from mild to severe.
The shingles vaccine works by stimulating the immune system to produce antibodies against the varicella-zoster virus. This immune response can sometimes cause reactions, which are typically mild and temporary. However, in some cases, more severe reactions can occur, highlighting the need for careful monitoring and management. As we explore the world of shingles vaccine reactions, it is essential to remember that the benefits of vaccination far outweigh the risks, and that most reactions are manageable with proper care.
Common Shingles Vaccine Reactions

Common shingles vaccine reactions include redness, swelling, and pain at the injection site. These reactions are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days. Some individuals may also experience systemic reactions such as fatigue, headache, and muscle pain. In rare cases, more severe reactions can occur, including allergic reactions, neurological problems, and autoimmune disorders.
Causes of Shingles Vaccine Reactions
The causes of shingles vaccine reactions are not fully understood but are thought to be related to the immune system's response to the vaccine. The vaccine contains a live, attenuated virus, which can cause an immune response in some individuals. This response can lead to the production of antibodies against the virus, which can sometimes cause reactions.Severe Shingles Vaccine Reactions
Severe shingles vaccine reactions are rare but can be serious. These reactions include anaphylaxis, a life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Other severe reactions include neurological problems such as Guillain-Barré syndrome, a rare autoimmune disorder that can cause muscle weakness and paralysis.
Managing Shingles Vaccine Reactions
Managing shingles vaccine reactions involves a combination of self-care and medical attention. Mild reactions can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers and antihistamines. More severe reactions require medical attention, and individuals should seek help immediately if they experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, or severe pain.Shingles Vaccine Reaction Symptoms

Shingles vaccine reaction symptoms can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the reaction. Common symptoms include:
- Redness, swelling, and pain at the injection site
- Fatigue
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Fever
- Chills
- Nausea and vomiting
More severe symptoms include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heartbeat
- Severe pain
- Muscle weakness
- Paralysis
Shingles Vaccine Reaction Treatment
Shingles vaccine reaction treatment depends on the severity of the reaction. Mild reactions can be treated with over-the-counter pain relievers and antihistamines. More severe reactions require medical attention, and individuals should seek help immediately if they experience symptoms such as difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, or severe pain.Shingles Vaccine Safety

The shingles vaccine is generally safe and effective. However, as with any vaccine, there are risks and benefits to consider. The benefits of the shingles vaccine include reducing the risk of developing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. The risks include mild to severe reactions, which can be managed with proper care.
Shingles Vaccine Side Effects
Shingles vaccine side effects are usually mild and temporary. Common side effects include: * Redness, swelling, and pain at the injection site * Fatigue * Headache * Muscle pain * Fever * Chills * Nausea and vomitingMore severe side effects include:
- Anaphylaxis
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Neurological problems
- Autoimmune disorders
Shingles Vaccine Efficacy
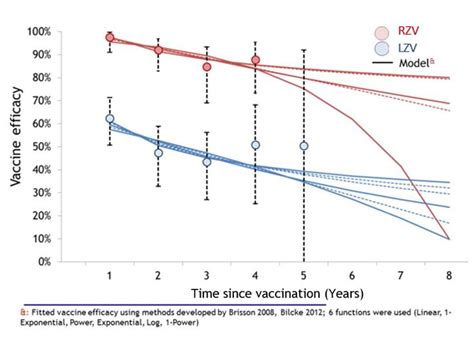
The shingles vaccine is highly effective in preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. Studies have shown that the vaccine can reduce the risk of developing shingles by approximately 50%. The vaccine is also effective in reducing the risk of postherpetic neuralgia, a long-term complication of shingles.
Shingles Vaccine Effectiveness
Shingles vaccine effectiveness can vary depending on the individual and the severity of the reaction. However, the vaccine is generally highly effective in preventing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. The vaccine is also effective in reducing the risk of long-term complications, making it a vital tool in the prevention of shingles.Shingles Vaccine Recommendations

The shingles vaccine is recommended for individuals aged 50 and older. The vaccine is also recommended for individuals who have a weakened immune system or are at high risk of developing shingles. The vaccine is typically given in two doses, with the second dose given 2-6 months after the first dose.
Shingles Vaccine Guidelines
Shingles vaccine guidelines vary depending on the individual and the severity of the reaction. However, the vaccine is generally recommended for individuals aged 50 and older. The vaccine is also recommended for individuals who have a weakened immune system or are at high risk of developing shingles.What are the common side effects of the shingles vaccine?
+Common side effects of the shingles vaccine include redness, swelling, and pain at the injection site, fatigue, headache, and muscle pain.
Can the shingles vaccine cause severe reactions?
+Yes, the shingles vaccine can cause severe reactions, including anaphylaxis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and neurological problems.
How effective is the shingles vaccine in preventing shingles?
+The shingles vaccine is highly effective in preventing shingles, reducing the risk by approximately 50%.
Who should get the shingles vaccine?
+The shingles vaccine is recommended for individuals aged 50 and older, as well as those with a weakened immune system or at high risk of developing shingles.
What are the benefits of getting the shingles vaccine?
+The benefits of getting the shingles vaccine include reducing the risk of developing shingles and postherpetic neuralgia, as well as reducing the risk of long-term complications.
In conclusion, the shingles vaccine is a vital tool in the prevention of shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. While reactions can occur, they are generally mild and temporary. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and management of shingles vaccine reactions is crucial for making informed decisions about vaccination. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the shingles vaccine, and to ask any questions you may have about this important topic. By working together, we can promote awareness and understanding of the shingles vaccine, and help to prevent this debilitating condition.
