Intro
Manage sodium levels with 5 expert tips, balancing electrolytes, hydration, and blood pressure, while avoiding hypernatremia and hyponatremia for optimal health.
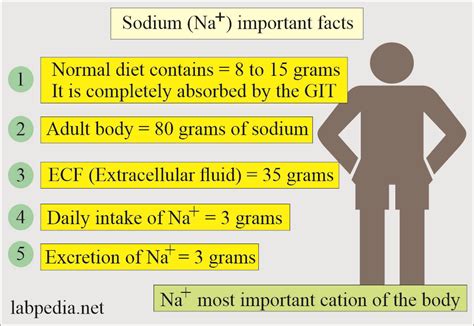
Maintaining the right balance of sodium in our bodies is crucial for our overall health and wellbeing. Sodium plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including nerve and muscle function, as well as maintaining the right balance of fluids. However, consuming too much sodium can lead to a range of health problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. In fact, the American Heart Association recommends that adults limit their daily sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams, and ideally no more than 1,500 milligrams if they are at risk for high blood pressure or heart disease.
The importance of managing sodium levels cannot be overstated. Excessive sodium consumption is a major public health concern, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimating that nearly 9 in 10 Americans consume too much sodium. This can lead to a range of serious health problems, including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, and even death. Furthermore, high sodium intake has been linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer, kidney stones, and osteoporosis. By understanding the risks associated with excessive sodium consumption and taking steps to manage our sodium intake, we can significantly reduce our risk of developing these conditions.
In addition to the physical health benefits, managing sodium levels can also have a significant impact on our mental health and wellbeing. Research has shown that a diet high in sodium can lead to increased symptoms of anxiety and depression, as well as reduced cognitive function. On the other hand, a balanced diet that is low in sodium can help to improve mood, reduce stress, and even improve sleep quality. By taking control of our sodium intake, we can take a significant step towards improving our overall health and wellbeing.
Sodium Level Basics
How Sodium Affects the Body
Sodium affects the body in a range of ways, from regulating fluid balance to facilitating nerve and muscle function. When we consume too much sodium, it can lead to a range of negative effects, including: * Increased blood pressure: Excessive sodium consumption can lead to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. * Fluid retention: Sodium helps to regulate the amount of water in our cells, but when we consume too much, our bodies retain excess fluid, leading to swelling, bloating, and discomfort. * Kidney strain: Our kidneys play a crucial role in filtering excess sodium from our blood, but when we consume too much, it can put a strain on our kidneys, leading to kidney disease and other problems.Managing Sodium Intake

High-Sodium Foods to Avoid
Some foods are notoriously high in sodium, and limiting our intake of these foods can help to reduce our overall sodium consumption. Here are some high-sodium foods to avoid: * Processed meats: Foods like bacon, sausage, and ham are often high in sodium. * Canned goods: Canned soups, vegetables, and meats are often high in sodium. * Frozen meals: Many frozen meals, including pizzas and TV dinners, are high in sodium. * Restaurant foods: Restaurant meals are often high in sodium, so it's a good idea to ask for nutrition information or opt for low-sodium options.Sodium Level Tips

Benefits of Low-Sodium Diet
Following a low-sodium diet can have a range of benefits, from reducing blood pressure to improving overall health and wellbeing. Here are some of the benefits of a low-sodium diet: * Reduced blood pressure: Limiting sodium intake can help to lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. * Improved cardiovascular health: A low-sodium diet can help to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and improve overall heart health. * Reduced fluid retention: Limiting sodium intake can help to reduce fluid retention and alleviate symptoms like swelling, bloating, and discomfort. * Improved kidney function: A low-sodium diet can help to reduce the strain on the kidneys and improve overall kidney function.Sodium Level Monitoring

When to Seek Medical Attention
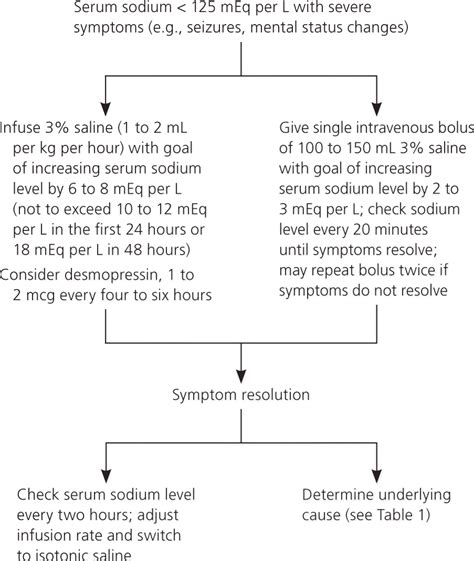
If we experience any symptoms of high or low sodium levels, it's essential to seek medical attention. Here are some symptoms to watch out for: * Severe headaches * Confusion or disorientation * Muscle weakness or cramps * Seizures or convulsions * Nausea or vomitingSodium Level Management Strategies
Common Sodium-Related Health Problems
Here are some common health problems related to high or low sodium levels: * High blood pressure: Excessive sodium consumption can lead to high blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and kidney disease. * Heart disease: High sodium intake can increase the risk of heart disease, including heart failure, heart attack, and stroke. * Kidney disease: Excessive sodium consumption can put a strain on the kidneys, leading to kidney disease and other problems.Conclusion and Next Steps

What is the recommended daily intake of sodium?
+The American Heart Association recommends that adults limit their daily sodium intake to less than 2,300 milligrams, and ideally no more than 1,500 milligrams if they are at risk for high blood pressure or heart disease.
What are the symptoms of high sodium levels?
+Symptoms of high sodium levels can include severe headaches, confusion or disorientation, muscle weakness or cramps, seizures or convulsions, and nausea or vomiting.
How can I reduce my sodium intake?
+There are many ways to reduce sodium intake, including reading food labels, choosing low-sodium options, cooking from scratch, and limiting processed foods.
