Intro
Identify heart attack symptoms, including chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea, to promptly seek medical help and prevent cardiac damage, learning key warning signs and risk factors.
Recognizing the signs of a heart attack is crucial for prompt medical attention and effective treatment. A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, occurs when the blood flow to the heart is blocked, causing damage to the heart muscle. The importance of understanding heart attack symptoms cannot be overstated, as it can significantly improve survival rates and reduce the risk of complications. In this article, we will delve into the world of heart attack symptoms, exploring the various signs, risk factors, and treatment options available.
The impact of heart attacks on individuals and their families can be devastating, making it essential to be aware of the warning signs. Heart attacks can strike anyone, regardless of age or health status, although certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing one. By being informed and taking proactive steps, individuals can reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their overall well-being. The journey to a healthier heart begins with knowledge, and this article aims to provide readers with a comprehensive understanding of heart attack symptoms and their implications.
The prevalence of heart disease is a significant concern worldwide, with heart attacks being a leading cause of death and disability. Despite advances in medical technology and treatment options, heart attacks remain a major health threat, highlighting the need for increased awareness and education. By understanding the signs and symptoms of a heart attack, individuals can take control of their health and seek medical attention promptly, improving their chances of survival and reducing the risk of long-term damage. In the following sections, we will explore the various aspects of heart attack symptoms, including the common signs, risk factors, and treatment options.
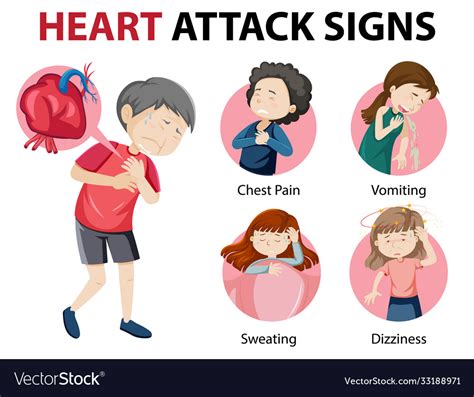
Common Heart Attack Symptoms
Risk Factors for Heart Attacks
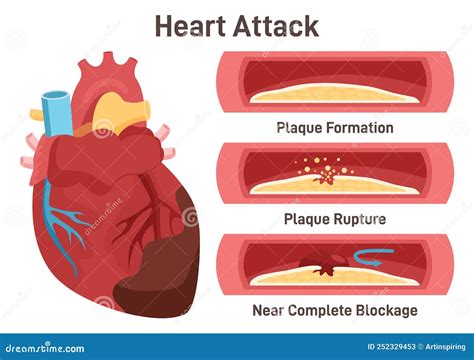
Certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of experiencing a heart attack, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, family history of heart disease, and lack of physical activity. By understanding these risk factors, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their overall health. For example, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.Understanding the Working Mechanism of Heart Attacks
Steps to Take During a Heart Attack
If you or someone you know is experiencing a heart attack, it is essential to take immediate action. The first step is to call emergency services, such as 911, and seek medical attention promptly. While waiting for medical help to arrive, the individual should sit or lie down in a comfortable position and try to remain calm. If the person is unconscious, CPR should be performed if possible. It is also essential to provide any relevant medical information, such as medications or medical history, to the emergency responders.Treatment Options for Heart Attacks

Prevention Strategies
Preventing heart attacks requires a combination of lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Some strategies for preventing heart attacks include maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress. Additionally, individuals with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to manage these conditions and reduce their risk of heart disease. By taking proactive steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their overall health.Heart Attack Recovery and Rehabilitation

Statistical Data on Heart Attacks
According to the American Heart Association, heart attacks are a leading cause of death and disability worldwide. In the United States alone, over 800,000 people experience a heart attack each year, resulting in significant economic and social burdens. The good news is that with prompt medical attention and effective treatment, many individuals can survive heart attacks and go on to lead healthy, active lives. By understanding the signs and symptoms of heart attacks, individuals can take control of their health and reduce their risk of heart disease.Heart Attack Prevention in Different Age Groups

Common Myths and Misconceptions about Heart Attacks
There are several common myths and misconceptions about heart attacks that can be misleading and even dangerous. For example, some individuals may believe that heart attacks only occur in older adults or that they are always preceded by severe symptoms. However, the reality is that heart attacks can strike anyone, regardless of age or health status, and may not always present with severe symptoms. By understanding the facts about heart attacks, individuals can take control of their health and reduce their risk of heart disease.Heart Attack Diagnosis and Testing
Heart Attack Treatment Options for Different Types of Heart Attacks
The treatment options for heart attacks depend on the type and severity of the attack. For example, STEMI (ST-elevation myocardial infarction) heart attacks, which are caused by a complete blockage of a coronary artery, require immediate medical attention and treatment with clot-busting drugs or primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). On the other hand, NSTEMI (non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction) heart attacks, which are caused by a partial blockage of a coronary artery, may be treated with medications and lifestyle changes. By understanding the different types of heart attacks and their treatment options, individuals can take control of their health and reduce their risk of heart disease.Heart Attack Recovery Tips

Heart Attack Support Groups and Resources
There are several support groups and resources available for individuals who have experienced a heart attack, including the American Heart Association, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. These organizations provide a wealth of information, support, and resources to help individuals manage their heart health and reduce their risk of future heart problems. By connecting with these resources, individuals can take control of their health and improve their overall well-being.What are the common symptoms of a heart attack?
+The common symptoms of a heart attack include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, lightheadedness or dizziness, pain or discomfort in the arms, back, neck, jaw, or stomach, and fatigue.
What are the risk factors for heart attacks?
+The risk factors for heart attacks include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, family history of heart disease, and lack of physical activity.
How can I reduce my risk of heart disease?
+You can reduce your risk of heart disease by maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, quitting smoking, and managing stress. Additionally, individuals with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes should work with their healthcare provider to manage these conditions and reduce their risk of heart disease.
What should I do if I experience symptoms of a heart attack?
+If you experience symptoms of a heart attack, you should call emergency services, such as 911, and seek medical attention promptly. While waiting for medical help to arrive, sit or lie down in a comfortable position and try to remain calm.
Can heart attacks be prevented?
+Yes, heart attacks can be prevented by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing chronic health conditions, and reducing risk factors. By taking proactive steps, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease and improve their overall health.
In conclusion, recognizing the signs of a heart attack is crucial for prompt medical attention and effective treatment. By understanding the common symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, individuals can take control of their health and reduce their risk of heart disease. We encourage readers to share this article with friends and family, and to take proactive steps to improve their heart health. By working together, we can reduce the incidence of heart attacks and improve the overall well-being of individuals and communities. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
