Intro
Identify 7 flu symptoms, including fever, cough, and fatigue. Learn about influenza signs, seasonal flu, and common cold differences, to manage symptoms effectively.
The common cold and flu are two of the most prevalent illnesses that affect people of all ages, backgrounds, and geographic locations. While both conditions share some similar symptoms, there are distinct differences between them. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective treatment and management. The flu, in particular, can be a severe and potentially life-threatening condition, especially for vulnerable populations such as the elderly, young children, and those with compromised immune systems. In this article, we will delve into the world of flu symptoms, exploring their causes, effects, and implications for our daily lives.
The flu, also known as influenza, is a highly contagious respiratory illness caused by the influenza virus. It can spread rapidly through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus. The flu season typically runs from October to May, with peak activity occurring between December and February. During this time, it's essential to be aware of the symptoms and take preventive measures to avoid contracting the illness. By recognizing the early warning signs of the flu, individuals can seek medical attention promptly, reducing the risk of complications and transmission to others.
The impact of the flu on our daily lives cannot be overstated. From missed workdays and school absences to hospitalizations and even fatalities, the consequences of the flu can be severe. Moreover, the flu can have a significant economic burden, with estimated costs ranging from billions to trillions of dollars annually. Therefore, it's crucial to understand the flu symptoms, their progression, and the available treatment options. By doing so, we can take proactive steps to protect ourselves, our loved ones, and our communities from the flu's devastating effects.
Introduction to Flu Symptoms
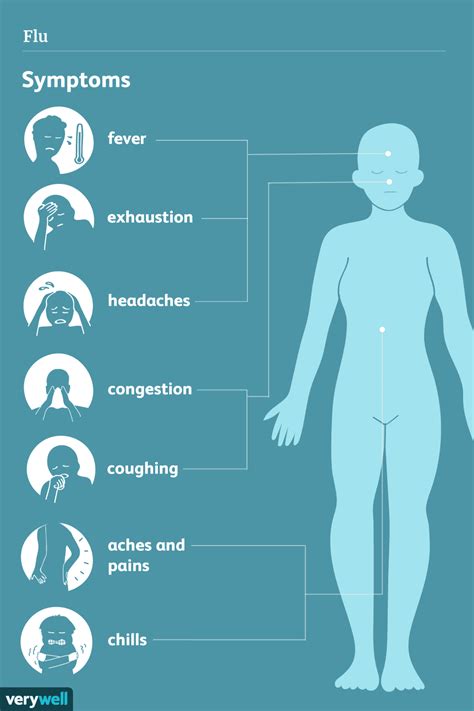
Types of Flu Symptoms
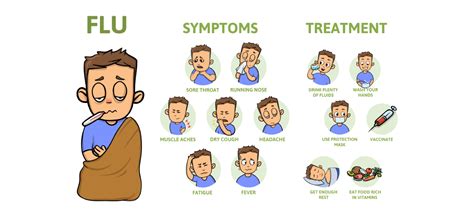
The flu symptoms can be categorized into two main types: respiratory and systemic. Respiratory symptoms affect the lungs, throat, and airways, while systemic symptoms affect the entire body. Some common flu symptoms include: * Fever and chills * Cough and sore throat * Runny or stuffy nose * Headache and fatigue * Muscle and body aches * Diarrhea and vomiting (more common in children)Causes of Flu Symptoms
Risk Factors for Flu Symptoms
Certain individuals are more susceptible to contracting the flu and experiencing severe symptoms. These risk factors include: * Age: Older adults, young children, and infants are more vulnerable to the flu. * Weakened immune system: People with chronic illnesses, such as diabetes, heart disease, or HIV/AIDS, are more prone to complications. * Pregnancy: Pregnant women are at higher risk of developing severe flu symptoms and complications.Diagnosis and Treatment of Flu Symptoms

Prevention of Flu Symptoms
Preventing the flu involves taking proactive steps to avoid contracting the virus. Some effective prevention strategies include: * Getting vaccinated: The flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent the flu and its complications. * Practicing good hygiene: Washing hands frequently, covering the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding close contact with others can help reduce the transmission of the flu. * Avoiding close contact: Avoiding close contact with others, especially during peak flu season, can help prevent the spread of the virus.Complications of Flu Symptoms

Managing Flu Symptoms
Managing flu symptoms involves a combination of self-care, medication, and medical attention. Some effective strategies for managing flu symptoms include: * Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broths, and electrolyte-rich beverages, can help replace lost fluids and electrolytes. * Resting: Getting plenty of rest can help the body recover from the flu and reduce the risk of complications. * Using a humidifier: Adding moisture to the air can help relieve congestion and coughing.Conclusion and Next Steps

We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with flu symptoms in the comments section below. Have you or a loved one ever contracted the flu? What steps did you take to manage the symptoms and prevent complications? Your stories and insights can help others better understand the flu and its effects. Let's work together to build a community that is informed, empowered, and committed to preventing the spread of the flu.
What are the most common flu symptoms?
+The most common flu symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, and fatigue.
How can I prevent the flu?
+You can prevent the flu by getting vaccinated, practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with others, and staying healthy through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
What are the complications of the flu?
+The flu can lead to severe complications, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinus and ear infections, especially in vulnerable populations like older adults, young children, and people with weakened immune systems.
How long does the flu last?
+The flu typically lasts for 7-10 days, but some people may experience symptoms for up to 2 weeks or more.
Can I take antibiotics to treat the flu?
+No, antibiotics are not effective against the flu virus. Antiviral medications, such as oseltamivir or zanamivir, may be prescribed by a doctor to help treat the flu.
